ARM and RISC-V represent two leading architectures in the technology pet space, each offering distinct advantages. ARM's widespread adoption and energy efficiency make it ideal for embedded and mobile devices, while RISC-V's open-source nature provides flexibility and customization for innovative pet technology applications. Choosing between ARM and RISC-V depends on factors like power consumption, cost, and development ecosystem compatibility.
Table of Comparison
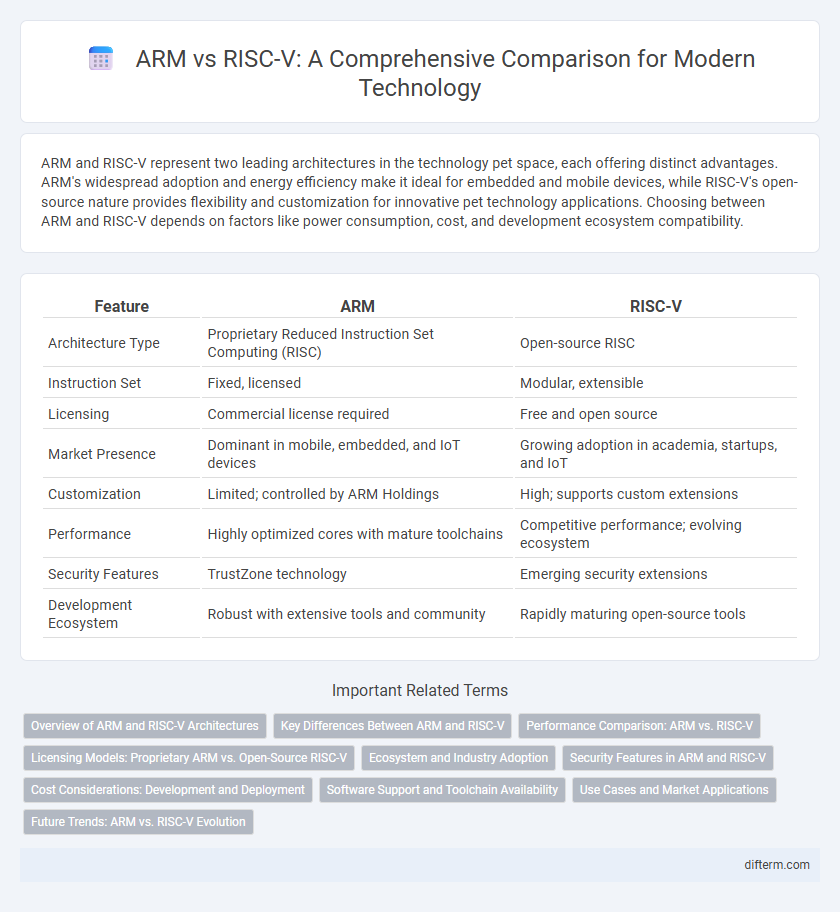
| Feature | ARM | RISC-V |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture Type | Proprietary Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC) | Open-source RISC |
| Instruction Set | Fixed, licensed | Modular, extensible |
| Licensing | Commercial license required | Free and open source |
| Market Presence | Dominant in mobile, embedded, and IoT devices | Growing adoption in academia, startups, and IoT |
| Customization | Limited; controlled by ARM Holdings | High; supports custom extensions |
| Performance | Highly optimized cores with mature toolchains | Competitive performance; evolving ecosystem |
| Security Features | TrustZone technology | Emerging security extensions |
| Development Ecosystem | Robust with extensive tools and community | Rapidly maturing open-source tools |
Overview of ARM and RISC-V Architectures
ARM architecture features a proprietary Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC) design widely adopted in mobile and embedded devices due to its energy efficiency and robust performance. RISC-V offers an open-source ISA (Instruction Set Architecture) allowing extensive customization and flexibility, attracting developers seeking innovation without licensing fees. Both architectures emphasize modularity and scalability but differ significantly in their ecosystem control and licensing models.
Key Differences Between ARM and RISC-V
ARM architecture features a proprietary instruction set with extensive ecosystem support, while RISC-V offers an open-source, modular instruction set allowing customizable extensions. ARM processors dominate mobile and embedded markets due to mature IP licensing and power efficiency, whereas RISC-V attracts innovation from academia and startups, promoting flexibility and reduced costs. Performance-wise, ARM designs often emphasize optimized, low-power cores, whereas RISC-V enables tailored implementations suited for specific applications via open hardware designs.
Performance Comparison: ARM vs. RISC-V
ARM processors exhibit mature, high-performance architectures with extensive software ecosystem support, enabling optimized execution in mobile and embedded systems. RISC-V offers customizable, open-source ISA advantages, showing competitive performance especially in specialized applications and research-driven developments. Benchmark analyses reveal ARM's dominance in power efficiency and throughput, while RISC-V's modularity provides scalable performance gains through tailored extensions.
Licensing Models: Proprietary ARM vs. Open-Source RISC-V
ARM operates under a proprietary licensing model requiring manufacturers to pay royalties and adhere to strict usage terms, which grants access to its mature ecosystem and extensive support. RISC-V employs an open-source licensing approach, allowing developers to use, modify, and implement the architecture without licensing fees, fostering innovation and customization. This fundamental difference in licensing impacts cost structures, flexibility, and the pace of technological advancements within the semiconductor industry.
Ecosystem and Industry Adoption
ARM maintains a dominant ecosystem with extensive industry adoption, supported by a vast array of software tools, IP cores, and well-established partnerships across mobile, automotive, and IoT sectors. RISC-V's open-source architecture has rapidly grown, attracting startups and academia due to its flexibility and lower licensing costs, fostering innovation in edge computing and specialized AI applications. The ongoing expansion of RISC-V's ecosystem is challenging ARM's market presence, with increasing support from silicon vendors and an emerging community-driven infrastructure for development and deployment.
Security Features in ARM and RISC-V
ARM architecture integrates extensive hardware-based security features, such as TrustZone technology, enabling secure and non-secure world execution environments to protect sensitive data and code. RISC-V, with its open-source nature, allows customizable security implementations, including support for Physical Memory Protection (PMP) and emerging cryptographic extensions designed to enhance system integrity. Both architectures aim to safeguard against modern security threats, but ARM offers mature, proprietary solutions while RISC-V provides flexible, community-driven security frameworks.
Cost Considerations: Development and Deployment
RISC-V offers a significant cost advantage over ARM due to its open-source architecture, eliminating licensing fees and reducing development expenses for hardware and software integration. ARM's proprietary designs require costly licensing agreements, which can substantially increase the total cost of ownership, especially for large-scale deployments. Companies seeking budget-efficient innovation often prefer RISC-V for customized processor development, benefiting from a collaborative ecosystem without recurring royalty payments.
Software Support and Toolchain Availability
ARM offers extensive software support and a mature toolchain ecosystem, including widely adopted compilers, debuggers, and integrated development environments (IDEs) from major vendors like Arm Development Studio and Keil. RISC-V's open-source architecture benefits from growing community-driven software support and expanding toolchain availability, with prominent tools such as GCC, LLVM, and RISC-V-specific SDKs gaining traction. While ARM leads in commercial-grade software maturity, RISC-V's customizable and free-to-use toolchains provide increasing flexibility for developers in embedded and IoT applications.
Use Cases and Market Applications
ARM architecture dominates mobile devices, embedded systems, and IoT applications due to its energy efficiency and extensive ecosystem support, powering billions of smartphones and tablets worldwide. RISC-V gains traction in custom silicon design, academic research, and emerging sectors like edge computing and AI accelerators because of its open-source nature and flexibility. Industrial automation, automotive control systems, and cloud data centers increasingly explore RISC-V for highly specialized workloads, while ARM remains prevalent in consumer electronics and established enterprise solutions.
Future Trends: ARM vs. RISC-V Evolution
ARM's future trends emphasize enhanced AI capabilities and broader integration in mobile and IoT devices, leveraging its established ecosystem and extensive software support. RISC-V's evolution capitalizes on its open-source architecture, driving innovation through customizable designs and growing adoption in edge computing and embedded systems. Market dynamics suggest a competitive landscape where ARM's maturity meets RISC-V's flexibility, fostering diverse advancements in semiconductor technology.
ARM vs RISC-V Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com