NVMe offers significantly faster data transfer speeds compared to SATA, leveraging the PCIe interface for low-latency access to storage. SATA drives, while more affordable and widely compatible, are limited by slower bandwidth and higher latency. For high-performance applications and gaming, NVMe provides superior speed and responsiveness, whereas SATA remains a cost-effective choice for general storage needs.
Table of Comparison
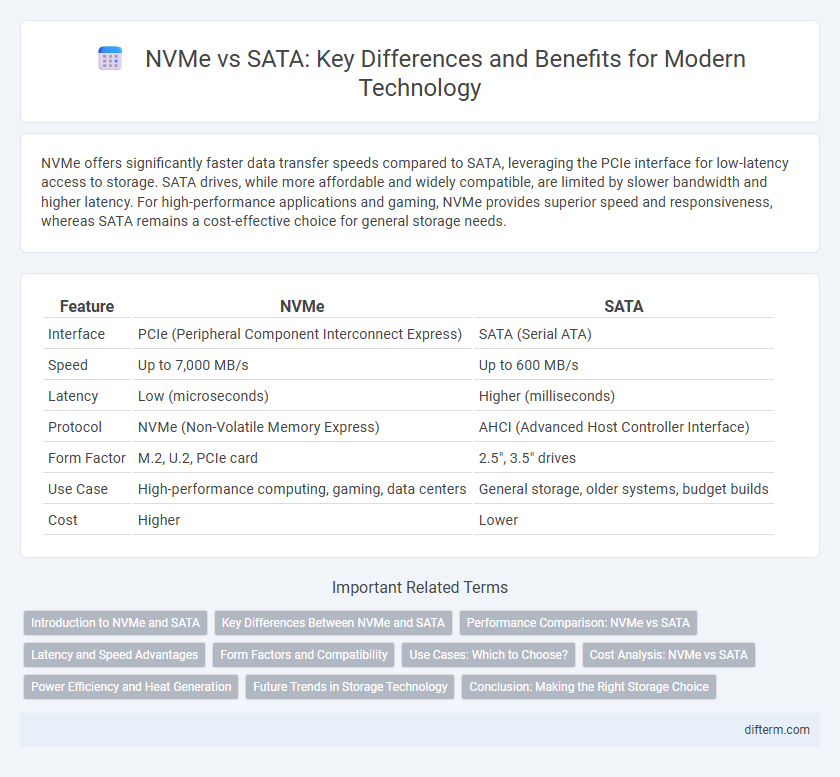
| Feature | NVMe | SATA |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) | SATA (Serial ATA) |
| Speed | Up to 7,000 MB/s | Up to 600 MB/s |
| Latency | Low (microseconds) | Higher (milliseconds) |
| Protocol | NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) | AHCI (Advanced Host Controller Interface) |
| Form Factor | M.2, U.2, PCIe card | 2.5", 3.5" drives |
| Use Case | High-performance computing, gaming, data centers | General storage, older systems, budget builds |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to NVMe and SATA
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a high-performance protocol designed specifically for SSDs, leveraging PCIe lanes to deliver faster data transfer speeds and lower latency compared to SATA. SATA (Serial ATA), originally developed for traditional hard drives, offers slower speeds due to its older interface limits, making it less ideal for modern SSD performance demands. NVMe's architecture supports parallelism and queue depth, significantly enhancing data throughput over the SATA interface.
Key Differences Between NVMe and SATA
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) delivers significantly higher data transfer speeds and lower latency compared to SATA (Serial ATA), leveraging the PCIe interface for direct connection to the CPU. SATA drives typically max out at 6 Gbps throughput, while NVMe SSDs achieve speeds exceeding 3,000 MB/s, ideal for high-performance computing and gaming. NVMe supports multiple command queues with thousands of commands per queue, vastly improving parallelism over SATA's single command queue architecture.
Performance Comparison: NVMe vs SATA
NVMe drives deliver significantly faster read and write speeds compared to SATA SSDs, reaching up to 3,500 MB/s versus SATA's 600 MB/s maximum throughput. NVMe leverages the PCIe interface, reducing latency and increasing parallelism, which enhances performance in high-demand applications like gaming, video editing, and database management. SATA drives remain affordable and compatible with older systems but lag behind NVMe in IOPS and bandwidth efficiency.
Latency and Speed Advantages
NVMe drives offer significantly lower latency than SATA drives due to direct communication with the CPU via the PCIe interface, reducing data transfer delays to microseconds. NVMe's parallelism capabilities and high IOPS result in speeds up to 5-7 times faster than SATA, which is limited by the SATA III interface's 6 Gbps maximum throughput. These advantages make NVMe the preferred choice for performance-critical applications requiring rapid data access and high bandwidth.
Form Factors and Compatibility
NVMe drives primarily use the M.2 and U.2 form factors, offering compact designs that fit modern motherboards and high-performance servers, while SATA drives commonly come in 2.5-inch and 3.5-inch sizes compatible with a wide range of legacy systems. NVMe's PCIe interface demands specific M.2 or U.2 slots on motherboards, limiting compatibility with older hardware that only supports SATA connections. SATA's widespread adoption ensures broader compatibility across devices, but NVMe's form factors deliver superior speed and efficiency in compatible systems.
Use Cases: Which to Choose?
NVMe drives excel in high-performance computing, gaming, and data-intensive applications due to their low latency and high throughput, making them ideal for professionals requiring rapid data access and multitasking capabilities. SATA SSDs remain suitable for everyday computing, budget builds, and storage expansion where cost-effectiveness and compatibility with older systems are priorities. Choosing between NVMe and SATA depends on workload demands, with NVMe preferred for speed-critical scenarios and SATA offering reliable performance for standard use cases.
Cost Analysis: NVMe vs SATA
NVMe drives typically command a higher price per gigabyte compared to SATA SSDs due to advanced PCIe interface technology and faster data transfer rates, which significantly enhance performance in demanding applications. SATA SSDs remain a cost-effective choice for general storage needs, offering solid reliability and speed improvements over traditional HDDs at a lower price point. Evaluating total cost of ownership involves balancing NVMe's premium pricing against its superior throughput and latency advantages for high-performance computing environments.
Power Efficiency and Heat Generation
NVMe drives exhibit superior power efficiency compared to SATA SSDs due to their ability to handle multiple parallel command queues, reducing idle power consumption. NVMe's advanced protocol minimizes CPU overhead, which directly translates to lower heat generation during intensive data transfers. In contrast, SATA SSDs typically consume more power and produce higher thermal output because of their older interface design and limited bandwidth.
Future Trends in Storage Technology
NVMe drives are rapidly surpassing SATA SSDs in performance due to lower latency and higher throughput, making them the preferred choice for emerging data-intensive applications such as AI and real-time analytics. Future storage technology trends emphasize the integration of NVMe over Fabrics (NVMe-oF) to extend ultra-fast access across networked environments, enhancing scalability and efficiency in data centers. Emerging non-volatile memory technologies like 3D XPoint and Resistive RAM (ReRAM) complement NVMe advancements, promising even faster storage solutions with greater endurance and energy efficiency.
Conclusion: Making the Right Storage Choice
NVMe storage delivers significantly faster data transfer speeds and lower latency compared to SATA, making it the superior choice for high-performance computing, gaming, and data-intensive applications. SATA drives offer greater affordability and broad compatibility, suitable for general storage needs and budget-conscious users. Evaluating specific use cases, budget constraints, and performance requirements is essential for selecting the optimal storage solution between NVMe and SATA.
NVMe vs SATA Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com