Progressive JPEG offers faster image loading by displaying a low-quality version that gradually improves, ideal for complex photographs with rich color gradients. SVG, as a vector format, ensures crisp, scalable graphics without loss of quality, perfect for logos, icons, and illustrations that require responsiveness across various screen sizes. Choosing between Progressive JPEG and SVG depends on the image type and performance needs, with JPEG excelling in photographic detail and SVG in scalability and sharpness.
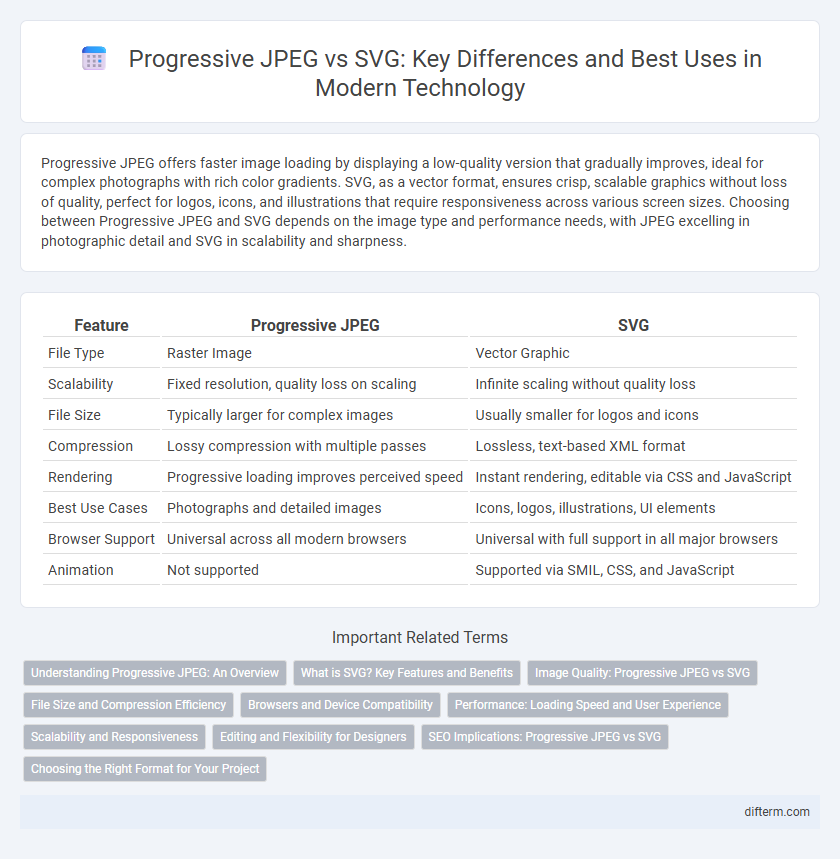
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Progressive JPEG | SVG |
|---|---|---|
| File Type | Raster Image | Vector Graphic |
| Scalability | Fixed resolution, quality loss on scaling | Infinite scaling without quality loss |
| File Size | Typically larger for complex images | Usually smaller for logos and icons |
| Compression | Lossy compression with multiple passes | Lossless, text-based XML format |
| Rendering | Progressive loading improves perceived speed | Instant rendering, editable via CSS and JavaScript |
| Best Use Cases | Photographs and detailed images | Icons, logos, illustrations, UI elements |
| Browser Support | Universal across all modern browsers | Universal with full support in all major browsers |
| Animation | Not supported | Supported via SMIL, CSS, and JavaScript |
Understanding Progressive JPEG: An Overview
Progressive JPEG is a raster image format designed to display images incrementally, improving perceived loading speed by rendering a low-quality version first before fully loading the image. This format uses multiple scans to progressively enhance image clarity, making it ideal for web use where user experience and load times are critical. Unlike SVG, which is a scalable vector graphic format suited for logos and icons, Progressive JPEG excels in handling complex photographs with rich color gradients.
What is SVG? Key Features and Benefits
SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) is an XML-based vector image format designed for defining two-dimensional graphics with support for interactivity and animation. Key features include resolution independence, enabling images to scale without loss of quality, and smaller file sizes compared to raster formats like Progressive JPEG, especially for images involving shapes and text. Benefits of SVG include enhanced performance on web platforms, easy editability with code or graphic software, and improved accessibility through semantic elements.
Image Quality: Progressive JPEG vs SVG
Progressive JPEG delivers improved image quality through multiple scan passes, enhancing perceived sharpness during loading, especially for complex photographic images. SVG, as a vector format, maintains infinitely scalable image quality without pixelation, ideal for logos, icons, and graphics requiring crisp edges at any resolution. For detail-rich photographs, Progressive JPEG offers smoother gradients, whereas SVG excels in preserving clarity for geometric shapes and text.
File Size and Compression Efficiency
Progressive JPEG uses multiple scans to load images incrementally, balancing moderate compression efficiency with smaller file sizes suitable for photographs. SVG, a vector format, offers superior compression efficiency for graphics and logos by storing scalable paths and shapes, resulting in significantly smaller file sizes for images with fewer colors and simple designs. File size for Progressive JPEG varies with image complexity, typically larger than SVG files for vector content, making SVG the preferred choice for sharp graphics and icons in web applications.
Browsers and Device Compatibility
Progressive JPEG images are widely supported across all modern browsers and devices, offering a faster initial load with successive image refinement, ideal for photographic content. SVGs provide superior scalability and resolution independence, ensuring sharp visuals on high-DPI displays, yet their support varies for complex filters and animations across some legacy browsers. Choosing between Progressive JPEG and SVG depends on browser compatibility needs and the type of graphic content, with SVG excelling in vector graphics and Progressive JPEG favored for detailed raster images on diverse devices.
Performance: Loading Speed and User Experience
Progressive JPEGs enhance loading speed by displaying a low-quality version of the image quickly, which gradually improves, providing a smoother user experience on slower connections. SVG files, being vector-based, offer faster loading times for graphics and icons due to their smaller file size and scalability without loss of quality. Choosing between Progressive JPEG and SVG depends on the image type--photos benefit from Progressive JPEG's efficient progressive rendering, while logos and illustrations perform best with SVG for optimal performance and clarity.
Scalability and Responsiveness
Progressive JPEG uses multiple scans to gradually enhance image quality, which improves loading on slower connections but lacks true scalability since it is raster-based. SVG, being a vector format, offers infinite scalability without loss of quality, making it ideal for responsive designs across various screen sizes and resolutions. SVG graphics adapt seamlessly to different devices, ensuring crisp visuals on everything from mobile phones to large monitors, whereas Progressive JPEGs can pixelate when scaled beyond their intended resolution.
Editing and Flexibility for Designers
Progressive JPEG supports gradual image rendering but lacks scalability and loses quality with repeated edits, limiting flexibility for designers. SVG offers infinite scalability and easily editable vector paths, making it ideal for precise modifications and responsive designs. Designers benefit from SVG's ability to maintain crisp visuals at any resolution and its compatibility with CSS and JavaScript for dynamic styling and animation.
SEO Implications: Progressive JPEG vs SVG
Progressive JPEG images enhance SEO by improving page load times and user experience through incremental rendering, which keeps visitors engaged and reduces bounce rates. SVG files offer superior scalability and smaller file sizes for vector graphics, boosting site speed and responsiveness--key factors in search engine rankings. Choosing between Progressive JPEG and SVG depends on the content type, as SEO benefits stem from optimizing image format based on image complexity and performance impact.
Choosing the Right Format for Your Project
Progressive JPEGs offer faster initial loading by displaying a low-quality image that progressively sharpens, making them ideal for photographic content where quick visual feedback is crucial. SVGs provide scalable, resolution-independent graphics best suited for logos, icons, and illustrations requiring crisp detail on various screen sizes without quality loss. Selecting the right format depends on balancing image complexity, scalability needs, and loading performance to optimize user experience in web and app projects.
Progressive JPEG vs SVG Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com