Facial landmarking identifies key points on a face such as the eyes, nose, and mouth to map facial structure, while face recognition uses these landmarks to verify or identify an individual. Accurate facial landmark detection improves the precision of face recognition systems by aligning facial features for better comparison. Advanced algorithms combine both techniques to enhance security and user authentication in various technology applications.
Table of Comparison
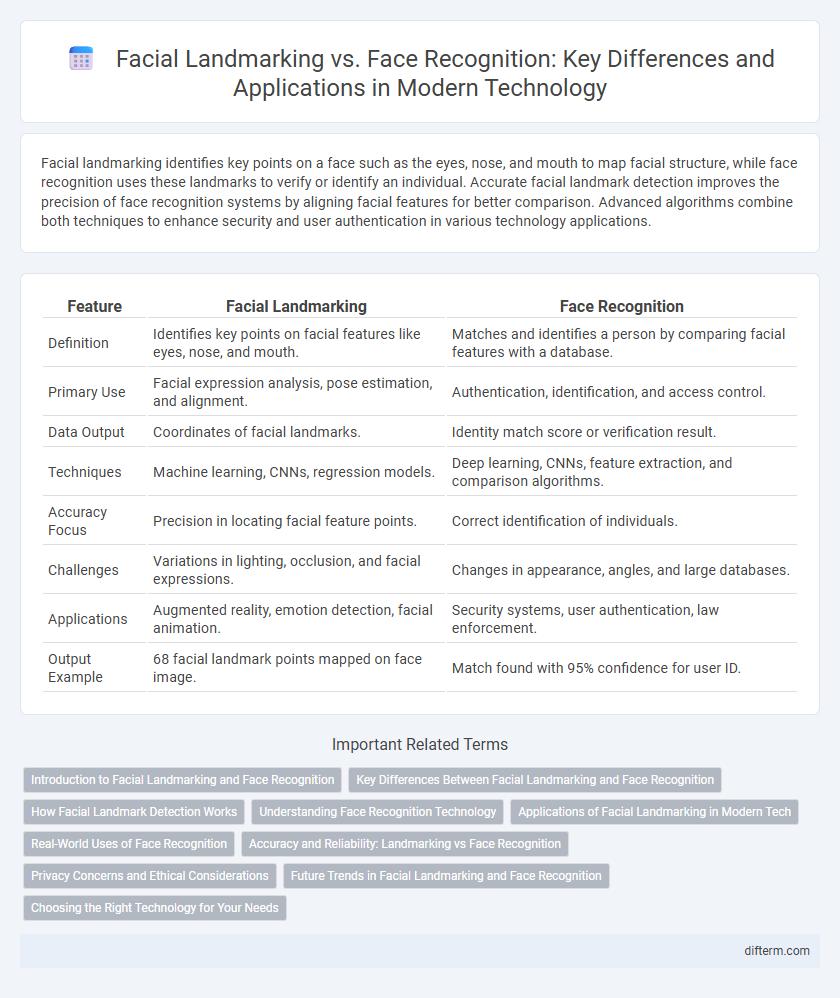
| Feature | Facial Landmarking | Face Recognition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Identifies key points on facial features like eyes, nose, and mouth. | Matches and identifies a person by comparing facial features with a database. |
| Primary Use | Facial expression analysis, pose estimation, and alignment. | Authentication, identification, and access control. |
| Data Output | Coordinates of facial landmarks. | Identity match score or verification result. |
| Techniques | Machine learning, CNNs, regression models. | Deep learning, CNNs, feature extraction, and comparison algorithms. |
| Accuracy Focus | Precision in locating facial feature points. | Correct identification of individuals. |
| Challenges | Variations in lighting, occlusion, and facial expressions. | Changes in appearance, angles, and large databases. |
| Applications | Augmented reality, emotion detection, facial animation. | Security systems, user authentication, law enforcement. |
| Output Example | 68 facial landmark points mapped on face image. | Match found with 95% confidence for user ID. |
Introduction to Facial Landmarking and Face Recognition
Facial landmarking involves detecting specific key points on a human face, such as the eyes, nose, and mouth, to analyze facial geometry and expressions. Face recognition uses these landmarks along with advanced algorithms to identify or verify individuals by comparing facial features against a database. Both technologies leverage machine learning and computer vision to enable applications in security, authentication, and augmented reality.
Key Differences Between Facial Landmarking and Face Recognition
Facial landmarking involves detecting specific key points on a face, such as the eyes, nose, and mouth, to analyze facial geometry, while face recognition identifies and verifies individuals based on unique facial features. Facial landmarking is primarily used for facial alignment, expression analysis, and tracking, whereas face recognition serves applications like identity verification and access control. The key difference lies in their purpose: landmarking maps facial structure, whereas recognition matches facial data against a database for identity authentication.
How Facial Landmark Detection Works
Facial landmark detection works by identifying key points on a human face, such as the corners of the eyes, the tip of the nose, and the edges of the mouth, using machine learning models trained on annotated facial images. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and regression-based approaches analyze facial features to accurately predict the coordinates of these landmarks in real-time. This process enables precise mapping of facial geometry, which is essential for applications like face alignment, expression analysis, and enhancing the accuracy of face recognition systems.
Understanding Face Recognition Technology
Facial landmarking involves pinpointing specific facial features such as eyes, nose, and mouth to create a geometric map, which enhances the accuracy of face recognition systems. Face recognition technology utilizes these landmarks to analyze facial patterns and compare them against a database for identification or verification purposes. Advanced algorithms and deep learning models improve recognition precision by interpreting facial landmarks in various lighting, angles, and expressions.
Applications of Facial Landmarking in Modern Tech
Facial landmarking plays a crucial role in modern technology by enabling precise mapping of key facial features such as eyes, nose, and mouth, which enhances the accuracy of facial analysis applications. It is widely used in augmented reality to align digital filters, in driver monitoring systems to detect alertness, and in medical diagnostics for assessing facial symmetry and muscle movement. Unlike face recognition technology that identifies individuals, facial landmarking focuses on feature localization, supporting various biometric and human-computer interaction applications.
Real-World Uses of Face Recognition
Face recognition technology is widely used in security systems, enabling real-time identification in airports, law enforcement, and mobile device authentication. Unlike facial landmarking, which detects key facial features for applications like emotion analysis or augmented reality, face recognition matches entire facial patterns to stored databases for identity verification. This distinction makes face recognition crucial for access control, surveillance, and personalized user experiences across various industries.
Accuracy and Reliability: Landmarking vs Face Recognition
Facial landmarking involves detecting key facial points with high precision, enabling accurate tracking of facial expressions and movements, which enhances reliability in dynamic environments. Face recognition systems compare these landmarks or entire facial features against databases, with accuracy heavily dependent on the quality of landmark detection and image resolution. Advanced face recognition algorithms using deep learning demonstrate superior accuracy in varied lighting and angles, but their reliability hinges on robust landmark extraction as a foundational step.
Privacy Concerns and Ethical Considerations
Facial landmarking focuses on identifying key facial features without necessarily revealing identity, offering a privacy-friendly alternative to full face recognition systems that analyze and store extensive biometric data. Ethical considerations emphasize minimizing misuse and unauthorized surveillance, as face recognition can facilitate invasive tracking and profiling. Implementing strict data protection regulations and transparent consent mechanisms is crucial to address privacy risks inherent in both technologies.
Future Trends in Facial Landmarking and Face Recognition
Future trends in facial landmarking emphasize enhanced precision through deep learning models that adapt to diverse facial expressions and occlusions, improving real-time applications in augmented reality and healthcare. Face recognition technology is advancing with multimodal biometric systems integrating 3D facial data and thermal imaging to boost accuracy and security in complex environments. Emerging research explores ethical AI frameworks to address privacy concerns while enabling widespread adoption in smart cities and personalized user experiences.
Choosing the Right Technology for Your Needs
Facial landmarking identifies key facial features such as eyes, nose, and mouth to analyze expressions or head poses, making it essential for applications like emotion detection and augmented reality. Face recognition compares facial patterns against a database to verify or identify individuals, crucial for security systems and identity verification. Selecting between these technologies depends on whether your goal is detailed facial analysis or accurate identification, aligning with the specific use case and performance requirements.
Facial landmarking vs Face recognition Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com