Secure Erase permanently removes data by overwriting the entire storage device, rendering retrieval impossible even with advanced recovery tools. File shredding targets individual files, overwriting them multiple times to prevent recovery while leaving other data intact. Choosing between Secure Erase and File Shredding depends on whether you need to wipe entire drives or selectively delete sensitive files with precision.
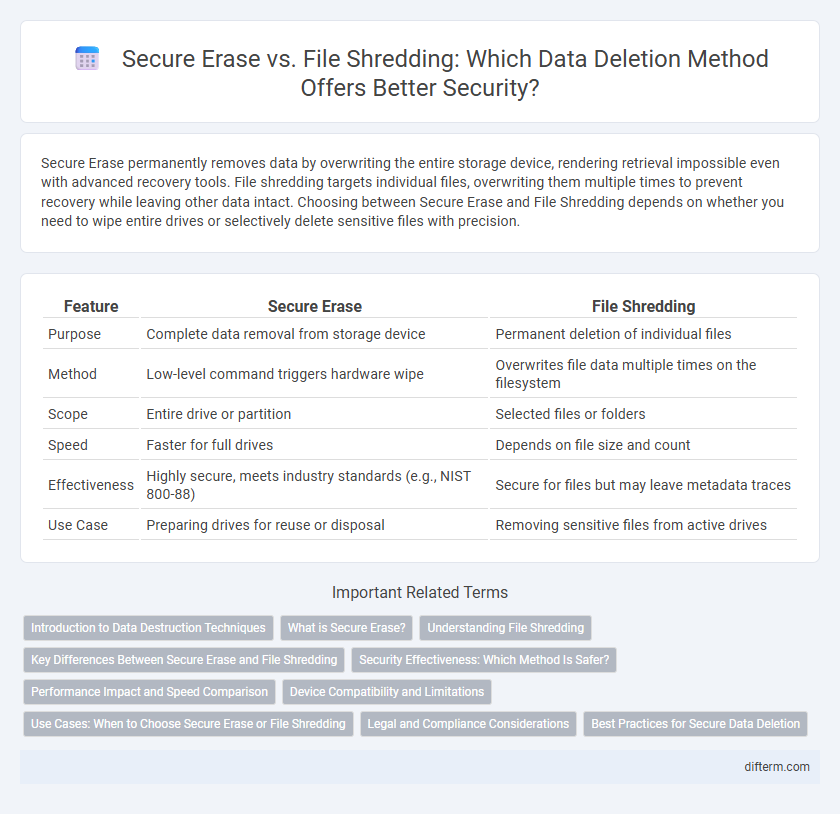
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Secure Erase | File Shredding |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Complete data removal from storage device | Permanent deletion of individual files |
| Method | Low-level command triggers hardware wipe | Overwrites file data multiple times on the filesystem |
| Scope | Entire drive or partition | Selected files or folders |
| Speed | Faster for full drives | Depends on file size and count |
| Effectiveness | Highly secure, meets industry standards (e.g., NIST 800-88) | Secure for files but may leave metadata traces |
| Use Case | Preparing drives for reuse or disposal | Removing sensitive files from active drives |
Introduction to Data Destruction Techniques
Secure Erase uses firmware commands to permanently delete all data on a storage device by overwriting every sector, ensuring complete data irretrievability. File Shredding targets individual files, repeatedly overwriting them to prevent recovery while leaving other data intact. Both techniques are essential for data destruction, with Secure Erase suited for full-drive sanitization and File Shredding ideal for selective file deletion.
What is Secure Erase?
Secure Erase is a data deletion method that permanently removes all information from a storage device by directly overwriting its memory cells at the hardware level. Unlike file shredding, which targets individual files and can sometimes leave recoverable traces, Secure Erase erases every bit of data across the entire drive, ensuring complete and irreversible data destruction. This process is widely used in SSDs and HDDs to protect sensitive information from recovery, particularly in enterprise security and data compliance scenarios.
Understanding File Shredding
File shredding is a method of securely deleting files by overwriting data multiple times to prevent recovery using forensic tools. Unlike secure erase, which targets entire storage devices, file shredding focuses on individual files or folders, making it suitable for selective data destruction. Effective file shredding uses algorithms such as DoD 5220.22-M, ensuring that sensitive information cannot be reconstructed or accessed after deletion.
Key Differences Between Secure Erase and File Shredding
Secure Erase permanently removes all data from storage media by overwriting every bit, ensuring recovery is impossible even with advanced forensic tools. File Shredding targets specific files, overwriting their data to prevent recovery but leaving other data intact on the device. The key difference lies in scope: Secure Erase wipes the entire drive, whereas File Shredding selectively destroys individual files.
Security Effectiveness: Which Method Is Safer?
Secure erase employs hardware-level commands that irreversibly overwrite data on storage devices, making recovery virtually impossible and offering superior security effectiveness compared to file shredding. File shredding repeatedly overwrites files at the software level but may leave traces recoverable with advanced forensic tools, especially on solid-state drives due to wear leveling. Evaluating security effectiveness, secure erase ensures a higher degree of data destruction, critical for protecting sensitive information against sophisticated recovery methods.
Performance Impact and Speed Comparison
Secure Erase offers superior performance impact by directly instructing storage hardware to delete data, resulting in faster execution compared to File Shredding. File Shredding relies on overwriting files multiple times at the software level, which significantly increases processing time and resource usage. Hardware-level Secure Erase is most efficient for solid-state drives (SSDs), providing near-instant data removal without degrading device lifespan.
Device Compatibility and Limitations
Secure Erase provides deep data removal by targeting the storage device's firmware, ensuring compatibility primarily with SSDs and newer hard drives that support this command, while older HDDs may not execute it effectively. File shredding operates at the software level, overwriting specific files multiple times, making it compatible across most devices but less reliable for SSDs due to wear-leveling and hidden storage areas. Limitations of Secure Erase include potential firmware bugs and lack of support on some devices, whereas file shredding cannot guarantee complete data removal from flash memory cells.
Use Cases: When to Choose Secure Erase or File Shredding
Secure Erase is ideal for permanently wiping entire drives during device decommissioning or before resale to prevent data recovery at the hardware level. File Shredding suits scenarios requiring selective deletion of sensitive files without affecting other data, commonly used for protecting confidentiality on active systems. Choosing between them depends on whether complete data destruction or targeted file removal aligns with security policies and operational needs.
Legal and Compliance Considerations
Secure erase methods comply with stringent data protection regulations by irreversibly removing all data at the storage device level, ensuring complete elimination required under laws like GDPR and HIPAA. File shredding, while effective for individual files, may leave remnants recoverable by forensic tools, potentially failing to meet regulatory standards for sensitive data disposal. Organizations must evaluate their compliance requirements and choose data destruction techniques that provide verifiable audit trails and align with legal mandates to avoid penalties and data breach liabilities.
Best Practices for Secure Data Deletion
Secure erase methods overwrite entire storage devices at the hardware level, ensuring complete data destruction beyond recovery, while file shredding targets specific files by overwriting their data multiple times with random patterns. Best practices for secure data deletion recommend using secure erase commands like ATA Secure Erase or NVMe Format Secure Erase for SSDs and HDDs, as these are more reliable and faster than software-based shredding. For sensitive data on individual files, combining file shredding tools with encryption enhances protection against forensic recovery, aligning with compliance standards such as NIST SP 800-88.
Secure Erase vs File Shredding Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com