Intrusion Detection systems monitor network traffic to identify suspicious activities and alert administrators to potential threats. Intrusion Prevention systems actively block or mitigate malicious actions in real-time, providing a proactive defense layer. Combining both enhances overall security by detecting threats early and preventing attacks from causing damage.
Table of Comparison
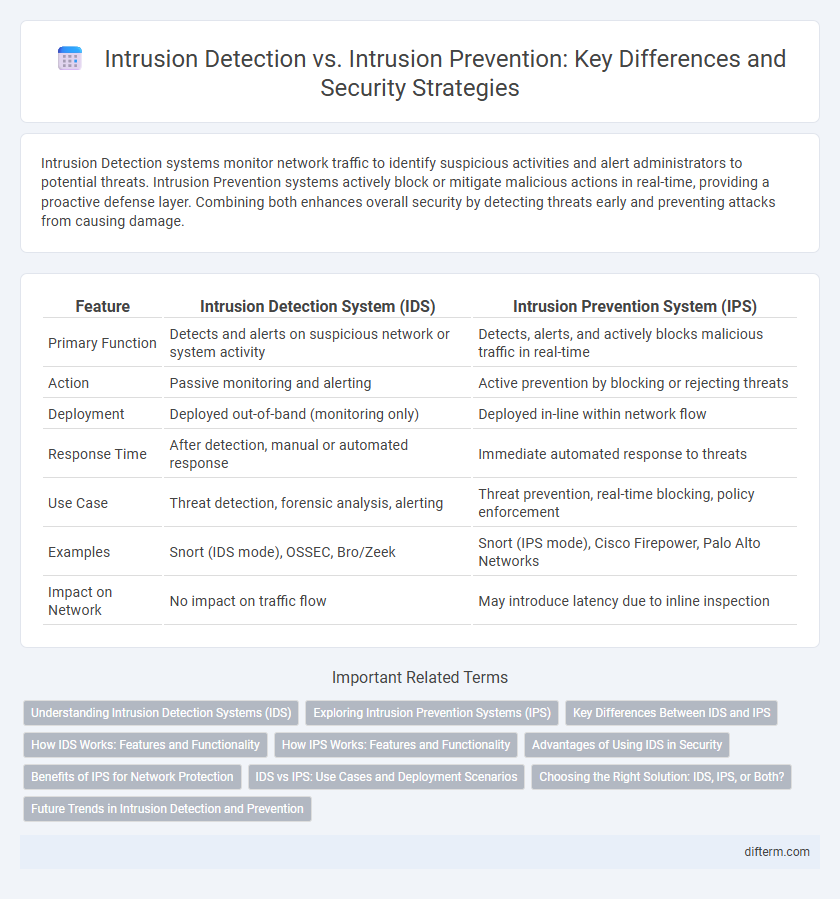
| Feature | Intrusion Detection System (IDS) | Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Detects and alerts on suspicious network or system activity | Detects, alerts, and actively blocks malicious traffic in real-time |
| Action | Passive monitoring and alerting | Active prevention by blocking or rejecting threats |
| Deployment | Deployed out-of-band (monitoring only) | Deployed in-line within network flow |
| Response Time | After detection, manual or automated response | Immediate automated response to threats |
| Use Case | Threat detection, forensic analysis, alerting | Threat prevention, real-time blocking, policy enforcement |
| Examples | Snort (IDS mode), OSSEC, Bro/Zeek | Snort (IPS mode), Cisco Firepower, Palo Alto Networks |
| Impact on Network | No impact on traffic flow | May introduce latency due to inline inspection |
Understanding Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) monitor network traffic and system activities to identify suspicious behavior and potential threats by analyzing data patterns and signatures. IDS provides real-time alerts without blocking traffic, enabling security teams to investigate breaches promptly. Unlike Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS), IDS focuses on detection and alerting, playing a critical role in early threat identification and incident response.
Exploring Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) actively monitor network traffic to identify and block potential threats in real-time, providing a proactive defense compared to Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) that only alert on suspicious activity. IPS deploy signature-based, anomaly-based, and behavior-based detection techniques to prevent unauthorized access, malware, and exploitation attempts before they cause harm. Implementing IPS enhances overall cybersecurity posture by reducing false positives and enabling automated response to evolving cyber threats.
Key Differences Between IDS and IPS
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) monitor network traffic and generate alerts when suspicious activity is detected, focusing primarily on identifying potential threats. Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) actively analyze and block malicious traffic in real-time to prevent security breaches before they occur. Unlike IDS, which is passive and alert-based, IPS provides proactive defense by automatically intervening to stop attacks.
How IDS Works: Features and Functionality
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) monitor network traffic and system activities to identify suspicious patterns indicative of potential security breaches using signature-based and anomaly-based detection techniques. Core features include real-time alerting, comprehensive logging, and traffic analysis to detect unauthorized access, malware, or policy violations without actively blocking threats. Functionality relies on sensors deployed across network nodes, leveraging behavioral analysis and protocol inspection to distinguish malicious activity from legitimate operations, enabling security teams to respond effectively to emerging threats.
How IPS Works: Features and Functionality
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) monitor network traffic in real-time to detect and block malicious activities automatically, using signature-based detection, anomaly detection, and behavior analysis. Key features include deep packet inspection, automated response to threats, and integration with other security tools for comprehensive protection. IPS functionality emphasizes proactive threat prevention by identifying suspicious patterns and enforcing security policies to minimize the risk of intrusions before damage occurs.
Advantages of Using IDS in Security
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) provide real-time monitoring and alerting capabilities, enabling security teams to quickly identify and respond to suspicious activities. IDS offers comprehensive visibility into network traffic without disrupting normal operations, which helps in forensic analysis and compliance auditing. These systems enhance security posture by detecting unknown threats and insider attacks that might bypass preventive controls.
Benefits of IPS for Network Protection
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) actively monitor network traffic to detect and block malicious activities in real-time, significantly reducing the risk of breaches. By preventing attacks before they infiltrate the network, IPS enhances overall security posture and lowers the potential impact of cyber threats. The automated response capabilities of IPS streamline threat mitigation, minimizing downtime and limiting damage to critical infrastructure.
IDS vs IPS: Use Cases and Deployment Scenarios
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are primarily designed for monitoring network traffic and alerting administrators about potential security breaches, making them ideal for environments requiring detailed forensic analysis and passive security oversight. Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) actively block or mitigate detected threats in real-time, suited for deployment in high-security networks where immediate threat response is critical to prevent damage. Organizations often deploy IDS in conjunction with IPS to balance comprehensive threat detection with proactive defense across varied network architectures.
Choosing the Right Solution: IDS, IPS, or Both?
Selecting the right security solution depends on the specific needs of your network environment: Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) monitor and alert on suspicious activity, while Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) actively block threats in real-time. For comprehensive protection, combining IDS and IPS provides both visibility and automated response, enhancing threat detection and mitigation capabilities. Evaluating factors such as network size, threat landscape, and resource availability guides the optimal integration of IDS, IPS, or a hybrid approach.
Future Trends in Intrusion Detection and Prevention
Future trends in intrusion detection and prevention emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance threat detection accuracy and response speed. Behavioral analytics and real-time data processing increasingly enable systems to identify sophisticated and zero-day attacks before significant damage occurs. Cloud-based intrusion detection and prevention platforms offer scalable, adaptive security solutions essential for protecting expanding digital ecosystems.
Intrusion Detection vs Intrusion Prevention Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com