Balancing privacy and security requires careful consideration of individual rights and public safety needs. Implementing strong encryption methods can protect personal data without compromising security measures. Organizations must adopt transparent policies to ensure trust while maintaining robust defense systems against threats.
Table of Comparison
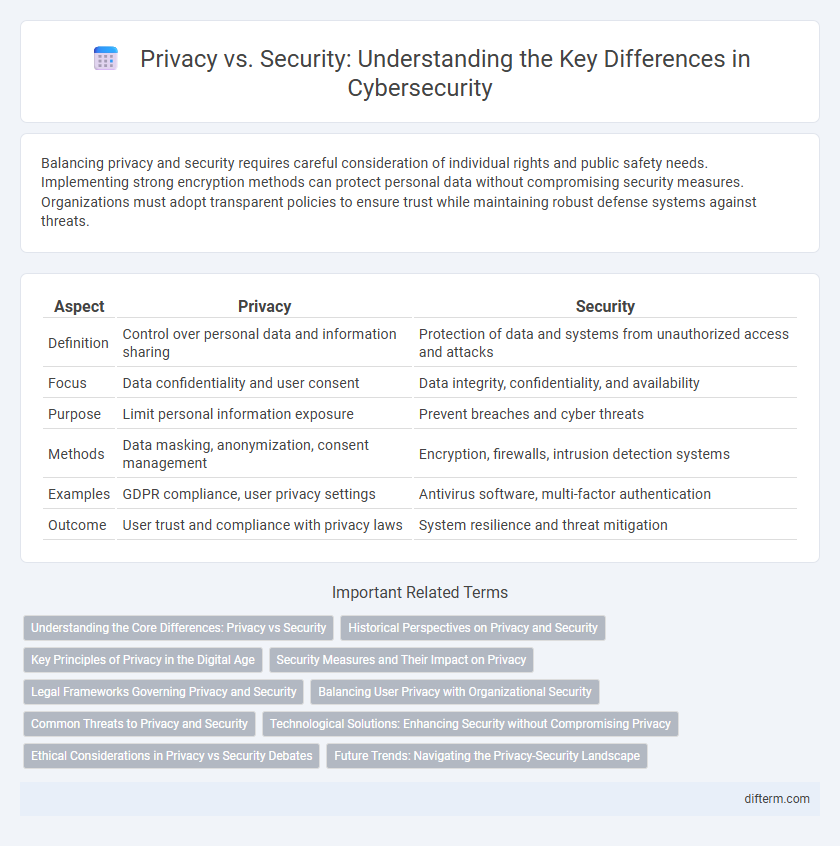
| Aspect | Privacy | Security |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Control over personal data and information sharing | Protection of data and systems from unauthorized access and attacks |
| Focus | Data confidentiality and user consent | Data integrity, confidentiality, and availability |
| Purpose | Limit personal information exposure | Prevent breaches and cyber threats |
| Methods | Data masking, anonymization, consent management | Encryption, firewalls, intrusion detection systems |
| Examples | GDPR compliance, user privacy settings | Antivirus software, multi-factor authentication |
| Outcome | User trust and compliance with privacy laws | System resilience and threat mitigation |
Understanding the Core Differences: Privacy vs Security
Privacy centers on controlling personal information and ensuring individuals' rights to confidentiality, while security focuses on protecting systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access or breaches. Privacy measures govern how data is collected, stored, and shared, emphasizing consent and transparency. Security employs tools like encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection to safeguard data integrity and prevent cyber threats.
Historical Perspectives on Privacy and Security
Historical perspectives on privacy and security reveal a complex interplay shaped by technological advancements and societal values. Early security measures often emphasized state control, frequently at the expense of individual privacy, as seen in surveillance practices during wartime and authoritarian regimes. Over time, evolving legal frameworks like the Fourth Amendment in the U.S. and international human rights laws have sought to balance national security interests with the protection of personal privacy.
Key Principles of Privacy in the Digital Age
The key principles of privacy in the digital age emphasize data minimization, user consent, and transparency in data handling practices. Robust encryption techniques and strict access controls safeguard personal information from unauthorized access or breaches. Compliance with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA ensures organizations uphold individuals' privacy rights while balancing security needs.
Security Measures and Their Impact on Privacy
Security measures such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and intrusion detection systems play a crucial role in protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access. However, these measures often require extensive data collection and monitoring, which can infringe on individual privacy rights. Balancing robust security protocols with privacy-preserving technologies like anonymization and secure data storage is essential to minimize privacy risks while maintaining effective protection against cyber threats.
Legal Frameworks Governing Privacy and Security
Legal frameworks governing privacy and security establish critical standards for data protection, mandating compliance with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. These laws define the boundaries for data collection, usage, and sharing, balancing individual privacy rights with organizational security responsibilities. Enforcement mechanisms and penalties for violations reinforce adherence, promoting transparency and accountability in handling sensitive information.
Balancing User Privacy with Organizational Security
Balancing user privacy with organizational security requires implementing robust encryption protocols that protect sensitive data without compromising network defenses. Organizations must enforce strict access controls and continuous monitoring to detect threats while respecting user anonymity and data minimization principles. Integrating privacy-by-design frameworks ensures compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA while maintaining a secure environment against cyberattacks.
Common Threats to Privacy and Security
Common threats to privacy and security include data breaches, malware attacks, and phishing schemes that compromise sensitive information. Unauthorized access and identity theft exploit vulnerabilities in personal and organizational data protections, leading to significant privacy violations. Robust encryption, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring are essential strategies to mitigate these pervasive security risks.
Technological Solutions: Enhancing Security without Compromising Privacy
Technological solutions such as end-to-end encryption and zero-trust architectures enhance security while preserving user privacy by minimizing data exposure. Advanced anonymization techniques, including differential privacy and homomorphic encryption, enable secure data analysis without revealing sensitive information. Implementing multi-factor authentication combined with privacy-preserving identity verification frameworks further strengthens system integrity without infringing on individual privacy rights.
Ethical Considerations in Privacy vs Security Debates
Ethical considerations in privacy versus security debates revolve around balancing individuals' rights to confidentiality with collective safety measures. Protecting user data demands transparent policies and informed consent to prevent abuses of surveillance and data collection. Ethical frameworks prioritize minimizing harm while ensuring security solutions respect personal freedoms and legal standards.
Future Trends: Navigating the Privacy-Security Landscape
Future trends in the privacy-security landscape emphasize the integration of advanced encryption methods with artificial intelligence-driven threat detection to balance protection and user confidentiality. Emerging technologies like homomorphic encryption and decentralized identity management enable secure data processing without compromising privacy. Organizations must adopt adaptive security frameworks that prioritize transparency and comply with evolving global privacy regulations to effectively navigate these complexities.
Privacy vs Security Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com