Network Access Control (NAC) enhances security by enforcing policies that control device access based on compliance and user roles, providing granular visibility and reducing threats from unauthorized devices. VPNs primarily secure data transmission by creating encrypted tunnels, but they offer less control over device security and access rights once the connection is established. Combining NAC with VPN can significantly strengthen security by authenticating devices before granting encrypted access, ensuring only compliant endpoints connect to sensitive networks.
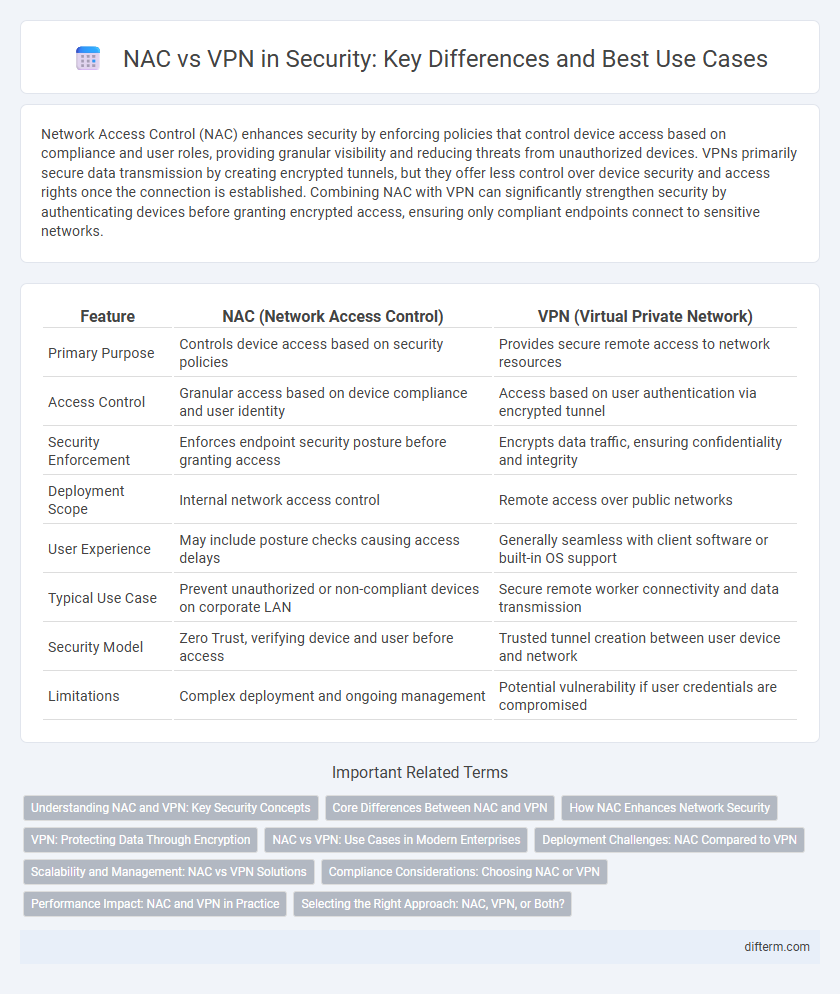
Table of Comparison
| Feature | NAC (Network Access Control) | VPN (Virtual Private Network) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Controls device access based on security policies | Provides secure remote access to network resources |
| Access Control | Granular access based on device compliance and user identity | Access based on user authentication via encrypted tunnel |
| Security Enforcement | Enforces endpoint security posture before granting access | Encrypts data traffic, ensuring confidentiality and integrity |
| Deployment Scope | Internal network access control | Remote access over public networks |
| User Experience | May include posture checks causing access delays | Generally seamless with client software or built-in OS support |
| Typical Use Case | Prevent unauthorized or non-compliant devices on corporate LAN | Secure remote worker connectivity and data transmission |
| Security Model | Zero Trust, verifying device and user before access | Trusted tunnel creation between user device and network |
| Limitations | Complex deployment and ongoing management | Potential vulnerability if user credentials are compromised |
Understanding NAC and VPN: Key Security Concepts
Network Access Control (NAC) enhances security by enforcing policies that verify devices and users before granting network access, ensuring only compliant endpoints connect. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) create encrypted tunnels to protect data transmission across insecure networks, focusing on confidentiality and remote access. Both NAC and VPN play critical roles in a comprehensive security strategy by combining access control with data protection.
Core Differences Between NAC and VPN
Network Access Control (NAC) enforces security policies by authenticating and authorizing devices before granting network access, ensuring only compliant endpoints connect. Virtual Private Network (VPN) creates an encrypted tunnel allowing remote users to securely access internal network resources, primarily focusing on confidentiality and data integrity. Unlike VPNs, NAC provides granular control over device posture and enforces remediation actions, while VPNs primarily secure data transmission without assessing device compliance.
How NAC Enhances Network Security
Network Access Control (NAC) enhances network security by enforcing strict policies that verify device compliance and user identity before granting access, reducing the risk of unauthorized entry and endpoint threats. Unlike VPNs, which primarily create encrypted tunnels for remote access, NAC offers dynamic visibility and control over connected devices, enabling real-time threat detection and remediation. This granular approach strengthens overall network integrity by preventing infected or non-compliant devices from compromising sensitive systems.
VPN: Protecting Data Through Encryption
VPNs protect data by encrypting information exchanged over the internet, ensuring confidentiality and preventing unauthorized access. By creating a secure tunnel between the user's device and the destination server, VPNs safeguard sensitive data from interception by hackers or surveillance entities. This encryption technology is essential for maintaining privacy and data integrity, especially on public or unsecured networks.
NAC vs VPN: Use Cases in Modern Enterprises
Network Access Control (NAC) and Virtual Private Networks (VPN) serve distinct functions in enterprise security: NAC ensures devices comply with security policies before granting network access, enhancing endpoint security and reducing internal threats; VPNs enable secure remote connectivity by encrypting data traffic over public networks, protecting data confidentiality and integrity. Modern enterprises deploy NAC to enforce dynamic access controls in hybrid environments, managing device posture and user authentication at the network edge, while VPNs remain crucial for securing offsite employee access and remote office connections. Combining NAC's policy-based access management with VPN's encrypted tunnels optimizes security frameworks, addressing diverse use cases such as zero trust implementation and secure remote workforces.
Deployment Challenges: NAC Compared to VPN
Network Access Control (NAC) deployment often faces challenges such as complex integration with existing infrastructure, diverse device compatibility, and continuous policy management, which require significant IT resources. In contrast, VPNs typically offer simpler deployment by primarily providing encrypted tunnels without granular endpoint compliance checks. These differences make NAC more resource-intensive to implement but offer enhanced security through detailed access control policies compared to the broader network protection VPNs provide.
Scalability and Management: NAC vs VPN Solutions
Network Access Control (NAC) offers superior scalability and centralized management compared to traditional VPN solutions, enabling organizations to enforce consistent security policies across diverse devices and access points. NAC integrates with existing directory services and security tools, providing granular control over user access and real-time device compliance monitoring. VPNs often face limitations in scaling due to increased configuration complexity and lack of dynamic endpoint assessment, impacting overall network security management.
Compliance Considerations: Choosing NAC or VPN
Network Access Control (NAC) provides granular visibility and enforcement of security policies at the device level, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards such as HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI-DSS by controlling endpoint posture before granting network access. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) primarily secure data transmission through encryption but lack comprehensive endpoint compliance checks, potentially leaving non-compliant devices connected. Organizations aiming for strict regulatory adherence often prefer NAC solutions for their proactive compliance enforcement and detailed access controls.
Performance Impact: NAC and VPN in Practice
Network Access Control (NAC) delivers superior performance impact compared to VPNs by enforcing security policies directly at the network edge, reducing latency and bandwidth overhead. VPNs introduce significant network overhead through encryption and tunneling, often resulting in slower connection speeds and increased latency. Enterprises seeking seamless user experience prioritize NAC to minimize performance degradation while maintaining robust security controls.
Selecting the Right Approach: NAC, VPN, or Both?
Network Access Control (NAC) provides granular security by enforcing policies based on user identity, device posture, and compliance status, making it ideal for internal network segmentation and mitigating insider threats. Virtual Private Network (VPN) offers encrypted tunnels for secure remote access, shielding data in transit from external threats but lacking detailed endpoint validation. Combining NAC and VPN enhances overall security posture by ensuring remote users connect through encrypted channels while their devices meet policy requirements before accessing network resources.
NAC vs VPN Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com