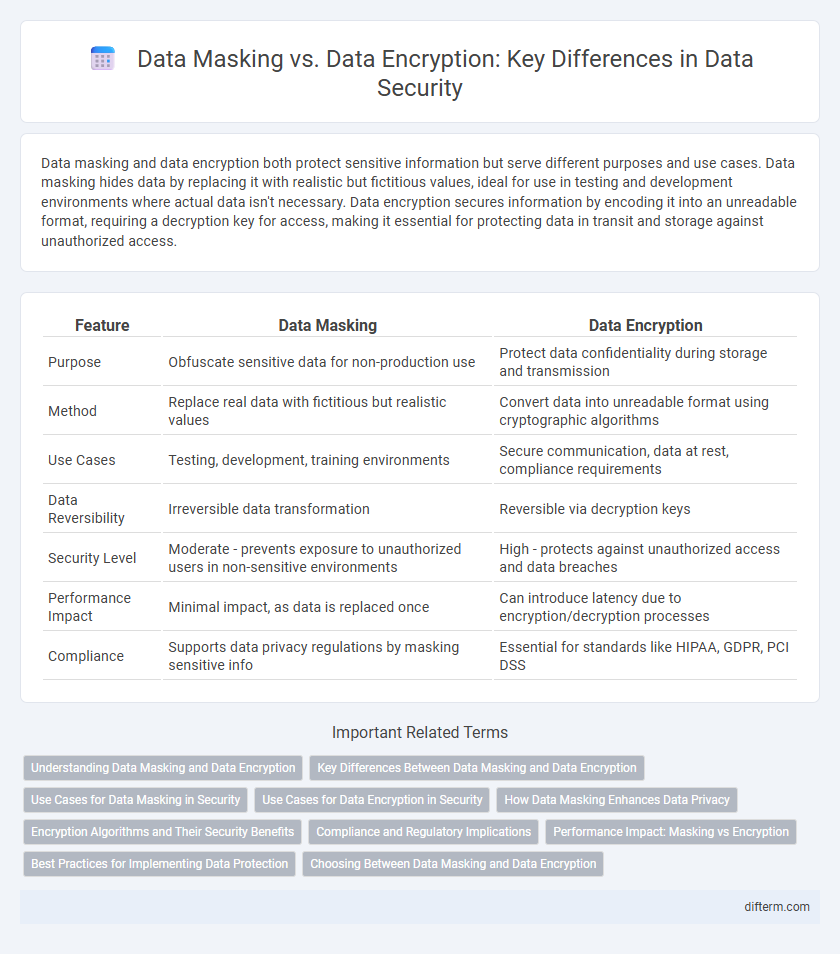
Data masking and data encryption both protect sensitive information but serve different purposes and use cases. Data masking hides data by replacing it with realistic but fictitious values, ideal for use in testing and development environments where actual data isn't necessary. Data encryption secures information by encoding it into an unreadable format, requiring a decryption key for access, making it essential for protecting data in transit and storage against unauthorized access.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Data Masking | Data Encryption |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Obfuscate sensitive data for non-production use | Protect data confidentiality during storage and transmission |
| Method | Replace real data with fictitious but realistic values | Convert data into unreadable format using cryptographic algorithms |
| Use Cases | Testing, development, training environments | Secure communication, data at rest, compliance requirements |
| Data Reversibility | Irreversible data transformation | Reversible via decryption keys |
| Security Level | Moderate - prevents exposure to unauthorized users in non-sensitive environments | High - protects against unauthorized access and data breaches |
| Performance Impact | Minimal impact, as data is replaced once | Can introduce latency due to encryption/decryption processes |
| Compliance | Supports data privacy regulations by masking sensitive info | Essential for standards like HIPAA, GDPR, PCI DSS |
Understanding Data Masking and Data Encryption
Data masking transforms sensitive information into a disguised version to prevent exposure during development and testing, maintaining data usability without revealing actual values. Data encryption converts data into an unreadable format using cryptographic algorithms, ensuring confidentiality and secure transmission or storage, accessible only with the correct decryption key. While data masking is ideal for non-production environments to protect privacy, encryption is essential for safeguarding data in transit and at rest across systems.
Key Differences Between Data Masking and Data Encryption
Data masking obfuscates sensitive information by replacing original data with fictitious but realistic values, allowing safe use in non-production environments without exposing actual data. Data encryption transforms data into a coded format using cryptographic algorithms and keys, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity during storage or transmission. While data masking is primarily used for anonymization in testing and development, encryption provides strong protection against unauthorized access in real-time operations.
Use Cases for Data Masking in Security
Data masking is primarily used in security to protect sensitive information in non-production environments such as development, testing, and training, where real data is unnecessary. It enables organizations to comply with data privacy regulations like GDPR and HIPAA by ensuring that unauthorized personnel cannot access actual data. Unlike data encryption, masking creates fake yet realistic data, reducing risks during data sharing and analysis without compromising operational efficiency.
Use Cases for Data Encryption in Security
Data encryption is essential for securing sensitive information during transmission and storage, particularly in applications such as online banking, e-commerce, and cloud services. It prevents unauthorized access by converting plaintext data into unreadable ciphertext, ensuring confidentiality and data integrity. Use cases include securing financial transactions, protecting personal health information (PHI) to comply with HIPAA regulations, and safeguarding corporate intellectual property from cyberattacks.
How Data Masking Enhances Data Privacy
Data masking enhances data privacy by replacing sensitive information with realistic but fictional data, ensuring that unauthorized users cannot access actual confidential details. This technique allows organizations to use data for testing, analysis, or training without exposing real personal or financial information, reducing the risk of data breaches. Unlike encryption, which secures data by transforming it into unreadable code requiring decryption, data masking creates safe data replicas, maintaining usability while preventing privacy violations.
Encryption Algorithms and Their Security Benefits
Encryption algorithms such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) provide robust data protection by transforming plaintext into ciphertext, making unauthorized access nearly impossible without the decryption key. AES, a symmetric key algorithm, is widely adopted for its efficiency and strong security in protecting sensitive data at rest and in transit. RSA, an asymmetric encryption method, enhances security by using a public-private key pair, facilitating secure data exchange and digital signatures critical for authentication and confidentiality.
Compliance and Regulatory Implications
Data masking and data encryption both play critical roles in meeting compliance and regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Data masking protects sensitive information by obfuscating data in non-production environments, ensuring that real data is not exposed during testing or development. Data encryption safeguards data at rest and in transit by converting plaintext into ciphertext, thereby ensuring confidentiality and integrity in accordance with regulatory mandates.
Performance Impact: Masking vs Encryption
Data masking generally has a lower performance impact compared to data encryption because it involves simpler transformations that do not require complex cryptographic computations. Encryption mandates resource-intensive algorithms to secure data, often resulting in higher CPU usage and latency, especially for large datasets or high-frequency transactions. Choosing data masking improves system responsiveness in non-critical environments, while encryption is essential when robust security outweighs performance concerns.
Best Practices for Implementing Data Protection
Data masking and data encryption are critical techniques for securing sensitive information, with masking providing obfuscation for non-production environments and encryption ensuring data confidentiality in transit and at rest. Best practices for implementing data protection include employing strong encryption algorithms like AES-256, applying role-based access controls to limit data exposure, and regularly auditing masking processes to maintain data integrity and compliance. Combining both methods strategically enhances overall security posture by balancing usability and protection across different use cases.
Choosing Between Data Masking and Data Encryption
Choosing between data masking and data encryption depends on the specific security requirements and use cases within an organization. Data masking is ideal for protecting sensitive information in non-production environments by obfuscating data while maintaining usability for testing and development. In contrast, data encryption secures data by converting it into an unreadable format that requires a decryption key, making it essential for protecting data at rest and in transit against unauthorized access.
Data Masking vs Data Encryption Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com