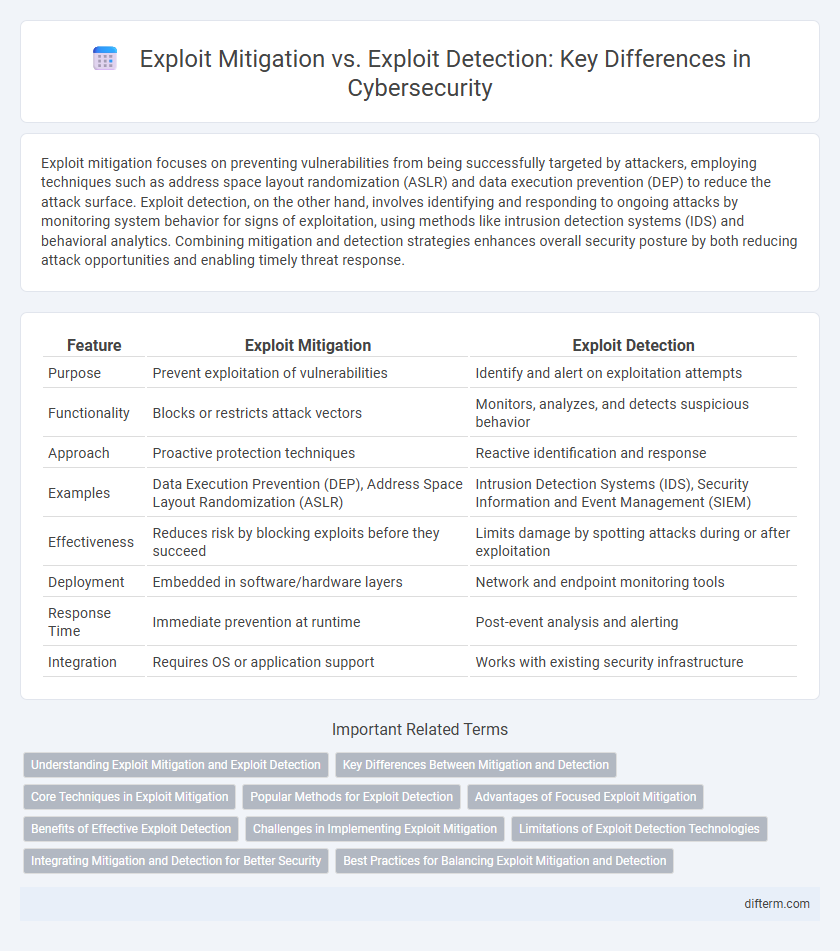
Exploit mitigation focuses on preventing vulnerabilities from being successfully targeted by attackers, employing techniques such as address space layout randomization (ASLR) and data execution prevention (DEP) to reduce the attack surface. Exploit detection, on the other hand, involves identifying and responding to ongoing attacks by monitoring system behavior for signs of exploitation, using methods like intrusion detection systems (IDS) and behavioral analytics. Combining mitigation and detection strategies enhances overall security posture by both reducing attack opportunities and enabling timely threat response.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Exploit Mitigation | Exploit Detection |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevent exploitation of vulnerabilities | Identify and alert on exploitation attempts |
| Functionality | Blocks or restricts attack vectors | Monitors, analyzes, and detects suspicious behavior |
| Approach | Proactive protection techniques | Reactive identification and response |
| Examples | Data Execution Prevention (DEP), Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) | Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) |
| Effectiveness | Reduces risk by blocking exploits before they succeed | Limits damage by spotting attacks during or after exploitation |
| Deployment | Embedded in software/hardware layers | Network and endpoint monitoring tools |
| Response Time | Immediate prevention at runtime | Post-event analysis and alerting |
| Integration | Requires OS or application support | Works with existing security infrastructure |
Understanding Exploit Mitigation and Exploit Detection
Exploit mitigation involves implementing proactive security measures such as address space layout randomization (ASLR), data execution prevention (DEP), and control flow integrity (CFI) to prevent attackers from successfully exploiting vulnerabilities. Exploit detection focuses on identifying and responding to exploit attempts through behavior analysis, signature matching, and anomaly detection systems. Combining both approaches enhances overall security by reducing attack surfaces and enabling timely incident response.
Key Differences Between Mitigation and Detection
Exploit mitigation proactively prevents attacks by strengthening system defenses through techniques such as control flow integrity and address space layout randomization, reducing the attack surface before exploitation occurs. Exploit detection focuses on identifying and responding to attacks in real-time by monitoring system behaviors, using anomaly detection and signature-based methods to recognize suspicious activities. Mitigation limits vulnerabilities and attack success, whereas detection emphasizes rapid identification and containment of potential breaches after they begin.
Core Techniques in Exploit Mitigation
Core techniques in exploit mitigation include Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR), Data Execution Prevention (DEP), and Control Flow Integrity (CFI), which collectively prevent attackers from reliably executing malicious code. ASLR randomizes memory addresses to make it difficult for exploits to locate victim data, while DEP enforces non-executable memory regions to block code injection attacks. CFI strengthens program control flow by ensuring execution follows legitimate paths, effectively reducing the risk of control-flow hijacking exploits.
Popular Methods for Exploit Detection
Popular methods for exploit detection include signature-based detection, which identifies known attack patterns by matching code signatures against a database, and anomaly-based detection, which monitors system behavior to flag deviations from established norms. Heuristic techniques analyze code behavior to detect unknown exploits, while sandboxing isolates suspicious processes to observe potentially malicious activity safely. Combining these detection methods enhances system security by providing comprehensive coverage against both known and emerging threats.
Advantages of Focused Exploit Mitigation
Focused exploit mitigation proactively blocks specific attack vectors by hardening vulnerabilities at the application or system level, significantly reducing the risk of exploitation. It minimizes false positives and resource overhead compared to broad detection systems, ensuring more efficient use of security resources. By preventing exploits before they occur, focused mitigation enhances overall system resilience and reduces incident response time.
Benefits of Effective Exploit Detection
Effective exploit detection enhances security by identifying and neutralizing threats before they can cause damage, minimizing potential data breaches and system compromises. It provides real-time alerts that enable rapid incident response, reducing downtime and limiting the impact of attacks. Continuous monitoring through exploit detection also improves overall threat intelligence, allowing organizations to adapt defenses against evolving attack techniques.
Challenges in Implementing Exploit Mitigation
Implementing exploit mitigation faces challenges such as balancing system performance with comprehensive protection, as techniques like address space layout randomization (ASLR) and data execution prevention (DEP) can introduce latency or compatibility issues. Ensuring coverage against zero-day vulnerabilities requires continuous updates and integration with threat intelligence, complicating deployment. Moreover, the complexity of modern software environments increases the difficulty of applying consistent mitigation controls without disrupting legitimate processes.
Limitations of Exploit Detection Technologies
Exploit detection technologies often struggle with zero-day vulnerabilities and polymorphic malware, limiting their effectiveness in identifying sophisticated attacks. These systems can generate high false-positive rates, overwhelming security teams and causing alert fatigue. Resource constraints and reliance on signature-based approaches further reduce their ability to detect novel exploits in real-time.
Integrating Mitigation and Detection for Better Security
Integrating exploit mitigation and detection enhances security by simultaneously preventing attacks and identifying threats in real-time. Mitigation techniques like ASLR and DEP reduce attack surfaces, while advanced detection systems monitor anomalies to rapidly respond to exploits. Combining these approaches creates a layered defense that improves threat resilience and reduces the risk of successful intrusions.
Best Practices for Balancing Exploit Mitigation and Detection
Effective exploit mitigation involves implementing robust security controls such as memory protection, address space layout randomization (ASLR), and control flow integrity to reduce vulnerability exposure. Complementing mitigation with advanced exploit detection techniques like behavioral analysis and anomaly-based intrusion detection systems enables rapid identification of novel threats. Balancing these approaches requires continuous monitoring, timely patch management, and adaptive response strategies to minimize attack surfaces while enhancing detection accuracy.
exploit mitigation vs exploit detection Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com