Endpoint protection focuses on securing individual devices such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets by deploying antivirus, anti-malware, and threat detection software directly on each device. Network protection safeguards the overall network infrastructure by monitoring traffic, preventing unauthorized access, and blocking malicious data packets before they reach endpoints. Combining endpoint and network protection enhances comprehensive security by addressing threats at both the device and network levels.
Table of Comparison
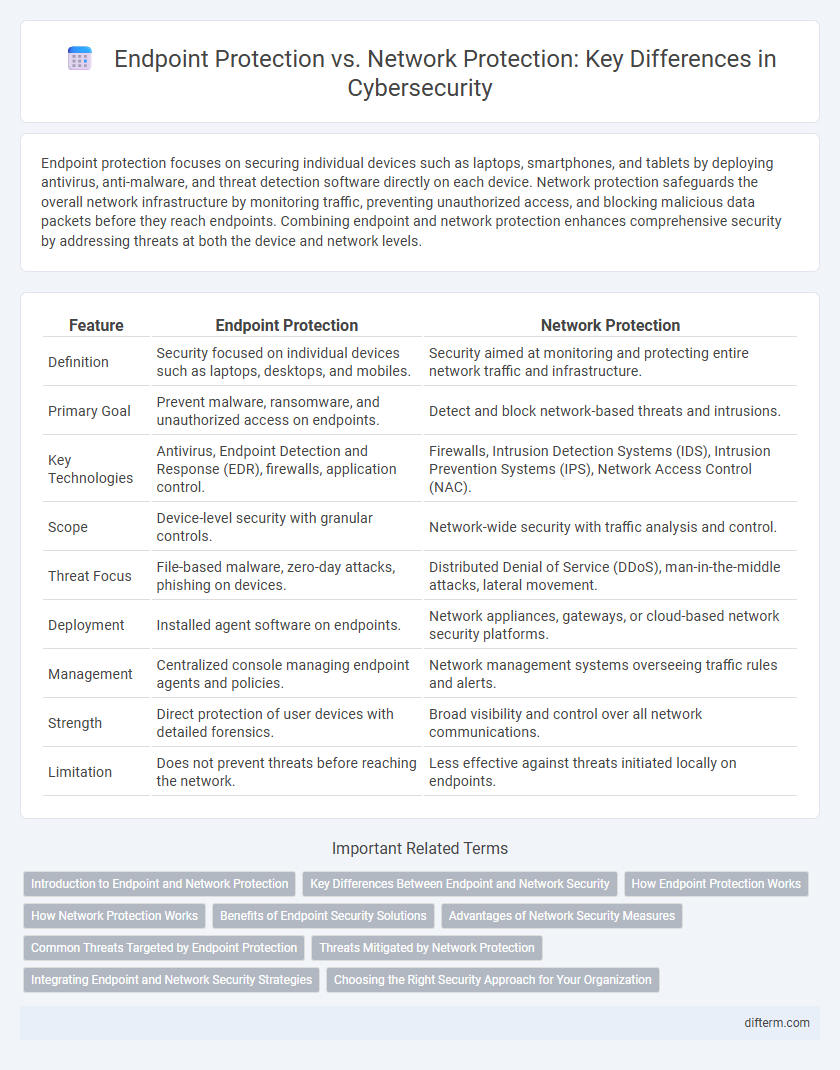
| Feature | Endpoint Protection | Network Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Security focused on individual devices such as laptops, desktops, and mobiles. | Security aimed at monitoring and protecting entire network traffic and infrastructure. |
| Primary Goal | Prevent malware, ransomware, and unauthorized access on endpoints. | Detect and block network-based threats and intrusions. |
| Key Technologies | Antivirus, Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), firewalls, application control. | Firewalls, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS), Network Access Control (NAC). |
| Scope | Device-level security with granular controls. | Network-wide security with traffic analysis and control. |
| Threat Focus | File-based malware, zero-day attacks, phishing on devices. | Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS), man-in-the-middle attacks, lateral movement. |
| Deployment | Installed agent software on endpoints. | Network appliances, gateways, or cloud-based network security platforms. |
| Management | Centralized console managing endpoint agents and policies. | Network management systems overseeing traffic rules and alerts. |
| Strength | Direct protection of user devices with detailed forensics. | Broad visibility and control over all network communications. |
| Limitation | Does not prevent threats before reaching the network. | Less effective against threats initiated locally on endpoints. |
Introduction to Endpoint and Network Protection
Endpoint protection safeguards individual devices such as laptops, smartphones, and desktops by detecting and mitigating malware, ransomware, and unauthorized access directly on the device. Network protection secures the entire network infrastructure by monitoring and filtering traffic, preventing intrusions, and blocking malicious activities at the perimeter or within internal segments. Both approaches are essential to form a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that addresses threats at both device and network levels.
Key Differences Between Endpoint and Network Security
Endpoint protection focuses on securing individual devices like laptops, smartphones, and desktops by detecting malware, managing applications, and enforcing policies directly on the endpoint. Network protection safeguards the entire IT infrastructure by monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing traffic, preventing unauthorized access, and detecting network-based threats using firewalls and intrusion detection systems. Key differences include the scope of security--device-specific versus infrastructure-wide--and the type of threats addressed, where endpoint protection targets device-level vulnerabilities and network protection defends against perimeter and internal network attacks.
How Endpoint Protection Works
Endpoint protection works by installing security software directly on individual devices, such as computers, smartphones, and tablets, to detect, prevent, and respond to cyber threats at the device level. It uses advanced techniques like antivirus scanning, firewall integration, behavior monitoring, and real-time threat intelligence to safeguard endpoints from malware, ransomware, phishing attacks, and unauthorized access. Endpoint protection often includes centralized management consoles that allow IT teams to enforce policies, deploy updates, and monitor security status across all connected devices.
How Network Protection Works
Network protection works by monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing traffic to prevent unauthorized access and cyber threats at the network level, utilizing firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS). These technologies analyze data packets in real-time, identifying malicious patterns and blocking suspicious activities before they reach endpoints. Network protection also employs encryption and segmentation to safeguard sensitive information and limit the spread of attacks across connected devices.
Benefits of Endpoint Security Solutions
Endpoint security solutions provide granular protection by safeguarding individual devices such as laptops, smartphones, and desktops against malware, ransomware, and unauthorized access. These solutions enable real-time threat detection and response at the device level, reducing the risk of data breaches and minimizing lateral movement within a network. By integrating advanced features like behavioral analysis, encryption, and multi-factor authentication, endpoint security enhances overall organizational resilience against evolving cyber threats.
Advantages of Network Security Measures
Network security measures provide comprehensive protection by monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing traffic across the entire network, reducing the risk of widespread attacks. They enable early detection of threats through centralized management and real-time analytics, enhancing response time and threat mitigation. Unlike endpoint protection, network security safeguards multiple devices simultaneously, ensuring consistent policy enforcement and minimizing vulnerabilities in interconnected systems.
Common Threats Targeted by Endpoint Protection
Endpoint protection primarily targets threats such as malware, ransomware, phishing attacks, and zero-day exploits that directly compromise individual devices like laptops and smartphones. These attacks often leverage vulnerabilities in operating systems or applications, making real-time detection and response on endpoints critical. Network protection, while essential for perimeter defense, cannot detect threats that bypass network filters and manifest directly on user devices.
Threats Mitigated by Network Protection
Network protection primarily mitigates threats such as Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, man-in-the-middle intrusions, and unauthorized access attempts by filtering and monitoring inbound and outbound traffic. It effectively detects and blocks malware propagation, phishing campaigns, and command-and-control communications before reaching endpoints. By leveraging firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and virtual private networks (VPNs), network protection fortifies the IT infrastructure against external and lateral threats.
Integrating Endpoint and Network Security Strategies
Integrating endpoint protection with network security strategies enhances overall threat detection and response capabilities by creating a unified defense system that monitors both device-level activities and network traffic patterns. This approach leverages endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools alongside network intrusion detection systems (NIDS) to offer comprehensive visibility into potential vulnerabilities and threat vectors across the entire IT environment. Organizations adopting integrated security frameworks reduce incident response times and improve protection against sophisticated attacks targeting multiple layers simultaneously.
Choosing the Right Security Approach for Your Organization
Endpoint protection focuses on securing individual devices such as laptops, smartphones, and desktops by preventing malware, unauthorized access, and data breaches directly at the device level. Network protection safeguards the entire network infrastructure, monitoring traffic for suspicious activity, blocking intrusions, and securing communication channels between devices and servers. Selecting the optimal security approach depends on assessing your organization's specific risk profile, device types, network complexity, and compliance requirements to implement a tailored solution that addresses both endpoint vulnerabilities and network threats effectively.
Endpoint protection vs network protection Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com