Sandboxing isolates applications in a restricted environment to prevent malicious code from affecting the host system, offering lightweight security with minimal resource overhead. Virtualization creates full virtual machines that emulate hardware, providing comprehensive isolation and control suitable for running multiple operating systems or complex workloads securely. Both techniques enhance system protection, but sandboxing is ideal for application-level security while virtualization supports broader infrastructure-level defenses.
Table of Comparison
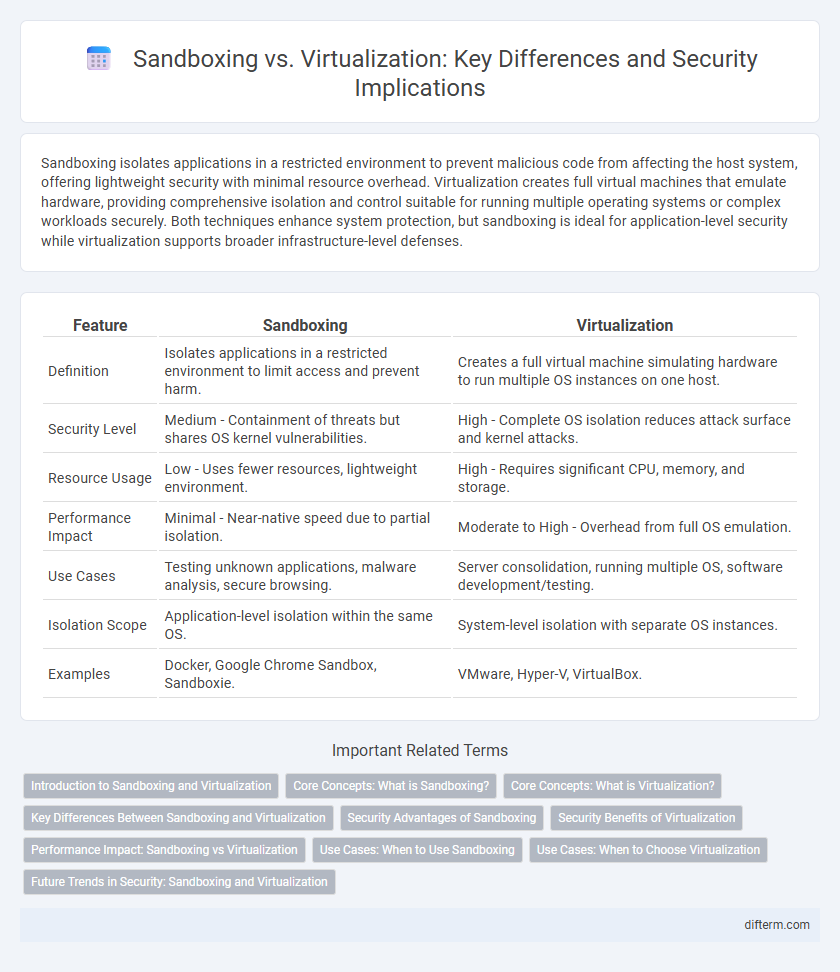
| Feature | Sandboxing | Virtualization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Isolates applications in a restricted environment to limit access and prevent harm. | Creates a full virtual machine simulating hardware to run multiple OS instances on one host. |
| Security Level | Medium - Containment of threats but shares OS kernel vulnerabilities. | High - Complete OS isolation reduces attack surface and kernel attacks. |
| Resource Usage | Low - Uses fewer resources, lightweight environment. | High - Requires significant CPU, memory, and storage. |
| Performance Impact | Minimal - Near-native speed due to partial isolation. | Moderate to High - Overhead from full OS emulation. |
| Use Cases | Testing unknown applications, malware analysis, secure browsing. | Server consolidation, running multiple OS, software development/testing. |
| Isolation Scope | Application-level isolation within the same OS. | System-level isolation with separate OS instances. |
| Examples | Docker, Google Chrome Sandbox, Sandboxie. | VMware, Hyper-V, VirtualBox. |
Introduction to Sandboxing and Virtualization
Sandboxing isolates applications within a controlled environment, restricting access to system resources and preventing malicious code from affecting the host system. Virtualization creates multiple independent virtual machines on a single physical server, enabling running separate operating systems and applications with dedicated resources. Both techniques enhance security by containing threats, but sandboxing is typically more lightweight and application-specific, while virtualization provides deeper system-level isolation.
Core Concepts: What is Sandboxing?
Sandboxing is a security mechanism that isolates applications or code in a restricted environment to prevent unauthorized access to the host system or sensitive data. This technique limits the execution environment by enforcing strict controls on system resources, network access, and file permissions. Sandboxing effectively contains potential threats, minimizing the impact of malware or untrusted code without affecting the underlying operating system.
Core Concepts: What is Virtualization?
Virtualization is a technology that allows multiple operating systems or applications to run simultaneously on a single physical machine by abstracting hardware resources into virtual machines. Each virtual machine operates independently with its own isolated environment, enabling efficient resource utilization and enhanced security through separation. This core concept underpins cloud computing, server consolidation, and secure application deployment by minimizing direct hardware dependencies.
Key Differences Between Sandboxing and Virtualization
Sandboxing isolates applications in a restricted environment to prevent malicious code from affecting the host system, whereas virtualization creates multiple independent virtual machines that emulate entire hardware systems. Sandboxing is lightweight with minimal resource overhead, making it ideal for testing and running untrusted code safely, while virtualization incurs higher resource usage due to full OS instances but offers stronger isolation and multi-OS capabilities. Key differences include the scope of isolation, resource consumption, and use cases, with sandboxing focusing on application-level containment and virtualization providing comprehensive system-level separation.
Security Advantages of Sandboxing
Sandboxing enhances security by isolating applications and processes from the underlying operating system, preventing malware from spreading or affecting critical system components. It provides granular control over resource access and limits the execution environment, reducing the attack surface for zero-day exploits and unauthorized code execution. Unlike virtualization, sandboxing offers lightweight, application-specific containment that supports real-time threat analysis and rapid rollback without impacting overall system performance.
Security Benefits of Virtualization
Virtualization enhances security by isolating operating systems and applications within contained virtual machines, preventing malware from spreading across the host system. It enables rapid recovery and snapshot capabilities, allowing administrators to quickly revert to secure states after an attack. Virtual environments also support micro-segmentation, reducing the attack surface by limiting lateral movement within the network.
Performance Impact: Sandboxing vs Virtualization
Sandboxing typically imposes lower performance overhead compared to virtualization due to its lightweight isolation mechanisms that run directly on the host OS, minimizing resource consumption. Virtualization involves emulating entire hardware environments, which can significantly increase CPU, memory, and I/O usage, leading to greater latency and reduced throughput. Performance impact differences are crucial when choosing between sandboxing for lightweight, application-level security and virtualization for robust, system-wide isolation.
Use Cases: When to Use Sandboxing
Sandboxing is ideal for isolating untrusted applications, malware analysis, and secure testing environments where changes cannot affect the host system. It is particularly effective for developers debugging new software, running suspicious files, and protecting endpoints from zero-day attacks. This containment approach offers lightweight, temporary environments without the overhead of full virtual machines.
Use Cases: When to Choose Virtualization
Virtualization is ideal for running multiple operating systems simultaneously on a single physical server, enabling efficient resource utilization and isolation in development, testing, and production environments. It supports complex enterprise applications requiring full OS-level separation and hardware abstraction for enhanced security and management. Virtualization also suits scenarios involving legacy software compatibility and robust disaster recovery strategies.
Future Trends in Security: Sandboxing and Virtualization
Sandboxing and virtualization are evolving to address increasingly sophisticated cyber threats by isolating applications and environments more effectively. Future trends emphasize the integration of AI-driven threat detection within both technologies to enhance real-time response and adaptive security measures. Advances in lightweight virtualization and container-based sandboxing promise improved performance without compromising isolation, enabling more scalable and flexible security frameworks.
Sandboxing vs Virtualization Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com