Cyber threat intelligence involves collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data about cyber threats to understand attacker motives, tactics, and potential targets. Cyber threat sharing refers to the collaborative exchange of this intelligence between organizations to enhance collective defense capabilities. Implementing both enables proactive identification and mitigation of cyber risks, improving overall security posture.
Table of Comparison
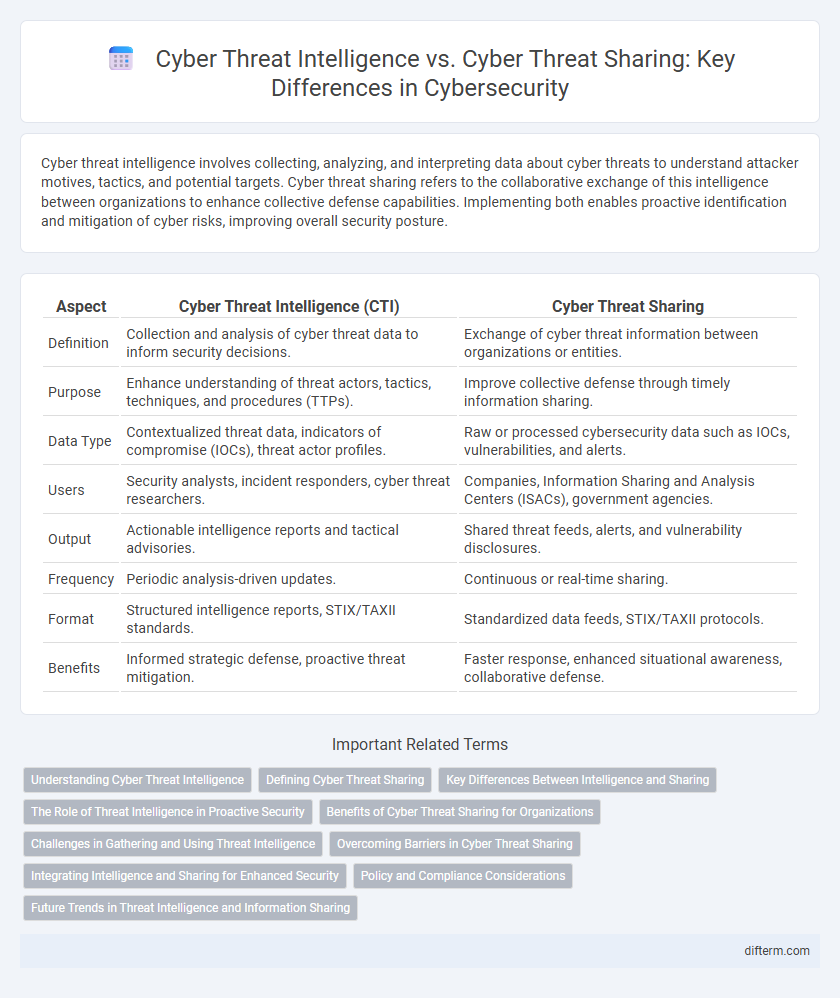
| Aspect | Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) | Cyber Threat Sharing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collection and analysis of cyber threat data to inform security decisions. | Exchange of cyber threat information between organizations or entities. |
| Purpose | Enhance understanding of threat actors, tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs). | Improve collective defense through timely information sharing. |
| Data Type | Contextualized threat data, indicators of compromise (IOCs), threat actor profiles. | Raw or processed cybersecurity data such as IOCs, vulnerabilities, and alerts. |
| Users | Security analysts, incident responders, cyber threat researchers. | Companies, Information Sharing and Analysis Centers (ISACs), government agencies. |
| Output | Actionable intelligence reports and tactical advisories. | Shared threat feeds, alerts, and vulnerability disclosures. |
| Frequency | Periodic analysis-driven updates. | Continuous or real-time sharing. |
| Format | Structured intelligence reports, STIX/TAXII standards. | Standardized data feeds, STIX/TAXII protocols. |
| Benefits | Informed strategic defense, proactive threat mitigation. | Faster response, enhanced situational awareness, collaborative defense. |
Understanding Cyber Threat Intelligence
Cyber threat intelligence (CTI) involves the systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of data about cyber threats to inform security decisions and proactively defend against attacks. It provides actionable insights on adversaries' motives, tactics, and vulnerabilities, enabling organizations to anticipate and mitigate risks more effectively. Unlike cyber threat sharing, which emphasizes exchanging information between entities, CTI focuses on generating tailored intelligence through rigorous analysis to support strategic cybersecurity measures.
Defining Cyber Threat Sharing
Cyber threat sharing involves the systematic exchange of threat data, indicators of compromise, and attack methodologies among organizations to enhance collective defense capabilities. This collaborative process allows cybersecurity teams to identify emerging threats faster and implement proactive measures based on shared intelligence. Unlike cyber threat intelligence, which focuses on analyzing and understanding threats, threat sharing emphasizes real-time distribution and collaboration across sectors and platforms.
Key Differences Between Intelligence and Sharing
Cyber threat intelligence involves the systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of data related to cyber threats to predict and prevent attacks, whereas cyber threat sharing refers to the exchange of raw or processed threat information between organizations to enhance collective defense. Intelligence emphasizes understanding threat actors, tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), providing actionable insights for proactive defense. Sharing concentrates on dissemination of indicators of compromise (IOCs) and alerts, promoting real-time collaboration but often lacks the analytical depth found in intelligence processes.
The Role of Threat Intelligence in Proactive Security
Cyber threat intelligence enables organizations to proactively identify and mitigate potential cyber threats by analyzing attacker tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs). It provides actionable insights that enhance threat detection, incident response, and risk management. Cyber threat sharing complements this by facilitating timely information exchange between entities, amplifying collective defense against emerging cyber threats.
Benefits of Cyber Threat Sharing for Organizations
Cyber threat sharing enhances organizational security by providing timely, actionable intelligence that improves threat detection and response capabilities. It enables collaboration among industry peers, fostering a collective defense approach that reduces individual risk exposure. Access to diverse threat data accelerates the identification of emerging cyber threats, allowing organizations to proactively strengthen their defenses.
Challenges in Gathering and Using Threat Intelligence
Cyber threat intelligence faces challenges such as data overload, accuracy issues, and the complexity of analyzing vast and diverse datasets from multiple sources. Cyber threat sharing encounters obstacles related to trust, legal constraints, and the standardization of formats for effective information exchange. Both require robust frameworks and advanced analytical tools to enhance the relevance and timeliness of threat insights for proactive defense.
Overcoming Barriers in Cyber Threat Sharing
Cyber threat intelligence involves the systematic collection and analysis of data on cyber threats to predict and prevent attacks, while cyber threat sharing focuses on the distribution of this information among organizations to enhance collective defense. Overcoming barriers in cyber threat sharing requires addressing concerns like data privacy, trust deficits, and inconsistent standards through robust encryption, legal frameworks, and standardized communication protocols. Improved collaboration platforms and incentivizing information exchange can further bolster effective threat sharing to strengthen cybersecurity resilience.
Integrating Intelligence and Sharing for Enhanced Security
Integrating cyber threat intelligence with cyber threat sharing amplifies an organization's ability to detect, analyze, and respond to emerging threats in real-time. Combining proprietary intelligence with collaborative data pools enables more accurate threat forecasting and faster mitigation strategies. This synergy fosters a proactive security posture by leveraging collective insights and automated information exchange across sectors.
Policy and Compliance Considerations
Cyber threat intelligence involves the collection, analysis, and dissemination of actionable information to proactively identify and mitigate cyber risks, requiring strict adherence to data privacy laws and organizational security policies. Cyber threat sharing emphasizes collaboration between entities to exchange threat data, necessitating clear guidelines on information classification, sharing protocols, and compliance with regulatory frameworks such as GDPR and HIPAA. Effective policy and compliance strategies must balance transparency and confidentiality while ensuring accountability and legal compliance during both intelligence gathering and threat sharing processes.
Future Trends in Threat Intelligence and Information Sharing
Future trends in cyber threat intelligence emphasize automation and artificial intelligence to enhance real-time detection and response capabilities. Cyber threat sharing platforms are evolving towards increased interoperability and standardized data formats to facilitate seamless collaboration across diverse organizations and industries. Blockchain technology is also being explored to ensure data integrity and trustworthiness in shared threat intelligence.
Cyber threat intelligence vs cyber threat sharing Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com