A firewall acts as a barrier that controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules, effectively blocking unauthorized access. An intrusion detection system (IDS) monitors network or system activities for malicious behavior and policy violations, alerting administrators to potential threats in real time. Combining both firewall and IDS technologies enhances overall security by preventing attacks while detecting suspicious activities that bypass firewall defenses.
Table of Comparison
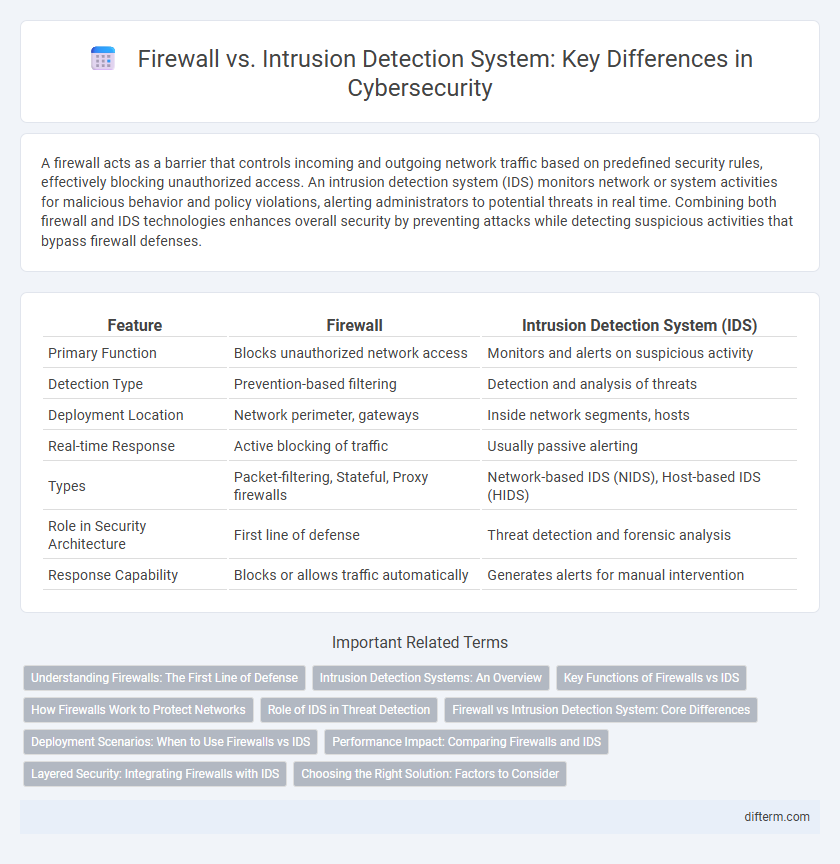
| Feature | Firewall | Intrusion Detection System (IDS) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Blocks unauthorized network access | Monitors and alerts on suspicious activity |
| Detection Type | Prevention-based filtering | Detection and analysis of threats |
| Deployment Location | Network perimeter, gateways | Inside network segments, hosts |
| Real-time Response | Active blocking of traffic | Usually passive alerting |
| Types | Packet-filtering, Stateful, Proxy firewalls | Network-based IDS (NIDS), Host-based IDS (HIDS) |
| Role in Security Architecture | First line of defense | Threat detection and forensic analysis |
| Response Capability | Blocks or allows traffic automatically | Generates alerts for manual intervention |
Understanding Firewalls: The First Line of Defense
Firewalls serve as the first line of defense by monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules, effectively blocking unauthorized access while allowing legitimate communication. They operate at various layers, including network, transport, and application layers, to provide a comprehensive barrier against cyber threats. Understanding firewall configurations and rule sets is crucial for preventing data breaches and maintaining robust network security.
Intrusion Detection Systems: An Overview
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) monitor network traffic to identify suspicious activities and potential security breaches in real time. Unlike firewalls that primarily act as a barrier by filtering incoming and outgoing traffic, IDS analyze packet data for patterns matching known attack signatures or abnormal behavior indicative of threats. Advanced IDS utilize machine learning algorithms to improve detection accuracy and reduce false positives, enhancing overall network security posture.
Key Functions of Firewalls vs IDS
Firewalls primarily enforce network access control by filtering incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules, effectively blocking unauthorized access and preventing malicious threats. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) monitor network traffic in real-time, analyzing data packets to identify suspicious activities or policy violations, and alert administrators to potential security breaches. While firewalls act as a barrier to unauthorized entry, IDS provide comprehensive surveillance and threat detection within the network environment.
How Firewalls Work to Protect Networks
Firewalls protect networks by filtering incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules, blocking unauthorized access while allowing legitimate communication. They monitor data packets, inspecting source and destination IP addresses, ports, and protocols to enforce network security policies. Unlike intrusion detection systems that detect and alert on suspicious activity, firewalls act as a proactive barrier preventing cyber threats from entering or leaving the network.
Role of IDS in Threat Detection
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) play a critical role in identifying potential security breaches by continuously monitoring network traffic for suspicious activity and known attack signatures. Unlike firewalls, which primarily enforce access control policies to block unauthorized traffic, IDS analyze traffic patterns to detect anomalies and alert administrators to possible intrusions. Effective threat detection through IDS enhances an organization's ability to respond proactively to cyberattacks, minimizing the risk of data loss or system compromise.
Firewall vs Intrusion Detection System: Core Differences
Firewalls function by controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules, effectively serving as a barrier between trusted and untrusted networks to prevent unauthorized access. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), on the other hand, monitor network or system activities for malicious actions or policy violations, generating alerts but not necessarily blocking traffic. The core difference lies in their roles: firewalls enforce access control to prevent attacks, while IDS focus on detecting and alerting on potential security breaches within the network.
Deployment Scenarios: When to Use Firewalls vs IDS
Firewalls are best deployed at network perimeters to block unauthorized access and control incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined security rules. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) should be implemented within the internal network to monitor and analyze traffic for suspicious activities or policy violations that firewalls might miss. Combining firewalls for perimeter defense with IDS for internal monitoring provides a layered security approach that enhances threat detection and response capabilities.
Performance Impact: Comparing Firewalls and IDS
Firewalls primarily control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules, generally causing minimal performance degradation due to their streamlined packet filtering processes. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), by continuously analyzing network traffic for suspicious activity and potential threats, require more processing power and can contribute to higher latency and resource consumption. Balancing security needs with system performance often involves deploying firewalls for baseline protection while leveraging IDS for in-depth monitoring without overwhelming network infrastructure.
Layered Security: Integrating Firewalls with IDS
Integrating firewalls with Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) enhances layered security by combining proactive traffic filtering and real-time threat monitoring. Firewalls enforce network access policies by blocking unauthorized connections at the perimeter, while IDS analyzes traffic patterns to detect suspicious activities and potential breaches within the network. This synergy improves early threat detection, minimizes false positives, and strengthens overall cyber defense against advanced persistent threats.
Choosing the Right Solution: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right security solution involves evaluating network architecture, threat landscape, and performance requirements. Firewalls provide primary defense by controlling traffic based on predefined rules, while intrusion detection systems (IDS) monitor network activity for suspicious behavior and potential breaches. Prioritizing real-time threat detection, resource availability, and integration capabilities ensures optimal protection tailored to specific organizational needs.
firewall vs intrusion detection system Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com