In real estate, a triple net lease requires the tenant to pay property taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs in addition to rent, transferring many expenses from landlord to tenant. A gross lease includes these expenses within the rent, providing the tenant with predictable monthly payments but often resulting in higher base rent. Understanding the differences between triple net and gross leases is essential for tenants and landlords to manage financial responsibilities and risks effectively.
Table of Comparison
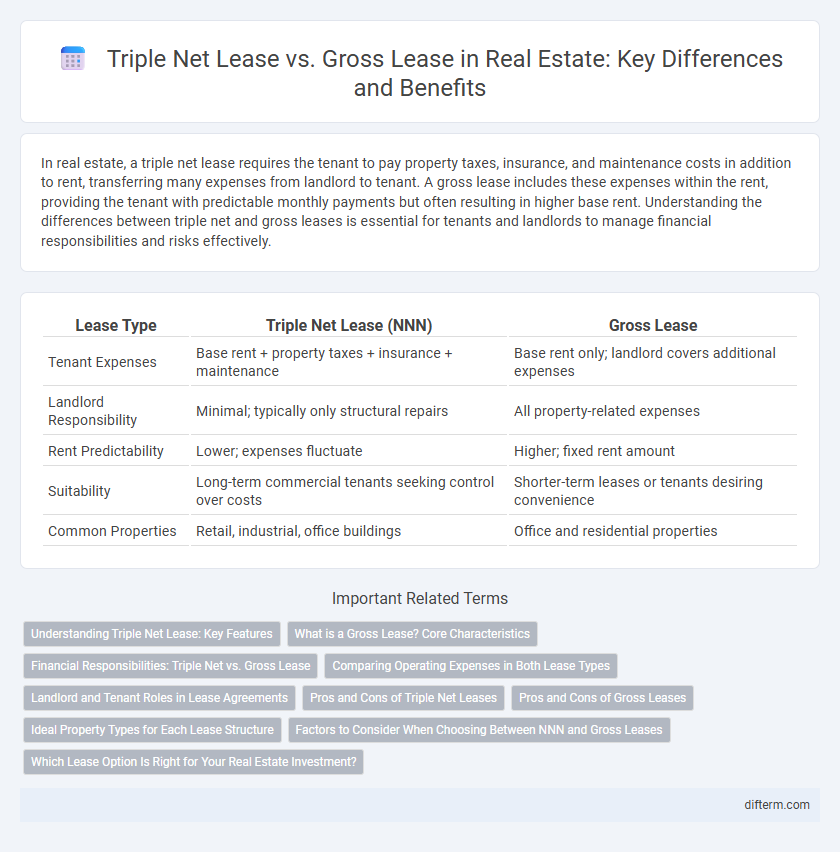
| Lease Type | Triple Net Lease (NNN) | Gross Lease |
|---|---|---|
| Tenant Expenses | Base rent + property taxes + insurance + maintenance | Base rent only; landlord covers additional expenses |
| Landlord Responsibility | Minimal; typically only structural repairs | All property-related expenses |
| Rent Predictability | Lower; expenses fluctuate | Higher; fixed rent amount |
| Suitability | Long-term commercial tenants seeking control over costs | Shorter-term leases or tenants desiring convenience |
| Common Properties | Retail, industrial, office buildings | Office and residential properties |
Understanding Triple Net Lease: Key Features
A triple net lease (NNN) requires tenants to pay property taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs in addition to base rent, transferring much of the financial responsibility from landlords to tenants. This leasing structure offers landlords predictable income streams and reduced management oversight, making it popular in commercial real estate. Understanding key features such as long-term lease terms and tenant obligations helps investors evaluate risk and cash flow stability in triple net lease agreements.
What is a Gross Lease? Core Characteristics
A gross lease in real estate is an agreement where the landlord covers all property expenses, including taxes, insurance, and maintenance, while the tenant pays a fixed rent amount. This type of lease simplifies budgeting for tenants, as they are not responsible for fluctuating operational costs. Gross leases are common in office and retail spaces, offering predictable monthly payments and reducing tenant risk.
Financial Responsibilities: Triple Net vs. Gross Lease
In a triple net lease, tenants are responsible for paying property taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs in addition to base rent, significantly reducing the landlord's financial obligations. Gross leases require tenants to pay a fixed rent amount, while landlords cover most operating expenses such as taxes, insurance, and repairs. Understanding these financial responsibilities helps investors and tenants evaluate risk, cash flow, and overall lease affordability in commercial real estate.
Comparing Operating Expenses in Both Lease Types
A triple net lease requires tenants to cover all operating expenses, including property taxes, insurance, and maintenance, resulting in lower base rent but higher variable costs. In contrast, a gross lease bundles these operating expenses into a higher, fixed rent, simplifying budgeting for tenants but often leading to a premium in rental price. Investors often prefer triple net leases for predictable net income, while tenants may favor gross leases for cost stability.
Landlord and Tenant Roles in Lease Agreements
In triple net leases, tenants assume responsibility for property taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs, reducing the landlord's financial obligations and risk. Conversely, in gross leases, landlords cover these expenses, simplifying payments for tenants but increasing the landlord's operational duties. Understanding these roles helps landlords optimize cash flow while tenants manage variable costs based on lease structure.
Pros and Cons of Triple Net Leases
Triple net leases (NNN) require tenants to cover property taxes, insurance, and maintenance, reducing landlord responsibilities and ensuring predictable income streams. Investors benefit from lower management costs and potentially higher returns, but tenants face unpredictable expenses and increased financial risk. The lease structure suits long-term, creditworthy tenants, while smaller or less stable businesses may prefer a gross lease for expense simplicity.
Pros and Cons of Gross Leases
Gross leases offer simplicity by bundling rent and operating expenses into a single payment, making budgeting predictable for tenants. However, landlords assume the risk of fluctuating property expenses, which can lead to higher overall costs if maintenance or taxes increase significantly. Tenants benefit from less financial variability, but may pay a premium to offset the landlord's risk exposure.
Ideal Property Types for Each Lease Structure
Triple net leases are ideal for single-tenant commercial properties such as retail stores, freestanding restaurants, and industrial warehouses, where tenants assume responsibility for property expenses including taxes, insurance, and maintenance. Gross leases suit multi-tenant office buildings and mixed-use developments, offering landlords predictable income by covering all operating costs within the rent. Property owners selecting lease structures should consider tenant profile, property type, and expense management preferences to optimize investment returns.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between NNN and Gross Leases
When choosing between triple net (NNN) and gross leases, consider factors such as risk allocation, expense predictability, and tenant responsibility for property taxes, insurance, and maintenance. NNN leases typically shift operational costs to tenants, reducing landlord liability but increasing tenant expenses, while gross leases provide fixed rent inclusive of expenses, offering budget certainty. Location, property type, and tenant financial stability also play critical roles in determining which lease structure aligns best with investment goals and cash flow preferences.
Which Lease Option Is Right for Your Real Estate Investment?
Choosing between a triple net lease and a gross lease depends on your investment goals and risk tolerance; triple net leases transfer property expenses like taxes, insurance, and maintenance to the tenant, resulting in lower landlord responsibilities and predictable income streams. Gross leases simplify budgeting with a fixed rent covering all expenses, appealing to investors seeking stable cash flow without managing variable costs. Evaluating local market conditions, tenant profile, and property type is essential to determine the optimal lease structure for maximizing real estate investment returns.
triple net lease vs gross lease Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com