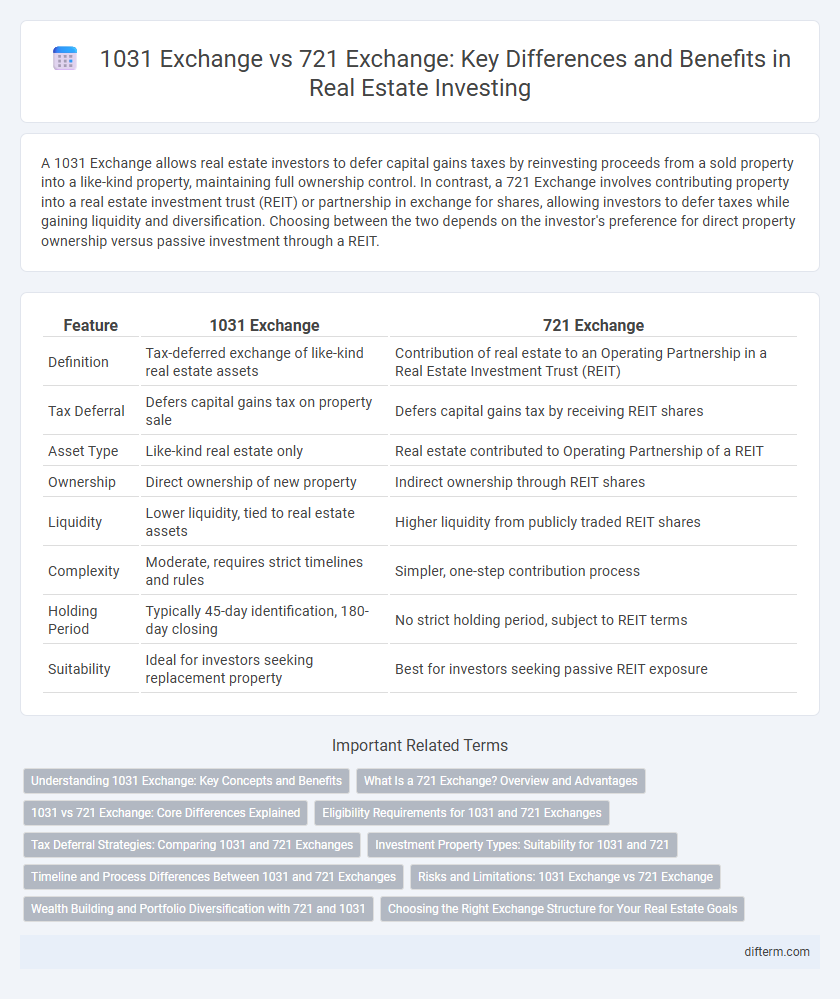
A 1031 Exchange allows real estate investors to defer capital gains taxes by reinvesting proceeds from a sold property into a like-kind property, maintaining full ownership control. In contrast, a 721 Exchange involves contributing property into a real estate investment trust (REIT) or partnership in exchange for shares, allowing investors to defer taxes while gaining liquidity and diversification. Choosing between the two depends on the investor's preference for direct property ownership versus passive investment through a REIT.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 1031 Exchange | 721 Exchange |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tax-deferred exchange of like-kind real estate assets | Contribution of real estate to an Operating Partnership in a Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) |
| Tax Deferral | Defers capital gains tax on property sale | Defers capital gains tax by receiving REIT shares |
| Asset Type | Like-kind real estate only | Real estate contributed to Operating Partnership of a REIT |
| Ownership | Direct ownership of new property | Indirect ownership through REIT shares |
| Liquidity | Lower liquidity, tied to real estate assets | Higher liquidity from publicly traded REIT shares |
| Complexity | Moderate, requires strict timelines and rules | Simpler, one-step contribution process |
| Holding Period | Typically 45-day identification, 180-day closing | No strict holding period, subject to REIT terms |
| Suitability | Ideal for investors seeking replacement property | Best for investors seeking passive REIT exposure |
Understanding 1031 Exchange: Key Concepts and Benefits
A 1031 Exchange allows real estate investors to defer capital gains taxes by reinvesting proceeds from the sale of a property into a like-kind property, preserving investment capital and enhancing portfolio growth. Key benefits include tax deferral, increased purchasing power, and the ability to diversify holdings without immediate tax consequences. Understanding timeline requirements, like the 45-day identification and 180-day closing rules, is critical to successfully completing a 1031 Exchange.
What Is a 721 Exchange? Overview and Advantages
A 721 Exchange, also known as an UPREIT (Umbrella Partnership Real Estate Investment Trust) transaction, allows real estate owners to contribute property into a REIT in exchange for operating partnership units, deferring capital gains taxes. This method offers liquidity and diversification benefits by converting illiquid real estate into tradable REIT shares with potential income streams and appreciation. Compared to a 1031 Exchange, a 721 Exchange provides more flexibility in property types accepted and can facilitate estate planning and portfolio management without the strict like-kind property requirement.
1031 vs 721 Exchange: Core Differences Explained
A 1031 Exchange allows real estate investors to defer capital gains taxes by exchanging like-kind properties, preserving investment capital and enabling portfolio growth. In contrast, a 721 Exchange involves contributing property to a Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) in exchange for shares, offering liquidity and diversification but potentially triggering different tax consequences. Key differences include the nature of the exchanged assets--direct property for property in 1031 versus property for REIT shares in 721--and their impact on investor control, tax deferral mechanics, and long-term investment strategy.
Eligibility Requirements for 1031 and 721 Exchanges
1031 exchanges require investors to reinvest proceeds from the sale of like-kind real estate properties, focusing on similar asset classes such as commercial or residential properties, and must adhere to strict timelines, including a 45-day identification and 180-day closing period. In contrast, 721 exchanges enable property owners to contribute real estate into a Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) or partnership in exchange for equity interests, generally demanding the transfer of property to a partnership or REIT with which the investor will hold ownership interest. Eligibility for 1031 exchanges is limited to real property used for business or investment purposes, while 721 exchanges specifically target the conversion of direct real estate holdings into partnership or REIT shares, offering more flexibility in asset type but requiring adherence to complex partnership regulations.
Tax Deferral Strategies: Comparing 1031 and 721 Exchanges
1031 Exchange allows real estate investors to defer capital gains taxes by reinvesting proceeds from the sale of a property into a like-kind property, maintaining investment continuity. Conversely, a 721 Exchange enables tax deferral by transferring real estate assets into a Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) in exchange for shares, offering liquidity and portfolio diversification. Both strategies optimize tax efficiency, with 1031 suited for direct property swaps and 721 preferable when seeking REIT exposure without immediate tax consequences.
Investment Property Types: Suitability for 1031 and 721
1031 exchanges are ideal for investors seeking to defer capital gains taxes by swapping like-kind investment properties, such as residential rental homes or commercial real estate, within the U.S. In contrast, 721 exchanges allow investors to contribute real estate into a real estate investment trust (REIT) or a real estate operating company (REOC), benefiting those holding diversified portfolios or seeking liquidity without immediate tax consequences. While 1031 exchanges suit direct property ownership with similar asset classes, 721 exchanges better serve complex investment structures involving multiple property types or institutional real estate investments.
Timeline and Process Differences Between 1031 and 721 Exchanges
The 1031 exchange requires investors to identify replacement properties within 45 days and close within 180 days, adhering to strict IRS timelines, while the 721 exchange offers more flexibility with no fixed identification period or closing deadline. The 1031 process involves direct property swaps or utilizing a qualified intermediary to defer capital gains taxes, whereas the 721 exchange involves contributing property into a real estate investment trust (REIT) with ownership in the partnership interests. These timeline and procedural distinctions significantly impact tax deferral strategies and investment planning in real estate transactions.
Risks and Limitations: 1031 Exchange vs 721 Exchange
1031 Exchange involves exchanging like-kind properties to defer capital gains taxes but carries risks such as strict timelines, identification rules, and potential IRS scrutiny. 721 Exchange, used in real estate investment trusts (REITs), allows property owners to contribute assets in exchange for partnership units, but faces limitations like illiquidity of REIT shares, limited control over assets, and dependence on REIT management performance. Both exchanges require careful consideration of tax implications, legal complexities, and potential market fluctuations that could impact investment value.
Wealth Building and Portfolio Diversification with 721 and 1031
The 1031 Exchange allows real estate investors to defer capital gains taxes by reinvesting proceeds into like-kind properties, promoting wealth building through property appreciation and income generation. The 721 Exchange enables investors to contribute real estate into a real estate investment trust (REIT) or partnership, facilitating portfolio diversification by gaining access to professionally managed assets and reducing direct property management responsibilities. Utilizing 721 Exchanges alongside 1031 strategies enhances long-term wealth accumulation while balancing risk across multiple property types and investment structures.
Choosing the Right Exchange Structure for Your Real Estate Goals
Choosing the right exchange structure between a 1031 Exchange and a 721 Exchange depends on your real estate investment objectives and tax planning strategy. A 1031 Exchange is ideal for deferring capital gains taxes by reinvesting proceeds into like-kind properties, preserving equity for property owners seeking to maintain direct ownership. In contrast, a 721 Exchange enables investors to contribute real estate assets into a Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT), offering liquidity and diversification while potentially deferring taxes and gaining access to professionally managed portfolios.
1031 Exchange vs 721 Exchange Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com