Pro forma statements in real estate provide projected financial performance based on estimated income, expenses, and market conditions, helping investors forecast returns. Actuals reflect the realized financial outcomes, revealing discrepancies between projected and real performance due to market fluctuations or unexpected costs. Analyzing the differences between pro forma and actuals enables more accurate future forecasting and informed investment decisions.
Table of Comparison
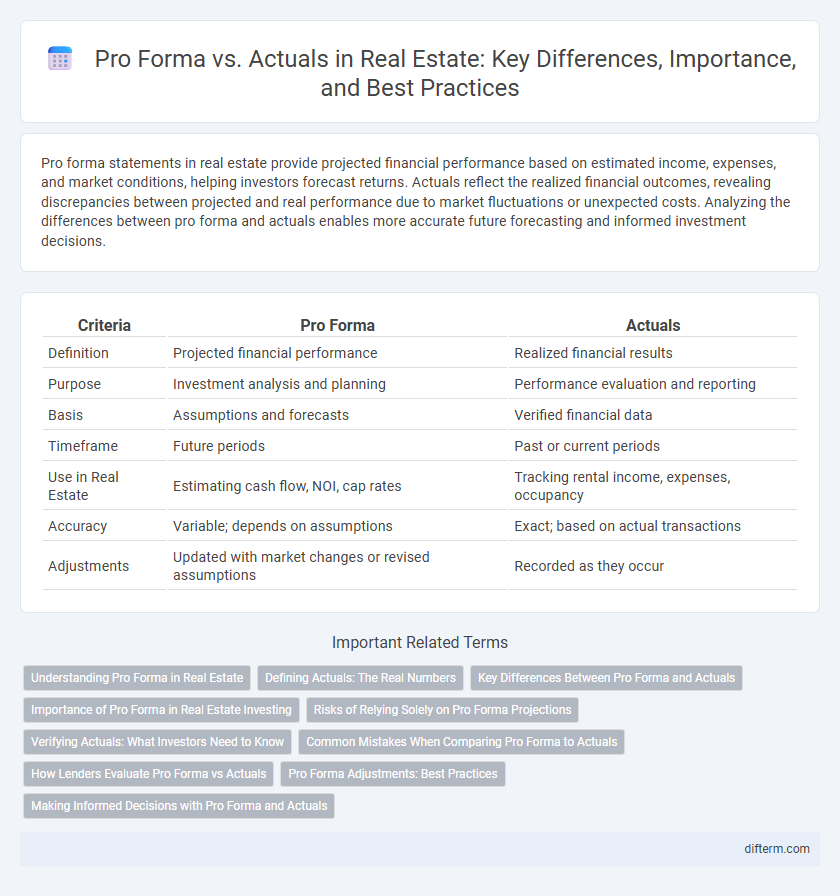
| Criteria | Pro Forma | Actuals |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Projected financial performance | Realized financial results |
| Purpose | Investment analysis and planning | Performance evaluation and reporting |
| Basis | Assumptions and forecasts | Verified financial data |
| Timeframe | Future periods | Past or current periods |
| Use in Real Estate | Estimating cash flow, NOI, cap rates | Tracking rental income, expenses, occupancy |
| Accuracy | Variable; depends on assumptions | Exact; based on actual transactions |
| Adjustments | Updated with market changes or revised assumptions | Recorded as they occur |
Understanding Pro Forma in Real Estate
Pro forma in real estate represents a financial projection estimating future income, expenses, and cash flow based on assumptions about market conditions, rental rates, and operating costs. It serves as a baseline for investors to evaluate potential property performance before acquisition, helping to assess viability and forecast returns. Comparing pro forma projections with actuals post-acquisition reveals variances that highlight discrepancies in market dynamics, management efficiency, and unforeseen expenses.
Defining Actuals: The Real Numbers
Actuals in real estate represent the verified financial figures derived from completed transactions, including actual rental income, operating expenses, and capital expenditures. These real numbers provide an accurate assessment of property performance, contrasting with pro forma estimates that project potential returns based on assumptions. Evaluating actuals helps investors identify discrepancies, assess risk, and make informed decisions grounded in historical data rather than predicted scenarios.
Key Differences Between Pro Forma and Actuals
Pro Forma financial statements project expected revenues, expenses, and cash flows for a real estate investment, serving as a forecast based on assumptions and market conditions. Actuals represent the real, recorded financial performance after the investment operates, reflecting true income, costs, and occupancy rates. Key differences include the reliance on estimates in pro forma versus verified data in actuals, with actuals providing a basis for assessing investment accuracy and adjusting future projections.
Importance of Pro Forma in Real Estate Investing
Pro forma statements play a crucial role in real estate investing by providing detailed financial projections that help investors evaluate the potential profitability and risks of a property before purchase. These forecasts estimate income, expenses, and cash flow, allowing investors to make informed decisions and compare different investment opportunities effectively. Comparing pro forma data with actuals after acquisition helps assess performance accuracy and guide future investment strategies.
Risks of Relying Solely on Pro Forma Projections
Pro forma projections often underestimate market volatility and unexpected expenses, leading to inaccurate assessments of a property's financial performance. Relying exclusively on these forecasts can mask cash flow shortfalls and inflate investor expectations, increasing financial risk. Incorporating actual operating data alongside pro forma estimates provides a more realistic evaluation, helping to mitigate potential losses in real estate investments.
Verifying Actuals: What Investors Need to Know
Verifying actuals involves comparing projected pro forma cash flows with real financial performance to identify discrepancies. Investors need accurate, detailed records of income, expenses, and capital expenditures to assess the property's true profitability and operational efficiency. Understanding variances between pro forma and actual data helps investors make informed decisions and manage risks effectively.
Common Mistakes When Comparing Pro Forma to Actuals
Common mistakes when comparing pro forma to actuals in real estate include overlooking timing differences in income and expenses, leading to inaccurate performance assessments. Failing to adjust for unforeseen market changes or operational delays often results in unrealistic expectations. Ignoring variances in assumptions such as rent growth or vacancy rates can significantly distort the comparison between projected and actual financial outcomes.
How Lenders Evaluate Pro Forma vs Actuals
Lenders evaluate pro forma financial statements by comparing projected cash flows, net operating income, and vacancy rates to actual performance data to assess the accuracy of forecasts and the borrower's risk profile. They prioritize actuals for validating the borrower's repayment ability, scrutinizing deviations from pro forma to identify potential risks in rental income and operating expenses. A significant variance between pro forma and actuals can impact loan approval, interest rates, and terms, emphasizing the importance of realistic and well-supported projections in real estate financing.
Pro Forma Adjustments: Best Practices
Pro Forma adjustments in real estate involve carefully estimating future income, expenses, and capital costs to present an accurate financial projection for investors. Best practices include thorough market research, incorporating conservative assumptions on rent growth and vacancy rates, and regularly updating the projections to reflect current market conditions. Transparent documentation of all assumptions and sensitivity analysis ensures more reliable decision-making and risk management.
Making Informed Decisions with Pro Forma and Actuals
Pro Forma financial statements provide projected revenue, expenses, and net operating income for real estate investments, enabling investors to forecast cash flow and assess potential returns. Actuals reflect the true financial performance, revealing variances between projections and real outcomes that are critical for accurate financial analysis. Comparing Pro Forma with Actuals helps investors identify discrepancies, refine future projections, and make informed decisions to optimize portfolio management and maximize investment value.
Pro Forma vs Actuals Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com