Lease options in real estate allow tenants to rent a property with the choice to buy it later, offering flexibility without the obligation to purchase. In contrast, lease purchase agreements legally bind tenants to buy the property after the lease term, providing certainty for both parties. Understanding the differences helps investors and buyers make informed decisions tailored to their financial and long-term goals.
Table of Comparison
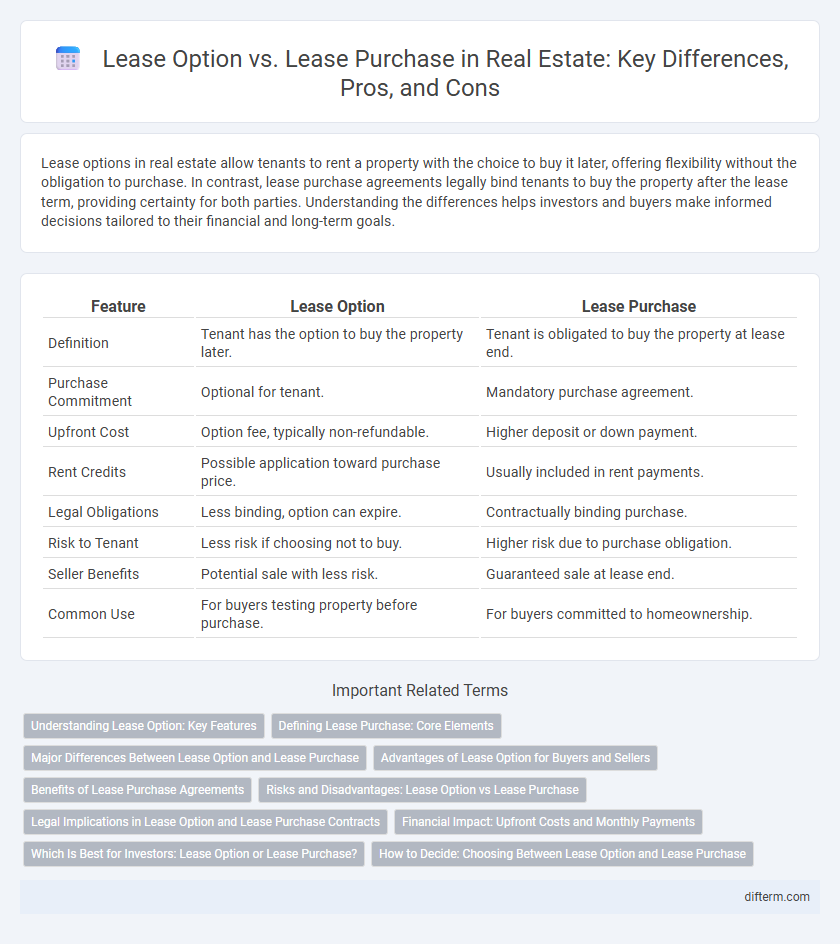
| Feature | Lease Option | Lease Purchase |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tenant has the option to buy the property later. | Tenant is obligated to buy the property at lease end. |
| Purchase Commitment | Optional for tenant. | Mandatory purchase agreement. |
| Upfront Cost | Option fee, typically non-refundable. | Higher deposit or down payment. |
| Rent Credits | Possible application toward purchase price. | Usually included in rent payments. |
| Legal Obligations | Less binding, option can expire. | Contractually binding purchase. |
| Risk to Tenant | Less risk if choosing not to buy. | Higher risk due to purchase obligation. |
| Seller Benefits | Potential sale with less risk. | Guaranteed sale at lease end. |
| Common Use | For buyers testing property before purchase. | For buyers committed to homeownership. |
Understanding Lease Option: Key Features
A Lease Option grants tenants the right, but not the obligation, to purchase the property within a specified period, usually by paying an option fee upfront. This arrangement allows potential buyers to lock in a purchase price while leasing the home, often with a portion of rent applied toward the down payment. Lease options provide flexibility, making them ideal for buyers who need time to improve credit or secure financing before committing to a purchase.
Defining Lease Purchase: Core Elements
Lease purchase agreements combine a traditional lease with a future commitment to buy the property, securing a predetermined purchase price and timeline. Core elements include an initial lease term, an option or obligation to purchase at the end of the lease, and often a portion of rent credits applied toward the down payment. This structure benefits buyers looking to build equity over time and sellers seeking assured buyers with reduced vacancy risk.
Major Differences Between Lease Option and Lease Purchase
Lease option agreements grant tenants the right to purchase the property within a specified period without an obligation to buy, whereas lease purchase contracts bind tenants to complete the purchase at the end of the lease term. Lease option typically requires a non-refundable option fee, providing flexibility, while lease purchase involves a legally binding contract that commits both parties. The distinction impacts financial risk, legal obligations, and negotiation leverage for buyers and sellers in residential real estate transactions.
Advantages of Lease Option for Buyers and Sellers
Lease option agreements provide buyers with flexibility, allowing them to lock in a purchase price while renting the property, which helps build equity without immediate commitment. Sellers benefit from steady rental income and reduced vacancy risk while maintaining the option to sell at a favorable price, attracting more prospective buyers. This arrangement often results in lower maintenance costs and greater financial security for both parties compared to traditional sales or lease-purchase contracts.
Benefits of Lease Purchase Agreements
Lease purchase agreements provide tenants the clear benefit of locking in a future purchase price, which safeguards against market fluctuations and builds equity through monthly payments. This arrangement offers flexibility by allowing tenants to test the property and neighborhood before fully committing to ownership. Investors also benefit from reduced vacancy risks and steady income during the lease term, increasing overall investment stability.
Risks and Disadvantages: Lease Option vs Lease Purchase
Lease option agreements carry risks such as non-refundable option fees and potential loss of equity if the tenant opts not to buy, leaving landlords with vacant properties. Lease purchase contracts bind both parties to complete the sale, exposing buyers to legal and financial penalties if they fail to secure financing or back out. Both arrangements can involve market fluctuations that affect property values, creating financial uncertainty for tenants and landlords alike.
Legal Implications in Lease Option and Lease Purchase Contracts
Lease option contracts grant tenants the right, but not the obligation, to purchase the property within a specified timeframe, creating fewer immediate legal obligations compared to lease purchase agreements that bind both parties to complete the sale. Legal implications in lease options often center on the enforceability of the option clause and the tenant's right to exercise the purchase, while lease purchase contracts impose binding purchase terms that, if breached, can lead to lawsuits for specific performance or damages. Ensuring clear contract language and understanding state-specific real estate laws is critical to mitigate risks in both lease option and lease purchase agreements.
Financial Impact: Upfront Costs and Monthly Payments
Lease option agreements typically require lower upfront costs, such as a non-refundable option fee, while monthly payments usually resemble standard rent with no additional equity buildup. Lease purchase contracts demand higher initial deposits and monthly payments that often include a premium portion applied toward the down payment or purchase price. Understanding these financial distinctions is vital for tenants aiming to balance immediate affordability with long-term homeownership goals.
Which Is Best for Investors: Lease Option or Lease Purchase?
Lease option agreements offer investors flexibility by allowing a right to purchase without an immediate commitment, reducing upfront risk and securing potential future ownership. Lease purchase contracts bind investors to an eventual sale, providing a clearer path to property acquisition but less exit strategy flexibility. Investors seeking maximum control with lower initial capital often prefer lease options, while those ready for firm investment typically choose lease purchases for long-term asset accumulation.
How to Decide: Choosing Between Lease Option and Lease Purchase
Evaluating lease option and lease purchase agreements hinges on upfront costs, contract flexibility, and long-term ownership goals. Lease options require lower initial investment with an option fee, allowing tenants to decide on buying later, while lease purchases involve a binding commitment to buy the property, often with a higher down payment. Assess financial stability, market conditions, and risk tolerance to select the best path for securing a future home or investment property.
Lease Option vs Lease Purchase Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com