Gross lease and net lease are two common commercial real estate leasing structures that impact tenants' financial responsibilities differently. In a gross lease, the tenant pays a fixed rent while the landlord covers property expenses such as taxes, insurance, and maintenance. Net leases shift some or all of these costs to the tenant, with variations including single, double, and triple net leases, where tenants pay for property taxes, insurance, and maintenance respectively.
Table of Comparison
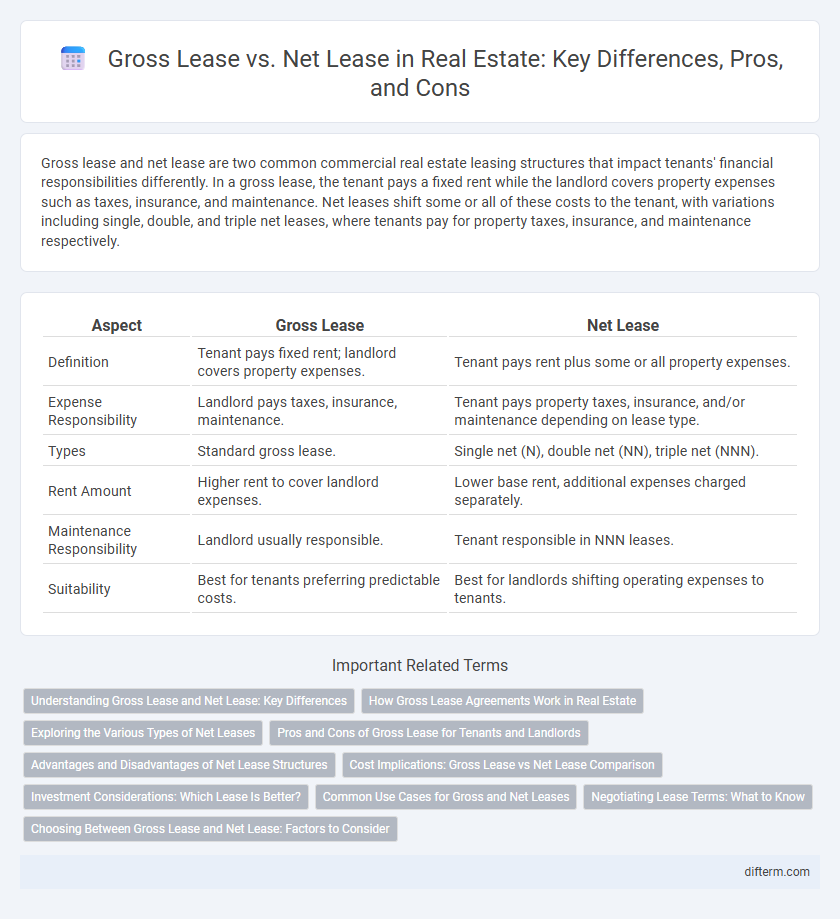
| Aspect | Gross Lease | Net Lease |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tenant pays fixed rent; landlord covers property expenses. | Tenant pays rent plus some or all property expenses. |
| Expense Responsibility | Landlord pays taxes, insurance, maintenance. | Tenant pays property taxes, insurance, and/or maintenance depending on lease type. |
| Types | Standard gross lease. | Single net (N), double net (NN), triple net (NNN). |
| Rent Amount | Higher rent to cover landlord expenses. | Lower base rent, additional expenses charged separately. |
| Maintenance Responsibility | Landlord usually responsible. | Tenant responsible in NNN leases. |
| Suitability | Best for tenants preferring predictable costs. | Best for landlords shifting operating expenses to tenants. |
Understanding Gross Lease and Net Lease: Key Differences
Gross lease requires tenants to pay a fixed rent amount covering all property expenses, including taxes, insurance, and maintenance, offering simplicity and predictable costs. Net lease shifts property expenses such as taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs to tenants either partially or fully, depending on whether it is a single, double, or triple net lease, leading to potentially lower base rent but variable costs. Understanding these key differences helps landlords and tenants make informed decisions aligned with financial risk and management preferences in commercial real estate.
How Gross Lease Agreements Work in Real Estate
Gross lease agreements in real estate require tenants to pay a fixed rent amount covering base rent and all operating expenses, such as property taxes, insurance, and maintenance fees. Landlords assume responsibility for variable costs, providing tenants with predictable monthly payments and simplified budgeting. This leasing structure is commonly used in commercial properties, offering straightforward expense management for tenants.
Exploring the Various Types of Net Leases
Net leases in real estate primarily include single net, double net, and triple net leases, each distributing property expenses differently between landlord and tenant. Single net leases require tenants to pay property taxes in addition to rent, while double net leases add maintenance costs to the tenant's responsibilities. Triple net leases shift most property expenses--taxes, insurance, and maintenance--to tenants, offering landlords predictable income streams and reduced management burdens.
Pros and Cons of Gross Lease for Tenants and Landlords
Gross lease offers tenants predictable monthly costs by including rent, property taxes, insurance, and maintenance in a single payment, simplifying budgeting. Landlords benefit from stable income and easier management of property expenses but assume all variable costs, which can reduce profitability during unexpected price increases. Tenants may pay a premium for this convenience, while landlords bear the financial risk of fluctuating operational costs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Net Lease Structures
Net lease structures offer landlords consistent and predictable income by shifting most property expenses, including taxes, insurance, and maintenance, onto tenants, which reduces management responsibilities and financial risk. However, tenants bear the potential for fluctuating operating costs, leading to higher variable expenses and increased financial uncertainty compared to gross leases. This balance of risk and responsibility makes net leases ideal for investors seeking steady returns, while potentially deterring tenants sensitive to unpredictable costs.
Cost Implications: Gross Lease vs Net Lease Comparison
Gross leases require tenants to pay a fixed rent amount covering all property expenses, simplifying budgeting but potentially resulting in higher overall costs as landlords factor maintenance and taxes into the rent. Net leases transfer property expenses such as taxes, insurance, and maintenance to tenants, often leading to lower base rent but variable and potentially unpredictable additional costs. Understanding the balance between fixed and variable expenses is crucial for tenants and landlords when evaluating the financial impact of gross versus net lease agreements in commercial real estate.
Investment Considerations: Which Lease Is Better?
Gross leases offer predictable expenses by bundling rent with operating costs, reducing financial risk for investors seeking stable cash flow. Net leases transfer property expenses such as taxes, insurance, and maintenance to tenants, potentially increasing investor returns but also exposure to variable costs. Evaluating tenant creditworthiness, market conditions, and risk tolerance is critical when deciding between gross and net leases for optimal real estate investment performance.
Common Use Cases for Gross and Net Leases
Gross leases are commonly used in office buildings and retail spaces where tenants prefer predictable monthly expenses, as landlords cover property taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs. Net leases are often favored in industrial and single-tenant commercial properties, allowing landlords to pass operating expenses to tenants, enhancing cost transparency and control. Triple net leases, a popular subtype, are prevalent in long-term investments like standalone retail stores and medical offices, minimizing landlord risk and providing steady income streams.
Negotiating Lease Terms: What to Know
When negotiating lease terms in real estate, understanding the differences between gross lease and net lease is crucial. Gross leases typically include rent plus all operating expenses, providing predictability in monthly payments, whereas net leases require tenants to pay base rent plus some or all property costs such as taxes, insurance, and maintenance. Carefully assess financial responsibilities and clarify expense obligations to avoid unexpected costs and ensure mutually beneficial lease agreements.
Choosing Between Gross Lease and Net Lease: Factors to Consider
Choosing between a gross lease and a net lease depends heavily on factors like maintenance responsibilities, budget predictability, and tenant preference for cost transparency. In a gross lease, landlords cover most operating expenses, offering tenants a fixed monthly rent, while net leases shift expenses such as property taxes, insurance, and maintenance to tenants, potentially lowering base rent but increasing variable costs. Location, property type, and market conditions also influence which lease structure maximizes financial benefits and operational efficiency for both landlords and tenants.
Gross Lease vs Net Lease Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com