Assessed value is the dollar value assigned to a property by a tax assessor to determine property taxes, often based on a percentage of market value and updated periodically. Appraised value is a professional estimate of a property's current market worth, determined by a licensed appraiser for purposes like sales, refinancing, or insurance. Understanding the difference between assessed and appraised values helps buyers and sellers make informed decisions during real estate transactions.
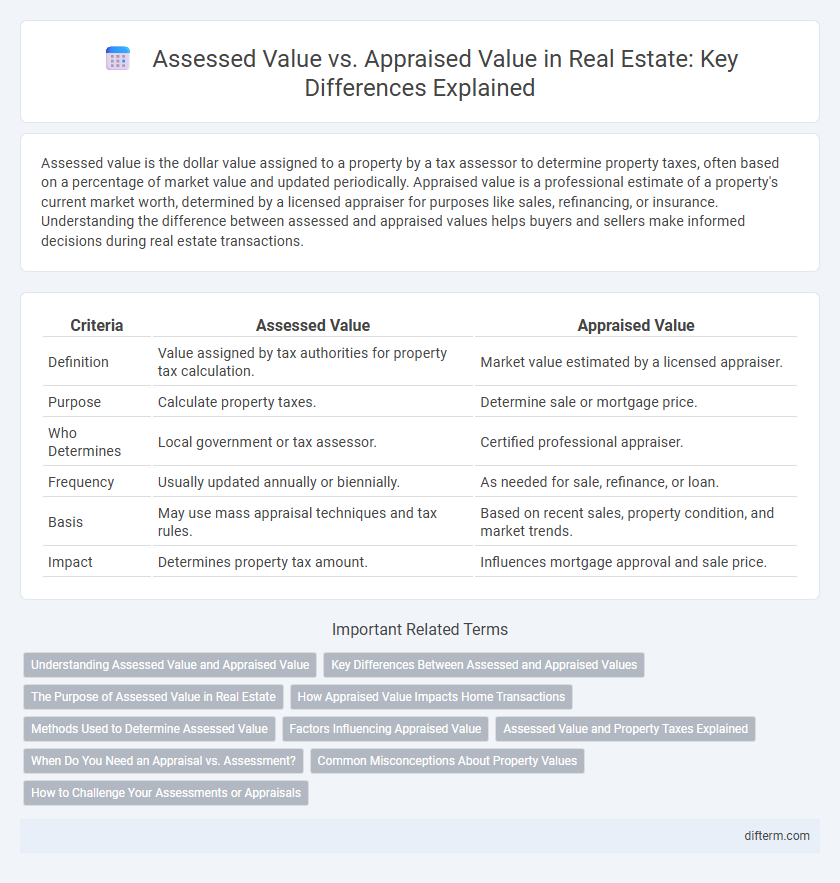
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Assessed Value | Appraised Value |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Value assigned by tax authorities for property tax calculation. | Market value estimated by a licensed appraiser. |
| Purpose | Calculate property taxes. | Determine sale or mortgage price. |
| Who Determines | Local government or tax assessor. | Certified professional appraiser. |
| Frequency | Usually updated annually or biennially. | As needed for sale, refinance, or loan. |
| Basis | May use mass appraisal techniques and tax rules. | Based on recent sales, property condition, and market trends. |
| Impact | Determines property tax amount. | Influences mortgage approval and sale price. |
Understanding Assessed Value and Appraised Value
Assessed value is the dollar value assigned to a property by a local tax assessor for property tax purposes, often based on market trends and property characteristics in the area. Appraised value is determined by a professional appraiser who evaluates the property's condition, location, and comparable sales to estimate its current market value. Understanding the difference is crucial for homeowners, as assessed values influence tax liabilities while appraised values impact mortgage approvals and sale prices.
Key Differences Between Assessed and Appraised Values
Assessed value is the dollar value assigned by a local tax assessor to determine property taxes, often based on standardized formulas and periodic assessments. Appraised value is the estimate of a property's market worth conducted by a licensed appraiser, considering current market conditions, comparable sales, and property features. Key differences include the purpose--tax calculation versus market value estimation--and the frequency of updates, with assessed values typically updated annually and appraisals conducted as needed.
The Purpose of Assessed Value in Real Estate
The assessed value in real estate serves as the basis for determining property taxes, reflecting a percentage of the market value set by local tax authorities. Unlike the appraised value, which is an expert estimate used mainly for buying, selling, or refinancing purposes, the assessed value directly influences the annual tax bill property owners must pay. Understanding how assessed value is calculated helps homeowners anticipate tax liabilities and assess property investment costs more accurately.
How Appraised Value Impacts Home Transactions
Appraised value directly influences home transactions by determining the loan amount a lender is willing to approve, ensuring the property meets or exceeds the purchase price. This valuation can affect negotiations between buyers and sellers, as a low appraisal may require price adjustments or additional down payment. Accurate appraisals are essential for securing mortgage financing and completing real estate deals efficiently.
Methods Used to Determine Assessed Value
Assessed value is primarily determined by local tax assessors who use mass appraisal techniques, analyzing comparable property sales, cost approaches, and income approaches depending on the property type. Methods often include reviewing market trends, property characteristics, and recent sales data to estimate taxable value for property tax purposes. This contrasts with appraised value, which is typically established through a detailed, property-specific inspection by a licensed appraiser.
Factors Influencing Appraised Value
Appraised value is determined by professional appraisers who analyze recent comparable sales, current market conditions, property size, location, and property condition to establish an accurate market price. Factors influencing appraised value include neighborhood trends, economic indicators, property improvements, and zoning regulations, which can significantly impact the final appraisal report. Unlike assessed value, which is often used for tax purposes, appraised value reflects the true market value based on comprehensive and up-to-date market analysis.
Assessed Value and Property Taxes Explained
Assessed value is the dollar value assigned to a property by a local tax assessor for the purpose of calculating property taxes, often based on a percentage of the market value determined through standardized formulas. Property taxes are then calculated by multiplying the assessed value by the local tax rate, directly impacting the homeowner's annual financial obligations. Understanding assessed value is crucial for property owners to anticipate tax liabilities and challenge assessments if necessary to ensure fairness and accuracy in tax bills.
When Do You Need an Appraisal vs. Assessment?
An appraisal is typically needed during property transactions such as buying, selling, refinancing, or securing a home equity loan to determine the market value based on current market conditions. An assessment is usually conducted annually or semi-annually by local government assessors to establish property taxes based on assessed value, which may not reflect the current market value. Homeowners require an appraisal to negotiate price or financing, while assessments are relied upon for accurate property tax calculations.
Common Misconceptions About Property Values
Assessed value is determined by local tax assessors to calculate property taxes, often reflecting a percentage of the market value rather than the full price. Appraised value is the estimated market value provided by a licensed appraiser based on recent sales and property conditions, crucial for mortgage approvals. Common misconceptions confuse assessed value with market value, leading homeowners to overestimate their property's worth or misunderstand tax assessments.
How to Challenge Your Assessments or Appraisals
To challenge your assessed or appraised value, start by reviewing the property tax assessment or appraisal report for errors in square footage, property condition, or comparable sales. Gather evidence such as recent comparable home sales, independent appraisals, or documentation of property defects to support your claim. Submit a formal appeal or reconsideration request to your local assessor's office or appraisal district, adhering to deadlines and providing all necessary documentation.
Assessed Value vs Appraised Value Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com