Due diligence in real estate pet transactions involves a thorough investigation of the property's condition, legal status, and compliance with pet-related regulations to ensure a sound investment. Contingency clauses provide buyers with contractual protections that allow them to back out or renegotiate the deal if certain pet-related conditions, such as approvals from homeowners' associations or pet policy compliance, are not met. Understanding the distinction between due diligence and contingency is crucial for navigating pet-friendly real estate deals with confidence and minimizing risks.
Table of Comparison
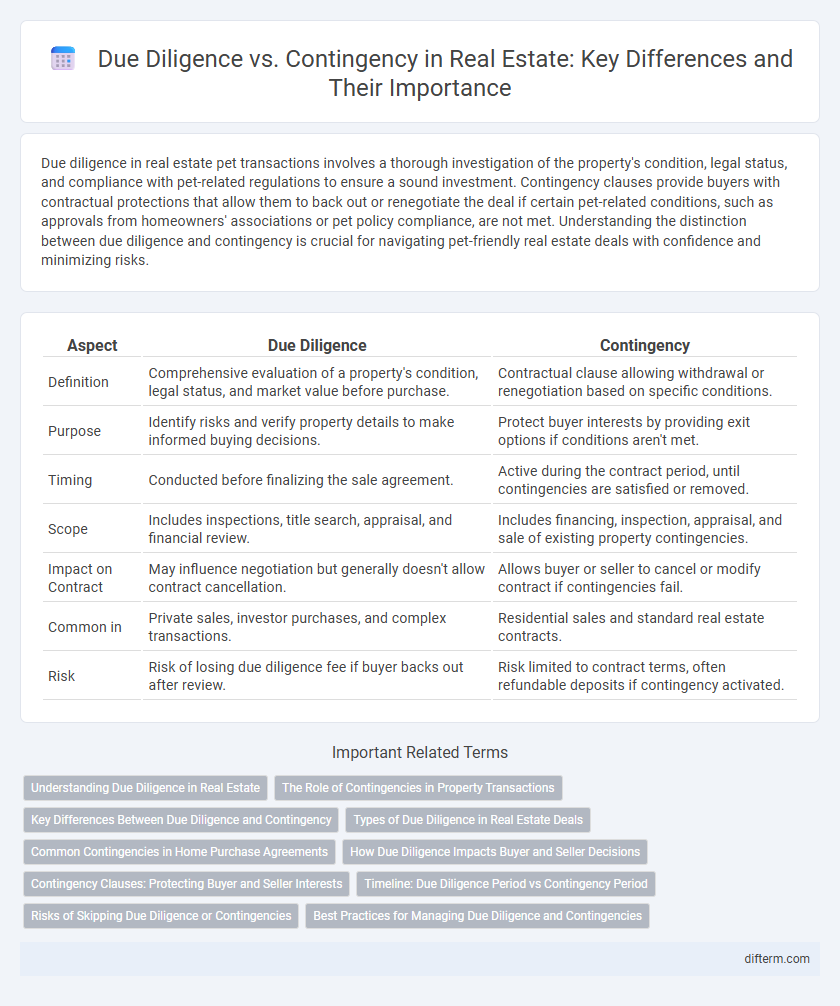
| Aspect | Due Diligence | Contingency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Comprehensive evaluation of a property's condition, legal status, and market value before purchase. | Contractual clause allowing withdrawal or renegotiation based on specific conditions. |
| Purpose | Identify risks and verify property details to make informed buying decisions. | Protect buyer interests by providing exit options if conditions aren't met. |
| Timing | Conducted before finalizing the sale agreement. | Active during the contract period, until contingencies are satisfied or removed. |
| Scope | Includes inspections, title search, appraisal, and financial review. | Includes financing, inspection, appraisal, and sale of existing property contingencies. |
| Impact on Contract | May influence negotiation but generally doesn't allow contract cancellation. | Allows buyer or seller to cancel or modify contract if contingencies fail. |
| Common in | Private sales, investor purchases, and complex transactions. | Residential sales and standard real estate contracts. |
| Risk | Risk of losing due diligence fee if buyer backs out after review. | Risk limited to contract terms, often refundable deposits if contingency activated. |
Understanding Due Diligence in Real Estate
Due diligence in real estate involves a comprehensive investigation of a property's legal, financial, and physical conditions before finalizing a transaction. It includes title searches, property inspections, and reviewing zoning laws to identify potential risks or liabilities. Understanding due diligence helps buyers make informed decisions and avoid costly surprises after purchase.
The Role of Contingencies in Property Transactions
Contingencies play a crucial role in property transactions by allowing buyers to protect themselves during the due diligence period, ensuring specific conditions such as financing approval, home inspections, and clear title are met before finalizing the purchase. These contractual provisions create legal safeguards that can terminate the contract or renegotiate terms if issues arise, minimizing financial risk. Understanding contingencies helps buyers and sellers navigate potential obstacles and proceed with greater confidence throughout the transaction process.
Key Differences Between Due Diligence and Contingency
Due diligence in real estate involves a comprehensive investigation of a property, including inspections, title checks, and financial assessments, ensuring buyers make informed decisions before finalizing a purchase. Contingencies are contractual clauses that allow buyers to back out or renegotiate if specific conditions, such as financing approval or appraisal values, are not met. Key differences include the proactive nature of due diligence as a thorough evaluation process versus the reactive legal protections provided by contingencies during the transaction phase.
Types of Due Diligence in Real Estate Deals
Due diligence in real estate deals involves thorough investigations such as title searches, property inspections, and financial reviews to ensure clear ownership, structural soundness, and accurate valuation. Contingencies are specific contractual clauses that allow buyers to back out or renegotiate if certain due diligence findings, like failed inspections or financing issues, arise. Understanding different types of due diligence--legal, physical, environmental, and financial--is crucial for mitigating risks and making informed investment decisions.
Common Contingencies in Home Purchase Agreements
Common contingencies in home purchase agreements include financing, appraisal, inspection, and title contingencies, each providing specific protections for buyers during due diligence. Financing contingencies allow buyers to back out if they cannot secure a mortgage, while appraisal contingencies ensure the property value meets the loan requirements. Inspection contingencies enable buyers to renegotiate or cancel based on property condition, and title contingencies confirm clear ownership before finalizing the sale.
How Due Diligence Impacts Buyer and Seller Decisions
Due diligence allows buyers to thoroughly inspect property conditions, title history, and financial disclosures, reducing risks and informing purchase decisions, while sellers benefit from a smoother transaction by proactively addressing potential issues. Contingencies provide legal protection by enabling contract termination under specific conditions, but due diligence empowers buyers and sellers to negotiate terms with greater confidence and clarity. Effective due diligence minimizes surprises and fosters trust, ultimately influencing the timing, pricing, and acceptance of real estate offers.
Contingency Clauses: Protecting Buyer and Seller Interests
Contingency clauses in real estate contracts serve as essential protections for both buyers and sellers by outlining specific conditions that must be met for the transaction to proceed, such as financing approval, home inspections, and appraisal results. These clauses help mitigate risks by allowing either party to cancel or renegotiate the deal if contingencies are not satisfied, ensuring informed decision-making and reducing potential financial losses. Effective use of contingency clauses enhances transaction transparency and builds trust between buyers and sellers in competitive real estate markets.
Timeline: Due Diligence Period vs Contingency Period
The due diligence period in real estate typically ranges from 7 to 21 days, allowing buyers to thoroughly inspect the property, review documents, and secure financing. In contrast, the contingency period, which varies based on contract terms, often overlaps but concludes upon removal of specific contingencies such as financing, appraisal, or inspection. Understanding these timelines is crucial for buyers and sellers to manage risk and ensure a smooth transaction process.
Risks of Skipping Due Diligence or Contingencies
Skipping due diligence or contingencies in real estate transactions significantly increases exposure to unforeseen risks such as undisclosed property defects, title issues, or financial liabilities. Buyers who bypass these critical safeguards may face costly repairs, legal disputes, or loss of earnest money deposits. Conducting thorough due diligence and including contingencies in the purchase agreement helps mitigate financial and legal risks, ensuring informed decision-making and contract enforceability.
Best Practices for Managing Due Diligence and Contingencies
Effective management of due diligence and contingencies in real estate involves thorough documentation review, timely inspections, and clear communication among all parties. Prioritizing deadlines and maintaining transparent records ensures risks are identified and addressed before closing. Leveraging specialized checklists and professional expertise enhances decision-making and protects client interests throughout the transaction.
Due Diligence vs Contingency Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com