Sovereign Wealth Funds (SWFs) are state-owned investment pools aimed at stabilizing the national economy and securing long-term wealth, typically investing in diverse assets with a conservative strategy. Hedge funds operate as private investment partnerships using aggressive tactics, including leverage and derivatives, to seek high returns for accredited investors. While SWFs prioritize national economic stability and intergenerational wealth preservation, hedge funds focus on maximizing short-term gains through high-risk strategies.
Table of Comparison
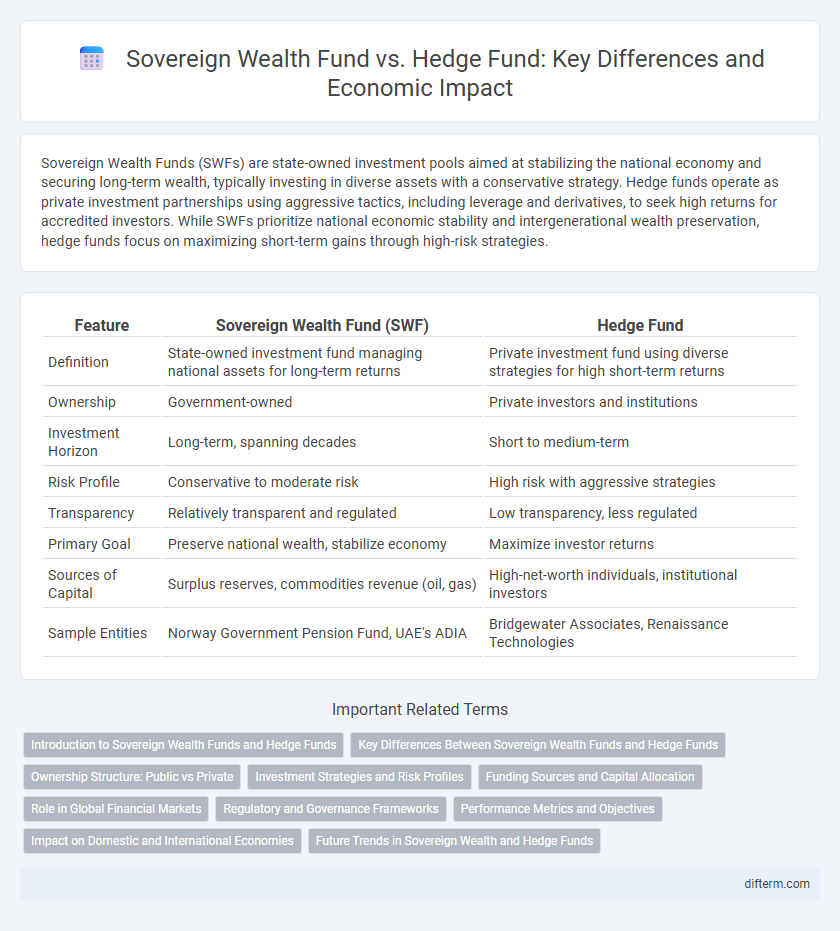
| Feature | Sovereign Wealth Fund (SWF) | Hedge Fund |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | State-owned investment fund managing national assets for long-term returns | Private investment fund using diverse strategies for high short-term returns |
| Ownership | Government-owned | Private investors and institutions |
| Investment Horizon | Long-term, spanning decades | Short to medium-term |
| Risk Profile | Conservative to moderate risk | High risk with aggressive strategies |
| Transparency | Relatively transparent and regulated | Low transparency, less regulated |
| Primary Goal | Preserve national wealth, stabilize economy | Maximize investor returns |
| Sources of Capital | Surplus reserves, commodities revenue (oil, gas) | High-net-worth individuals, institutional investors |
| Sample Entities | Norway Government Pension Fund, UAE's ADIA | Bridgewater Associates, Renaissance Technologies |
Introduction to Sovereign Wealth Funds and Hedge Funds
Sovereign Wealth Funds (SWFs) are state-owned investment vehicles managing national reserves to achieve long-term financial objectives, often sourced from commodities, trade surpluses, or fiscal surpluses. Hedge funds are private investment partnerships utilizing diverse strategies like leverage, derivatives, and short selling to generate high-risk, high-return opportunities for accredited investors. Both funds play crucial roles in global financial markets but differ significantly in ownership, risk profiles, and investment horizons.
Key Differences Between Sovereign Wealth Funds and Hedge Funds
Sovereign Wealth Funds (SWFs) are state-owned investment vehicles focusing on long-term stability and national economic objectives, while Hedge Funds are private investment firms seeking high returns through aggressive strategies. SWFs typically invest in a diversified portfolio including stocks, bonds, real estate, and infrastructure, prioritizing risk management and economic impact. Hedge Funds employ leverage, derivatives, and short-selling techniques to maximize short-term gains, often accepting higher risk levels for potentially greater returns.
Ownership Structure: Public vs Private
Sovereign Wealth Funds (SWFs) are state-owned investment vehicles funded by national reserves or surplus revenues, reflecting public ownership and strategic economic objectives. Hedge Funds operate as private investment partnerships, owned by private entities or individuals, focusing on high-risk, high-return financial strategies. The public ownership of SWFs ensures long-term national interests, whereas hedge funds prioritize shareholder profits within a private, flexible structure.
Investment Strategies and Risk Profiles
Sovereign wealth funds primarily invest in long-term, diversified portfolios including equities, bonds, real estate, and infrastructure, focusing on national economic stability and intergenerational wealth preservation. Hedge funds pursue aggressive, high-return strategies such as leveraged buyouts, short selling, and derivatives trading, targeting short- to medium-term gains with elevated risk exposure. Sovereign wealth funds exhibit lower risk profiles due to broad asset allocation and state backing, while hedge funds accept higher volatility and credit risks to achieve alpha generation.
Funding Sources and Capital Allocation
Sovereign wealth funds are state-owned investment pools primarily funded by national reserves, revenues from natural resources, or fiscal surpluses, focusing on long-term capital preservation and strategic national interests. Hedge funds, in contrast, raise capital from high-net-worth individuals and institutional investors, employing aggressive and diverse strategies to maximize short-term, risk-adjusted returns. Capital allocation in sovereign wealth funds tends to emphasize stable assets like bonds and infrastructure, while hedge funds allocate dynamically across equities, derivatives, and alternative investments.
Role in Global Financial Markets
Sovereign wealth funds (SWFs) manage state-owned assets to achieve long-term national economic stability and support fiscal policies, often investing in infrastructure, energy, and strategic sectors worldwide. Hedge funds deploy aggressive investment strategies aimed at maximizing short-term returns through derivatives, leverage, and arbitrage, influencing market liquidity and price efficiency. Both entities significantly impact global financial markets by affecting capital flows, asset prices, and risk distribution but operate with contrasting objectives and investment horizons.
Regulatory and Governance Frameworks
Sovereign Wealth Funds operate under stringent regulatory and governance frameworks established by national governments to ensure transparency, accountability, and alignment with public policy objectives. Hedge Funds, in contrast, are subject to less rigid regulations, primarily focused on investor protection and market integrity, often governed by private entities with flexible governance structures. The distinct regulatory environments influence risk management practices, investor confidence, and strategic decision-making within each fund type.
Performance Metrics and Objectives
Sovereign wealth funds prioritize long-term capital preservation and stable returns, often using metrics like return on investment (ROI), net asset value (NAV) growth, and risk-adjusted returns such as the Sharpe ratio. Hedge funds focus on generating high absolute returns through aggressive strategies, measuring performance by metrics like alpha, beta, and internal rate of return (IRR). Objectives differ as sovereign wealth funds aim for sustainable wealth accumulation aligned with national interests, while hedge funds target maximizing profit within shorter time horizons and higher risk tolerances.
Impact on Domestic and International Economies
Sovereign Wealth Funds (SWFs) primarily invest in long-term assets to stabilize domestic economies and generate wealth for future generations, significantly influencing national fiscal health and infrastructure development. Hedge Funds engage in high-risk, short-term investments, often impacting international markets through speculative activities that can increase liquidity but also volatility. The contrasting investment horizons and strategies of SWFs and Hedge Funds result in varied effects on global economic stability, capital flows, and market confidence.
Future Trends in Sovereign Wealth and Hedge Funds
Sovereign wealth funds are increasingly adopting environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to future-proof investments and align with global sustainability targets, driving substantial capital flows into renewable energy and technology sectors. Hedge funds are exploring advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning strategies to enhance predictive analytics and portfolio optimization, responding to growing market volatility and regulatory changes. Collaboration between sovereign wealth funds and hedge funds is anticipated to rise, leveraging long-term capital stability with agile risk management techniques to maximize returns in evolving economic landscapes.
Sovereign Wealth Fund vs Hedge Fund Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com