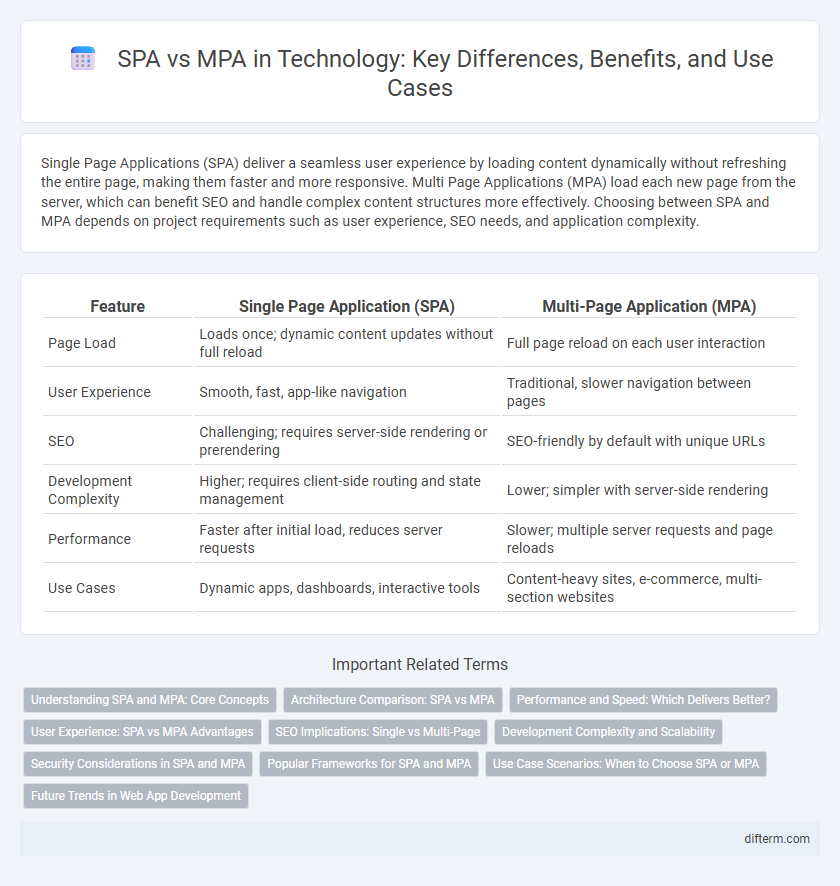
Single Page Applications (SPA) deliver a seamless user experience by loading content dynamically without refreshing the entire page, making them faster and more responsive. Multi Page Applications (MPA) load each new page from the server, which can benefit SEO and handle complex content structures more effectively. Choosing between SPA and MPA depends on project requirements such as user experience, SEO needs, and application complexity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Single Page Application (SPA) | Multi-Page Application (MPA) |
|---|---|---|
| Page Load | Loads once; dynamic content updates without full reload | Full page reload on each user interaction |
| User Experience | Smooth, fast, app-like navigation | Traditional, slower navigation between pages |
| SEO | Challenging; requires server-side rendering or prerendering | SEO-friendly by default with unique URLs |
| Development Complexity | Higher; requires client-side routing and state management | Lower; simpler with server-side rendering |
| Performance | Faster after initial load, reduces server requests | Slower; multiple server requests and page reloads |
| Use Cases | Dynamic apps, dashboards, interactive tools | Content-heavy sites, e-commerce, multi-section websites |
Understanding SPA and MPA: Core Concepts
Single Page Applications (SPA) load a single HTML page and dynamically update content as the user interacts, enhancing speed and user experience by reducing full page reloads. Multi Page Applications (MPA) reload the entire page with each user interaction, facilitating better SEO and handling complex applications with multiple distinct pages. SPA relies heavily on JavaScript frameworks like React or Angular for client-side rendering, while MPA typically uses server-side rendering technologies such as ASP.NET or Django.
Architecture Comparison: SPA vs MPA
Single-Page Applications (SPA) utilize a client-side architecture where content dynamically updates without full page reloads, enhancing speed and user experience by minimizing server requests. Multi-Page Applications (MPA) rely on server-side rendering, loading separate HTML pages for each interaction, which can result in slower navigation but better SEO and initial load performance. The SPA architecture favors rich interactions and smoother transitions, while MPA provides a more traditional structure with distinct page contexts and simpler state management.
Performance and Speed: Which Delivers Better?
Single Page Applications (SPAs) offer faster initial load times by fetching content dynamically without full page reloads, enhancing user experience and perceived speed. Multi Page Applications (MPAs), while potentially slower due to repeated server requests, can deliver better performance on SEO and initial page load for complex sites with multiple distinct pages. Optimization techniques like caching, lazy loading, and server-side rendering impact both SPA and MPA performance, but SPAs generally excel in responsiveness and seamless navigation speed.
User Experience: SPA vs MPA Advantages
Single Page Applications (SPA) enhance user experience by providing faster load times and seamless navigation without full page reloads, resulting in fluid interactions and reduced server requests. Multi-Page Applications (MPA) excel in SEO and initial load performance by delivering separate pages optimized for specific content, which improves discoverability and scalability for complex websites. SPAs are ideal for dynamic, app-like experiences, while MPAs suit content-rich sites requiring robust architecture and easier maintenance.
SEO Implications: Single vs Multi-Page
Single Page Applications (SPAs) often face SEO challenges due to dynamic content loading and reliance on JavaScript, potentially hindering search engine crawlers from properly indexing pages. Multi-Page Applications (MPAs) inherently support better SEO because each page has a unique URL and static content, making it easier for search engines to discover and rank individual pages. Implementing server-side rendering (SSR) or prerendering for SPAs can mitigate SEO issues by providing crawlable HTML versions of dynamic content.
Development Complexity and Scalability
Single Page Applications (SPA) offer lower development complexity due to their streamlined client-side rendering and reduced need for full-page reloads, which simplifies user interface interactions. Multi Page Applications (MPA) present higher development complexity as each page requires separate backend processing and routing, increasing the coding and maintenance effort. In terms of scalability, MPAs handle large-scale projects more effectively by distributing loads across multiple pages and servers, whereas SPAs may face performance bottlenecks as the application grows unless optimized carefully.
Security Considerations in SPA and MPA
Single Page Applications (SPA) face unique security challenges such as cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities and token management complexities due to their heavy reliance on client-side code and APIs. Multi Page Applications (MPA) inherently reduce some client-side attack surfaces by loading pages from the server for each request, which can simplify authentication and session management but may increase exposure to server-side vulnerabilities. Effective security strategies for both SPA and MPA include implementing robust input validation, secure cookie handling, and proper Content Security Policy (CSP) configurations to mitigate common web attacks.
Popular Frameworks for SPA and MPA
Popular frameworks for Single Page Applications (SPA) include React, Angular, and Vue.js, which enable dynamic content rendering and seamless user experiences without full page reloads. For Multi-Page Applications (MPA), frameworks like Ruby on Rails, Django, and ASP.NET MVC offer robust server-side rendering and traditional page navigation suited for content-rich websites. Choosing between SPA and MPA frameworks depends on project requirements such as interactivity, SEO needs, and performance considerations.
Use Case Scenarios: When to Choose SPA or MPA
Single Page Applications (SPAs) excel in dynamic, user-interactive scenarios such as social media platforms, dashboards, and online editors where seamless, fast user experiences are critical. Multi-Page Applications (MPAs) are better suited for content-rich websites like e-commerce sites, blogs, or corporate portals that require SEO optimization and complex page hierarchies. Choosing SPA or MPA depends on factors like application complexity, SEO needs, user interaction frequency, and development scalability requirements.
Future Trends in Web App Development
Future trends in web app development emphasize the integration of Single Page Applications (SPA) with progressive enhancement techniques to improve performance and user experience across devices. Multi-Page Applications (MPA) are evolving by incorporating server-side rendering and micro frontend architectures to enhance scalability and SEO. Advances in frameworks like React, Vue, and Angular are driving innovation, enabling seamless hybrid models that combine SPA interactivity with MPA robustness.
SPA vs MPA Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com