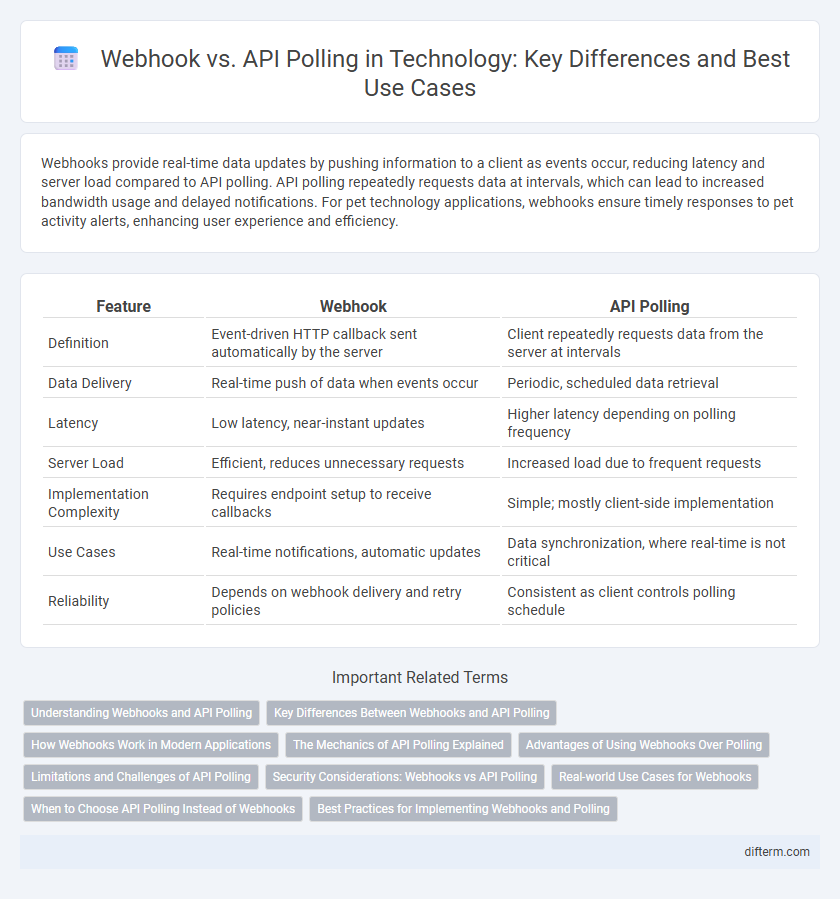
Webhooks provide real-time data updates by pushing information to a client as events occur, reducing latency and server load compared to API polling. API polling repeatedly requests data at intervals, which can lead to increased bandwidth usage and delayed notifications. For pet technology applications, webhooks ensure timely responses to pet activity alerts, enhancing user experience and efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Webhook | API Polling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Event-driven HTTP callback sent automatically by the server | Client repeatedly requests data from the server at intervals |
| Data Delivery | Real-time push of data when events occur | Periodic, scheduled data retrieval |
| Latency | Low latency, near-instant updates | Higher latency depending on polling frequency |
| Server Load | Efficient, reduces unnecessary requests | Increased load due to frequent requests |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires endpoint setup to receive callbacks | Simple; mostly client-side implementation |
| Use Cases | Real-time notifications, automatic updates | Data synchronization, where real-time is not critical |
| Reliability | Depends on webhook delivery and retry policies | Consistent as client controls polling schedule |
Understanding Webhooks and API Polling
Webhooks enable real-time data delivery by sending automated notifications to an endpoint when an event occurs, reducing the need for constant server requests. API polling involves repeatedly sending requests at regular intervals to check for new data, which can increase latency and server load. Understanding the efficiency and event-driven nature of webhooks versus the interval-based checking of API polling is crucial for optimizing application performance.
Key Differences Between Webhooks and API Polling
Webhooks provide real-time data delivery by pushing updates automatically from the server to the client upon event occurrence, whereas API polling requires the client to repeatedly request data at regular intervals, which can increase latency and resource consumption. Webhooks reduce unnecessary network traffic and improve efficiency by sending data only when changes happen, while API polling may lead to missed updates or delayed responses due to fixed polling intervals. Security considerations differ as webhooks often rely on validating payload signatures, and API polling depends on secure request authentication, impacting implementation complexity.
How Webhooks Work in Modern Applications
Webhooks enable real-time data transfer by sending automated HTTP POST requests from a server to a client when specific events occur, reducing latency compared to API polling. Modern applications utilize webhooks to streamline communication between services, allowing instant updates without the need for continuous resource-intensive requests. This event-driven architecture enhances efficiency by delivering only relevant information as it happens, minimizing network traffic and server load.
The Mechanics of API Polling Explained
API polling operates by repeatedly sending requests to a server at fixed intervals to check for new data or updates, which can lead to increased latency and higher resource consumption. Each poll involves an HTTP request-response cycle where the client asks the server for the latest status, often resulting in redundant data transmissions when no changes have occurred. This contrasts with webhooks, which deliver real-time updates by having the server push data to the client instantly upon event occurrence, reducing unnecessary network traffic.
Advantages of Using Webhooks Over Polling
Webhooks provide real-time data delivery by automatically pushing updates as soon as events occur, reducing latency compared to API polling which relies on periodic requests. They significantly lower server load and bandwidth usage since data is transmitted only when necessary, unlike polling which generates constant network traffic. This event-driven mechanism ensures more efficient resource utilization and faster response times in applications.
Limitations and Challenges of API Polling
API polling faces significant limitations such as increased latency and inefficiency due to repeated requests that can lead to unnecessary bandwidth consumption. It also imposes a higher load on server resources, affecting scalability and potentially causing rate limiting or throttling issues. Additionally, the delay between polls limits real-time data accuracy, hindering responsiveness in time-sensitive applications.
Security Considerations: Webhooks vs API Polling
Webhooks reduce security risks by delivering real-time data directly to a specified URL, minimizing the need for constant authentication requests and limiting attack surfaces. API polling requires frequent requests, increasing exposure to potential interception and unauthorized access due to repetitive authentication processes. Implementing HTTPS, validating payloads, and employing token-based authentication are crucial for securing both webhooks and API polling mechanisms.
Real-world Use Cases for Webhooks
Webhooks enable real-time data synchronization in e-commerce platforms by instantly notifying inventory management systems of stock changes, reducing latency compared to API polling. In payment processing, webhooks provide immediate alerts for transaction statuses, enhancing fraud detection and customer experience. Continuous integration tools leverage webhooks to trigger automated builds and tests upon code commits, streamlining development workflows efficiently.
When to Choose API Polling Instead of Webhooks
API polling is preferable when real-time data delivery is non-essential, and systems require periodic updates at fixed intervals for synchronization or monitoring purposes. Polling is advantageous in environments lacking webhook support or where inbound connections are restricted by firewalls or network policies. It also suits scenarios demanding explicit control over request timing and retry logic to handle rate limits and transient failures effectively.
Best Practices for Implementing Webhooks and Polling
When implementing webhooks, ensure secure endpoints with proper validation and retries to handle missed events, enhancing real-time data synchronization. For API polling, optimize request frequency to balance system load and data freshness, utilizing exponential backoff strategies to reduce unnecessary calls. Combining both methods strategically can maximize efficiency and reliability in event-driven architectures.
webhook vs API polling Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com