Python virtualenv provides isolated environments for managing dependencies within a single operating system, allowing developers to maintain project-specific packages without interference. Docker containers encapsulate the entire runtime environment, including the application, libraries, and system tools, ensuring consistent execution across diverse environments. Using Docker offers greater portability and scalability compared to virtualenv, which is primarily suited for dependency management in Python projects.
Table of Comparison
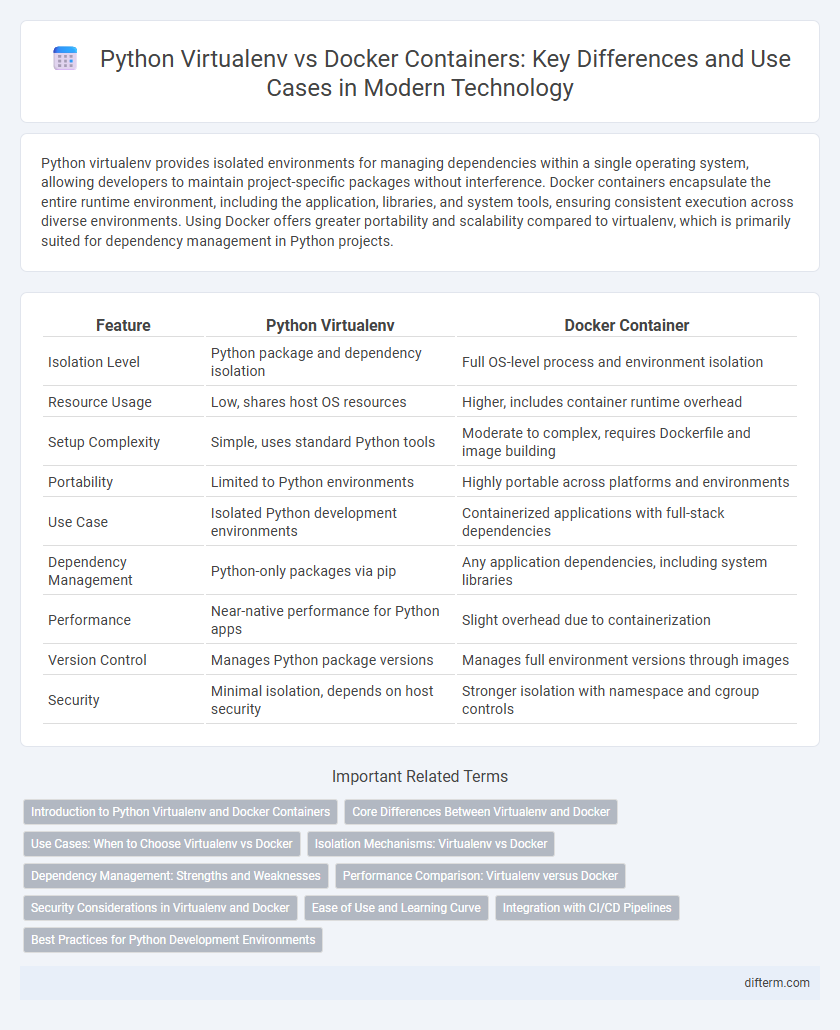
| Feature | Python Virtualenv | Docker Container |
|---|---|---|
| Isolation Level | Python package and dependency isolation | Full OS-level process and environment isolation |
| Resource Usage | Low, shares host OS resources | Higher, includes container runtime overhead |
| Setup Complexity | Simple, uses standard Python tools | Moderate to complex, requires Dockerfile and image building |
| Portability | Limited to Python environments | Highly portable across platforms and environments |
| Use Case | Isolated Python development environments | Containerized applications with full-stack dependencies |
| Dependency Management | Python-only packages via pip | Any application dependencies, including system libraries |
| Performance | Near-native performance for Python apps | Slight overhead due to containerization |
| Version Control | Manages Python package versions | Manages full environment versions through images |
| Security | Minimal isolation, depends on host security | Stronger isolation with namespace and cgroup controls |
Introduction to Python Virtualenv and Docker Containers
Python Virtualenv creates isolated environments for managing dependencies and Python versions within a single system, enabling developers to avoid conflicts between projects. Docker containers package applications along with their entire runtime environment, including libraries and system tools, ensuring consistent execution across different machines. Both tools enhance development workflows by providing environment consistency but operate at different levels of isolation and deployment scope.
Core Differences Between Virtualenv and Docker
Python virtualenv isolates Python package dependencies within a specific project environment, ensuring consistent library versions without affecting the global system. Docker containers encapsulate entire applications along with their runtime, libraries, and system tools, enabling platform-independent deployment across diverse environments. Virtualenv operates at the Python environment level, while Docker provides comprehensive OS-level virtualization, supporting multiple languages and services beyond Python.
Use Cases: When to Choose Virtualenv vs Docker
Python virtualenv is ideal for managing isolated Python environments during development, testing, and running applications with specific dependency versions on a single system. Docker containers extend beyond Python isolation by packaging complete application environments including OS-level libraries, making them suitable for deployment, scaling, and microservices architecture. Choose virtualenv for lightweight, Python-specific workflows, while Docker excels in replicable, cross-platform deployments requiring full environment consistency.
Isolation Mechanisms: Virtualenv vs Docker
Virtualenv isolates Python environments by creating separate directories with independent package installations, relying on the host OS for system resources and dependencies. Docker containers provide stronger isolation by encapsulating the entire application, including its runtime, libraries, and system tools, within lightweight, portable containers using OS-level virtualization. This difference makes Docker more suitable for consistent environments across varied deployments, while Virtualenv primarily addresses Python dependency conflicts within a single OS.
Dependency Management: Strengths and Weaknesses
Python virtualenv isolates dependencies within individual projects, ensuring consistent Python package versions and preventing conflicts across environments. Docker containers provide more comprehensive dependency management by encapsulating the entire application stack, including the OS, libraries, and runtime, offering higher reproducibility and environment parity across different systems. Virtualenv is lightweight but limited to Python packages, while Docker's isolation extends beyond Python, supporting multi-language dependencies but with added complexity and resource overhead.
Performance Comparison: Virtualenv versus Docker
Python virtualenv offers lightweight environment isolation by creating separate directories for dependencies, resulting in faster startup times and minimal resource overhead compared to Docker containers. Docker containers provide full OS-level virtualization, which ensures consistent environments across different systems but introduces additional runtime overhead and slower performance due to containerization layers. For CPU-bound and memory-intensive applications, virtualenv tends to deliver better performance, while Docker excels in reproducibility and deployment scalability despite slightly reduced execution speed.
Security Considerations in Virtualenv and Docker
Docker containers provide a higher level of isolation compared to Python virtualenv by encapsulating applications along with their entire runtime environment, reducing the attack surface linked to the host system. Virtualenv isolates Python dependencies within the same operating system environment but lacks kernel-level security boundaries, making it less effective against vulnerabilities that affect the underlying OS. Security best practices recommend using Docker for deploying applications requiring strict isolation and sandboxing, while virtualenv suits development environments with less stringent security demands.
Ease of Use and Learning Curve
Python virtualenv offers a straightforward and lightweight solution for creating isolated development environments, making it easy for beginners to manage dependencies without modifying the global Python installation. Docker containers provide a more comprehensive environment encapsulation, supporting consistency across different systems but require understanding containerization concepts and Docker CLI commands, which introduces a steeper learning curve. While virtualenv is optimal for developers focused on Python projects, Docker's versatility benefits those needing to manage complex multi-service applications or ensure cross-platform compatibility.
Integration with CI/CD Pipelines
Python virtualenv provides isolated environments for dependencies, ensuring consistent application behavior during CI/CD pipeline stages without system-wide package conflicts. Docker containers encapsulate the entire runtime environment, including the OS, dependencies, and application code, enabling greater consistency and portability across diverse CI/CD infrastructures. Integrating Docker with CI/CD pipelines streamlines deployment and testing by packaging applications into self-contained units, reducing "works on my machine" issues effectively.
Best Practices for Python Development Environments
Python virtualenv provides isolated Python environments for managing dependencies on a per-project basis, allowing developers to avoid conflicts between packages. Docker containers encapsulate the entire runtime environment, including the operating system, libraries, and Python interpreter, ensuring consistent deployment across different machines. Best practices recommend using virtualenv for local development and lightweight isolation while leveraging Docker containers for production, continuous integration, and delivering reproducible builds.
python virtualenv vs docker container Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com