Lossless compression preserves the original data perfectly, making it ideal for pet technology applications where accurate sensor readings and health records are crucial. Lossy compression reduces file size by removing some data, which may compromise the integrity of pet images or audio but is useful for efficient storage and faster transmission. Choosing between lossless and lossy compression depends on whether data fidelity or storage efficiency is the priority in managing pet technology systems.
Table of Comparison
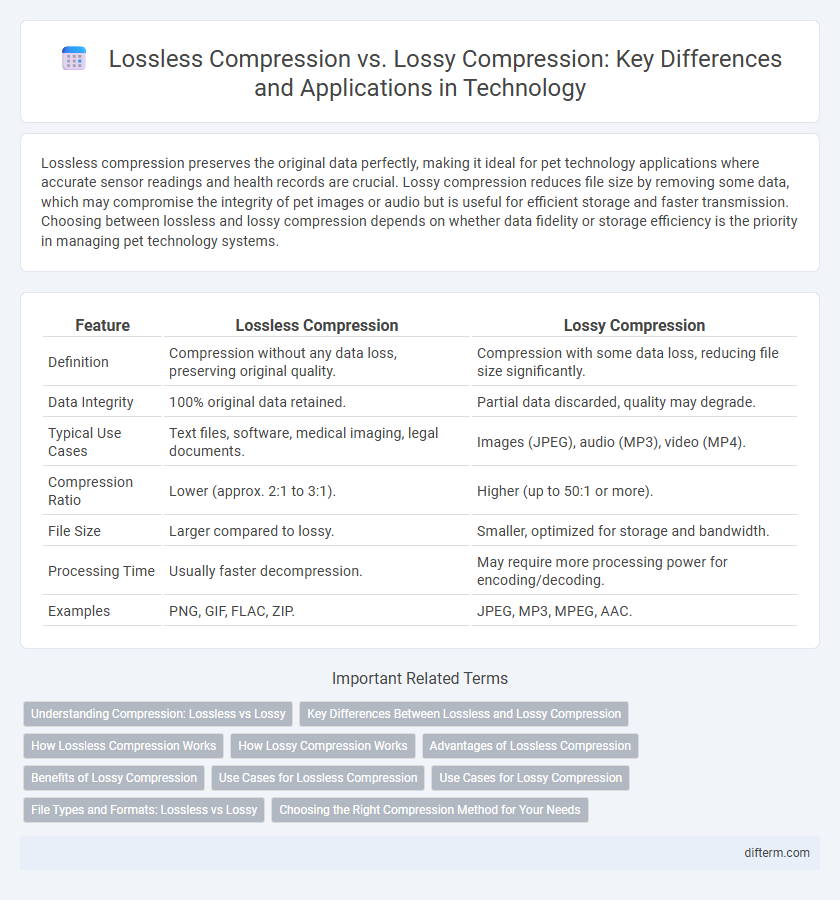
| Feature | Lossless Compression | Lossy Compression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Compression without any data loss, preserving original quality. | Compression with some data loss, reducing file size significantly. |
| Data Integrity | 100% original data retained. | Partial data discarded, quality may degrade. |
| Typical Use Cases | Text files, software, medical imaging, legal documents. | Images (JPEG), audio (MP3), video (MP4). |
| Compression Ratio | Lower (approx. 2:1 to 3:1). | Higher (up to 50:1 or more). |
| File Size | Larger compared to lossy. | Smaller, optimized for storage and bandwidth. |
| Processing Time | Usually faster decompression. | May require more processing power for encoding/decoding. |
| Examples | PNG, GIF, FLAC, ZIP. | JPEG, MP3, MPEG, AAC. |
Understanding Compression: Lossless vs Lossy
Lossless compression preserves original data by encoding it efficiently, enabling perfect reconstruction of the input file without any quality loss, commonly used for text, software, and archival purposes. Lossy compression reduces file size by permanently eliminating some data, optimizing for perceptual quality at the cost of accuracy, widely applied in multimedia formats like JPEG, MP3, and MPEG. Key factors in choosing between lossless and lossy compression include the necessity for exact data retrieval, acceptable quality degradation, and storage or bandwidth constraints.
Key Differences Between Lossless and Lossy Compression
Lossless compression preserves original data integrity by enabling exact reconstruction from compressed files, ideal for text and software. Lossy compression reduces file size by permanently eliminating some data, which can degrade quality but is efficient for multimedia like images and audio. Key differences include data fidelity, file size reduction, and typical use cases, with lossless offering perfect accuracy and lossy prioritizing storage efficiency.
How Lossless Compression Works
Lossless compression works by identifying and eliminating redundant data without any loss of information, allowing the original file to be perfectly reconstructed. Techniques such as Huffman coding, Run-Length Encoding (RLE), and Lempel-Ziv-Welch (LZW) compression analyze data patterns and replace repeated sequences with shorter representations. This method is essential for applications requiring exact data restoration, including text files, software, and medical imaging.
How Lossy Compression Works
Lossy compression reduces file size by permanently eliminating less important data, relying on algorithms that approximate the original content to maintain perceptual quality. It exploits human sensory limitations, discarding inaudible audio frequencies or imperceptible visual details, thereby achieving higher compression ratios compared to lossless methods. Common lossy formats such as MP3 for audio and JPEG for images balance efficiency and quality by selectively removing redundant or less critical information.
Advantages of Lossless Compression
Lossless compression preserves the original data integrity, enabling exact reconstruction of the original file without any loss of quality, which is crucial for applications like medical imaging, text files, and software archives. It ensures data reliability and accuracy, making it ideal for sensitive information and archival purposes. Furthermore, lossless algorithms such as PNG and FLAC enable efficient storage and faster transmission while maintaining the original content intact.
Benefits of Lossy Compression
Lossy compression significantly reduces file sizes by eliminating non-essential data, making it ideal for streaming media and online content delivery where bandwidth optimization is critical. This compression method enhances user experience by enabling faster download speeds and efficient storage on devices with limited capacity. Despite minor quality degradation, lossy compression maintains acceptable visual or audio fidelity for most practical applications, balancing performance and resource management effectively.
Use Cases for Lossless Compression
Lossless compression is essential for use cases requiring exact data reproduction, such as medical imaging, legal documents, and software distribution, where data integrity is critical. It preserves the original file quality by compressing data without any loss, making it ideal for archival storage and scientific research datasets. Applications in fields like digital forensics and technical manuals rely heavily on lossless methods like PNG, FLAC, and ZIP formats to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Use Cases for Lossy Compression
Lossy compression is widely used for multimedia files such as images, audio, and video, where reducing file size is critical for faster transmission and storage efficiency. Common applications include streaming services like Netflix and Spotify, which prioritize bandwidth optimization while maintaining acceptable quality. This type of compression is essential in mobile apps and online platforms to enhance user experience by enabling quicker downloads and reduced data consumption.
File Types and Formats: Lossless vs Lossy
Lossless compression retains original data integrity by encoding file types such as PNG, FLAC, and ZIP without quality degradation, making it ideal for images, audio, and documents requiring exact reproduction. Lossy compression reduces file size by permanently eliminating some data, commonly used in JPEG, MP3, and MPEG formats, which are preferred for web images, streaming media, and videos where some quality loss is acceptable. Choosing between these formats hinges on the balance between file size efficiency and fidelity requirements in applications like archival storage or multimedia playback.
Choosing the Right Compression Method for Your Needs
Lossless compression preserves original data integrity by encoding information without any loss, making it ideal for applications requiring exact replication such as document archiving, medical imaging, and software distribution. Lossy compression reduces file size by permanently removing some data, suitable for multimedia files like photos, videos, and audio where minor quality loss is acceptable to save storage and bandwidth. Selecting the right compression method depends on prioritizing either data fidelity or file size reduction based on specific use cases and performance requirements.
Lossless compression vs Lossy compression Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com