Elasticsearch and Solr are leading open-source search platforms designed for scalable, real-time data retrieval and analytics in technology pet applications. Elasticsearch offers distributed search capabilities with an easy-to-use RESTful API, making it ideal for dynamic data environments and rapid indexing. Solr excels with advanced full-text search features and customizable faceted navigation, providing robust options for complex query requirements and enterprise-level deployments.
Table of Comparison
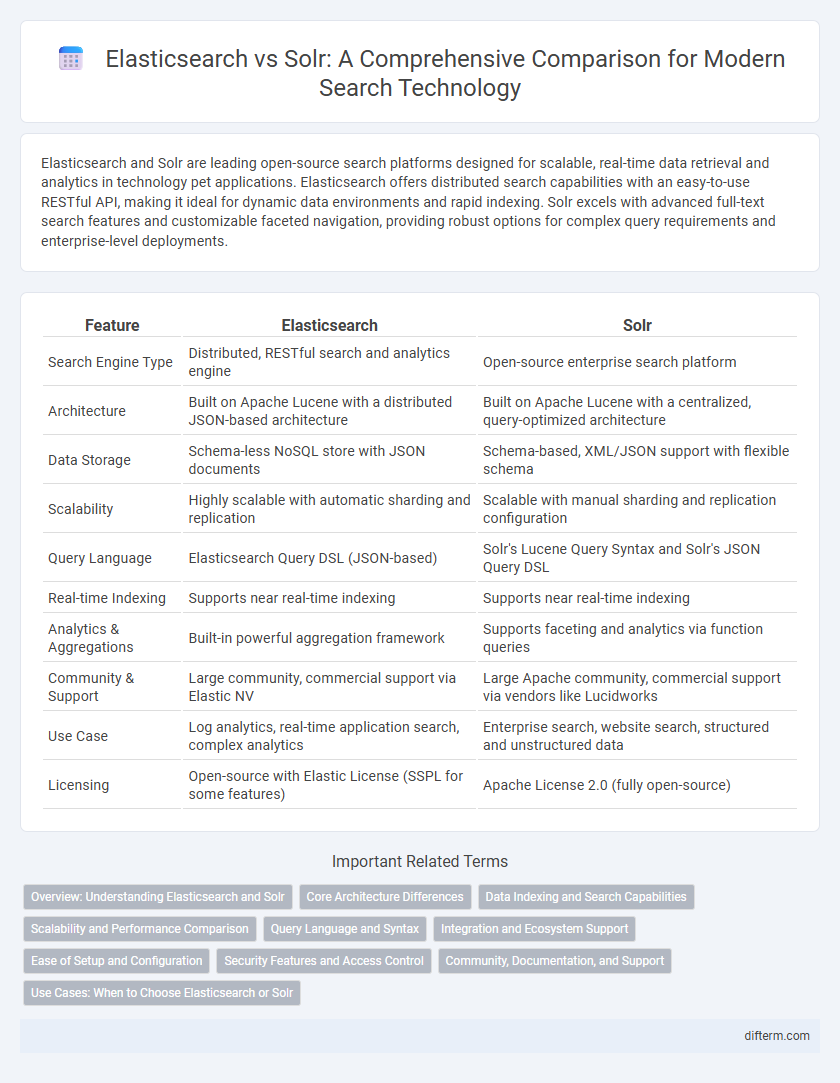
| Feature | Elasticsearch | Solr |
|---|---|---|
| Search Engine Type | Distributed, RESTful search and analytics engine | Open-source enterprise search platform |
| Architecture | Built on Apache Lucene with a distributed JSON-based architecture | Built on Apache Lucene with a centralized, query-optimized architecture |
| Data Storage | Schema-less NoSQL store with JSON documents | Schema-based, XML/JSON support with flexible schema |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with automatic sharding and replication | Scalable with manual sharding and replication configuration |
| Query Language | Elasticsearch Query DSL (JSON-based) | Solr's Lucene Query Syntax and Solr's JSON Query DSL |
| Real-time Indexing | Supports near real-time indexing | Supports near real-time indexing |
| Analytics & Aggregations | Built-in powerful aggregation framework | Supports faceting and analytics via function queries |
| Community & Support | Large community, commercial support via Elastic NV | Large Apache community, commercial support via vendors like Lucidworks |
| Use Case | Log analytics, real-time application search, complex analytics | Enterprise search, website search, structured and unstructured data |
| Licensing | Open-source with Elastic License (SSPL for some features) | Apache License 2.0 (fully open-source) |
Overview: Understanding Elasticsearch and Solr
Elasticsearch and Solr are powerful open-source search platforms built on Apache Lucene, designed for full-text search and real-time analytics. Elasticsearch offers a distributed, RESTful search and analytics engine known for scalability, near real-time indexing, and ease of integration with the Elastic Stack. Solr provides advanced full-text search capabilities, flexible configuration, and a mature ecosystem, excelling in complex search applications with strong support for faceted search and extensive customization.
Core Architecture Differences
Elasticsearch utilizes a distributed, JSON-based RESTful architecture built on top of Apache Lucene, enabling real-time, scalable search and analytics with automatic shard allocation and replication. Solr, also based on Apache Lucene, employs a more traditional, XML-configured architecture emphasizing advanced full-text search features and higher customization through plugin support. Elasticsearch's schema-less design contrasts with Solr's predefined schema approach, impacting flexibility and ease of dynamic data handling.
Data Indexing and Search Capabilities
Elasticsearch excels in real-time distributed indexing, enabling rapid data ingestion and retrieval across large-scale, diverse datasets with its JSON document-oriented architecture. Solr offers powerful full-text search capabilities with advanced faceting and filtering, leveraging Apache Lucene for highly customizable query execution and scalability in enterprise environments. Both platforms support complex indexing strategies and multi-index search but Elasticsearch's native RESTful API facilitates easier integration and faster horizontal scaling in cloud-native applications.
Scalability and Performance Comparison
Elasticsearch offers superior scalability through its distributed architecture and automatic shard allocation, enabling efficient handling of large datasets and real-time search operations. Solr, built on Apache Lucene, provides robust performance with customizable configurations but often requires manual tuning for optimal scalability in large clusters. Elasticsearch's near real-time indexing and horizontal scaling capabilities make it a preferred choice for applications demanding rapid, scalable search performance.
Query Language and Syntax
Elasticsearch uses a JSON-based Query DSL that offers intuitive, flexible syntax for complex search queries, supporting full-text search, filtering, and aggregations with ease. Solr employs the Lucene query syntax and supports multiple query parsers like DisMax and Extended DisMax, making it versatile but sometimes more complex for advanced queries. Elasticsearch's query language is often favored for RESTful integration and real-time analytics, whereas Solr's syntax excels in precise text search tuning and custom scoring.
Integration and Ecosystem Support
Elasticsearch offers seamless integration with the Elastic Stack, including Kibana for visualization and Beats for data ingestion, enhancing its ecosystem support for real-time analytics. Solr integrates well with Apache Hadoop and various Java-based tools, providing robust support for large-scale data processing environments. Both platforms support RESTful APIs, but Elasticsearch's native integration with Logstash and its extensive plugin ecosystem give it an edge in flexible deployment scenarios.
Ease of Setup and Configuration
Elasticsearch offers a more intuitive and simplified setup process with RESTful APIs and built-in JSON configuration, enabling faster deployment and easier scaling. Solr requires XML-based configuration files and often demands more manual tuning, contributing to a steeper learning curve for initial setup. Elasticsearch's dynamic schema and automatic node discovery streamline cluster management compared to Solr's static schema and manual shard allocation.
Security Features and Access Control
Elasticsearch offers robust security features through the Elastic Stack Security, including role-based access control (RBAC), encryption at rest and in transit, and audit logging, making it suitable for enterprise environments requiring stringent data protection. Solr provides authentication and authorization via integration with Apache Ranger or Kerberos, along with SSL/TLS for encrypted communication, but it often requires additional configuration to achieve a comparable security posture. Both platforms support fine-grained access control mechanisms, but Elasticsearch's native security features deliver a more streamlined and comprehensive approach for managing user permissions and securing clusters.
Community, Documentation, and Support
Elasticsearch offers a more extensive and active community with frequent updates and a wealth of user-generated content across forums and GitHub. Its documentation is comprehensive, regularly maintained, and beginner-friendly, making it easier for new users to adopt and troubleshoot. Solr, while having a smaller community, provides robust official documentation and strong enterprise support through the Apache Software Foundation and commercial vendors, appealing to organizations seeking formal support agreements.
Use Cases: When to Choose Elasticsearch or Solr
Elasticsearch excels in real-time log and event data analysis, making it ideal for monitoring applications, metrics, and security analytics due to its distributed architecture and high scalability. Solr is preferred for complex enterprise search scenarios requiring advanced text analysis, faceted search, and rich document handling, often integrating well with Hadoop ecosystems. Organizations should choose Elasticsearch for fast indexing and real-time search capabilities, while Solr suits cases demanding sophisticated content management and extensive customization.
Elasticsearch vs Solr Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com