Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger that records transactions in a sequential, immutable chain of blocks, enhancing security and transparency. Distributed ledgers, more broadly, can be structured in various ways beyond chains of blocks, allowing for more flexible data storage and consensus methods. Both technologies revolutionize data management by enabling decentralized and tamper-resistant recording systems.
Table of Comparison
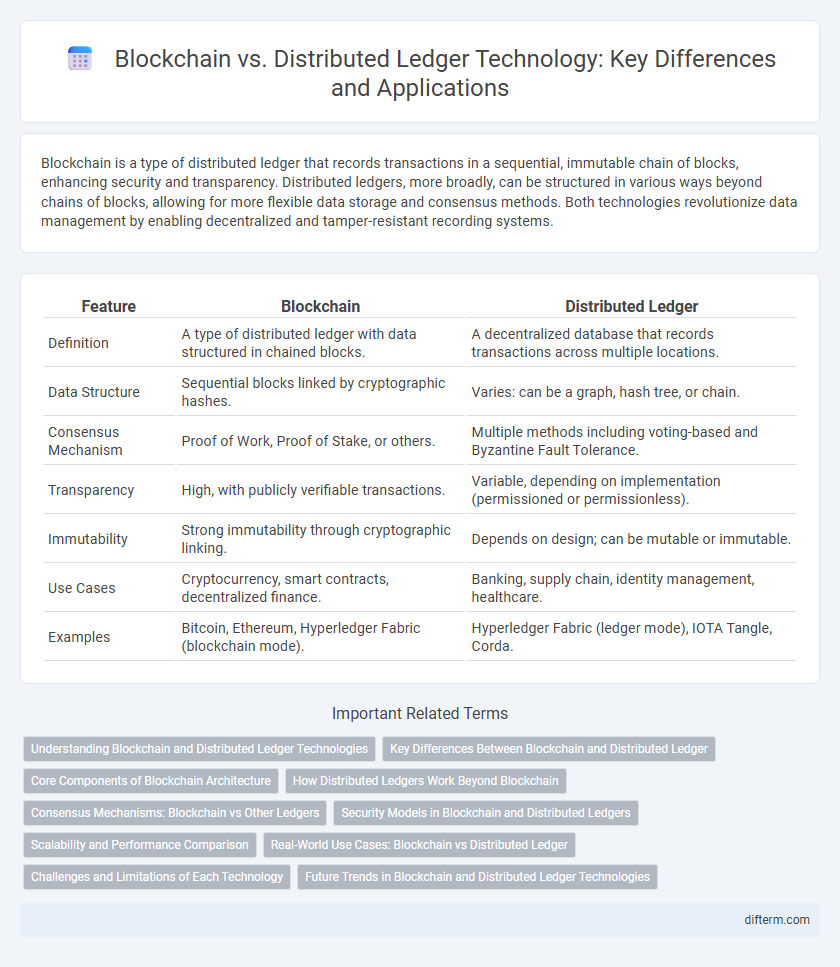
| Feature | Blockchain | Distributed Ledger |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A type of distributed ledger with data structured in chained blocks. | A decentralized database that records transactions across multiple locations. |
| Data Structure | Sequential blocks linked by cryptographic hashes. | Varies: can be a graph, hash tree, or chain. |
| Consensus Mechanism | Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, or others. | Multiple methods including voting-based and Byzantine Fault Tolerance. |
| Transparency | High, with publicly verifiable transactions. | Variable, depending on implementation (permissioned or permissionless). |
| Immutability | Strong immutability through cryptographic linking. | Depends on design; can be mutable or immutable. |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrency, smart contracts, decentralized finance. | Banking, supply chain, identity management, healthcare. |
| Examples | Bitcoin, Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric (blockchain mode). | Hyperledger Fabric (ledger mode), IOTA Tangle, Corda. |
Understanding Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technologies
Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology (DLT) that records transactions in a secure, immutable chain of blocks, ensuring transparency and trust among participants. Distributed ledger technology encompasses various systems, including blockchain, that enable decentralized data recording across multiple nodes without a central authority. Understanding the key differences helps in selecting the appropriate technology for use cases such as supply chain management, financial services, and digital identity verification.
Key Differences Between Blockchain and Distributed Ledger
Blockchain is a specific type of distributed ledger technology (DLT) characterized by its use of chained blocks containing transaction data secured through cryptographic hashing. Distributed ledgers are a broader category of databases that distribute information across multiple nodes to enhance transparency and reduce the need for a central authority, with blockchain as one implementation within this category. Key differences include blockchain's linear, append-only structure versus distributed ledgers' potential for varied data structures and consensus mechanisms beyond the block-based model.
Core Components of Blockchain Architecture
Blockchain architecture is anchored by core components such as cryptographic hashing, decentralized consensus mechanisms, and the immutable ledger to ensure data integrity and security. Distributed ledger technology (DLT) shares the decentralized data storage feature but differs by allowing various consensus protocols beyond proof-of-work, enhancing scalability and flexibility. Smart contracts and peer-to-peer networking further distinguish blockchain by enabling automated, trustless transactions within a transparent, tamper-resistant framework.
How Distributed Ledgers Work Beyond Blockchain
Distributed ledgers operate by maintaining a decentralized database where transactions are recorded across multiple nodes, ensuring transparency and security without relying solely on blockchain's chain of blocks structure. They utilize consensus mechanisms like Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) or Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG) to validate and synchronize data efficiently among participants. This architecture enables faster transaction speeds and scalability compared to traditional blockchain implementations, expanding use cases in finance, supply chain, and identity verification.
Consensus Mechanisms: Blockchain vs Other Ledgers
Consensus mechanisms in blockchain primarily rely on protocols such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) to validate transactions and secure the network by achieving agreement among distributed nodes. Other distributed ledgers utilize alternative consensus algorithms like Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) and Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG), which often prioritize faster transaction finality and scalability over the computational intensity of blockchain methods. The choice of consensus mechanism directly influences network security, transaction speed, and energy efficiency in distributed ledger technologies.
Security Models in Blockchain and Distributed Ledgers
Blockchain employs a cryptographic security model using hash functions and consensus algorithms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake to ensure data integrity and prevent tampering. Distributed Ledgers utilize a broader range of security mechanisms, often incorporating permissioned access controls and Byzantine Fault Tolerance protocols to maintain consistent and secure transaction records. The immutable nature of blockchain's chain structure contrasts with the flexible, often permissioned architectures of distributed ledgers optimized for enterprise security needs.
Scalability and Performance Comparison
Blockchain and distributed ledger technologies differ significantly in scalability and performance, with traditional blockchains often facing bottlenecks due to consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work, which limit transaction throughput to around 7 transactions per second. Distributed ledgers utilize alternative consensus algorithms and data structures that enhance scalability, achieving thousands of transactions per second, making them more suitable for enterprise applications requiring high performance. The flexibility in node participation and transaction validation processes in distributed ledgers further optimizes network efficiency and reduces latency compared to conventional blockchain networks.
Real-World Use Cases: Blockchain vs Distributed Ledger
Blockchain technology powers cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin by enabling secure, transparent, and immutable transactions across decentralized networks. Distributed ledgers extend beyond blockchain by supporting various data structures and consensus mechanisms, optimizing supply chain management and cross-border payments through enhanced scalability and flexibility. Real-world applications highlight blockchain's dominance in financial services, while distributed ledgers gain traction in healthcare data sharing and government record-keeping.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Technology
Blockchain faces scalability challenges due to its consensus mechanisms, which often result in slower transaction speeds and higher energy consumption compared to traditional databases. Distributed Ledgers offer more flexibility and can handle higher transaction volumes but struggle with interoperability issues and lack of standardized protocols. Both technologies face regulatory uncertainty and privacy concerns, limiting widespread adoption across industries.
Future Trends in Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technologies
Future trends in blockchain and distributed ledger technologies emphasize increased interoperability and scalability through technologies like sharding and layer-2 solutions, enabling faster and more efficient transactions across multiple networks. The integration of blockchain with artificial intelligence and Internet of Things (IoT) is driving advancements in automated smart contracts and enhanced data security. Quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms are also being developed to protect distributed ledgers against emerging quantum computing threats.
Blockchain vs Distributed Ledger Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com