Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) specializes in monitoring and defending individual devices by detecting threats and providing real-time response capabilities. Network Detection and Response (NDR) complements EDR by analyzing network traffic patterns to identify larger, stealthy attacks that span multiple endpoints. Combining EDR and NDR creates a comprehensive security posture, enabling both granular device-level protection and holistic network-wide threat detection.
Table of Comparison
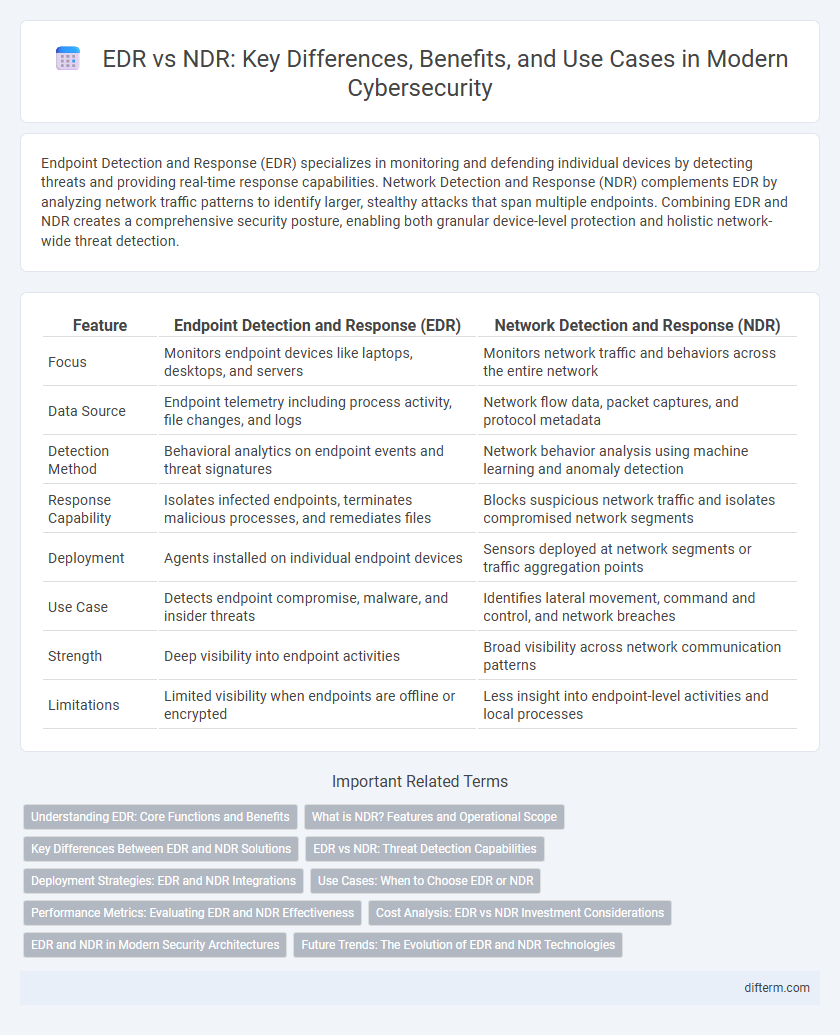
| Feature | Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) | Network Detection and Response (NDR) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Monitors endpoint devices like laptops, desktops, and servers | Monitors network traffic and behaviors across the entire network |
| Data Source | Endpoint telemetry including process activity, file changes, and logs | Network flow data, packet captures, and protocol metadata |
| Detection Method | Behavioral analytics on endpoint events and threat signatures | Network behavior analysis using machine learning and anomaly detection |
| Response Capability | Isolates infected endpoints, terminates malicious processes, and remediates files | Blocks suspicious network traffic and isolates compromised network segments |
| Deployment | Agents installed on individual endpoint devices | Sensors deployed at network segments or traffic aggregation points |
| Use Case | Detects endpoint compromise, malware, and insider threats | Identifies lateral movement, command and control, and network breaches |
| Strength | Deep visibility into endpoint activities | Broad visibility across network communication patterns |
| Limitations | Limited visibility when endpoints are offline or encrypted | Less insight into endpoint-level activities and local processes |
Understanding EDR: Core Functions and Benefits
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions provide continuous monitoring, threat detection, and automated response for endpoints such as laptops, desktops, and servers. EDR systems collect and analyze data in real time to identify suspicious activities, enabling rapid containment and remediation of malware and cyberattacks. The technology enhances security posture by offering detailed visibility into endpoint behavior, threat hunting capabilities, and forensic analysis to prevent advanced persistent threats (APTs).
What is NDR? Features and Operational Scope
Network Detection and Response (NDR) is a cybersecurity technology that identifies, investigates, and mitigates threats within network traffic using advanced analytics and machine learning. Its key features include real-time network monitoring, anomaly detection, threat intelligence integration, and automated incident response. NDR operates across the entire network infrastructure, providing visibility into encrypted traffic, lateral movement, and insider threats, complementing Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) by focusing on network-level insights.
Key Differences Between EDR and NDR Solutions
EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) focuses on monitoring, detecting, and responding to threats at the endpoint level, using behavioral analysis and threat intelligence to protect devices like laptops, desktops, and servers. NDR (Network Detection and Response) analyzes network traffic data using machine learning and anomaly detection to identify intrusions and suspicious activity across the entire network infrastructure. Key differences include EDR's direct interaction with endpoints and forensic capabilities versus NDR's broader network visibility and ability to detect lateral movement and zero-day threats.
EDR vs NDR: Threat Detection Capabilities
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) primarily focuses on detecting and responding to threats at the device level, utilizing behavioral analysis and real-time monitoring to identify suspicious activities on endpoints. Network Detection and Response (NDR) enhances threat detection by analyzing network traffic patterns and anomalies, providing broader visibility across an organization's entire network infrastructure. Combining EDR and NDR enables comprehensive threat detection capabilities by correlating endpoint data with network-based indicators to identify sophisticated cyber threats more effectively.
Deployment Strategies: EDR and NDR Integrations
EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) deployment focuses on installing agents directly on endpoints to monitor and analyze endpoint activities, enabling detailed threat detection and response capabilities at the device level. NDR (Network Detection and Response) integrates with existing network infrastructure by leveraging network traffic data from sensors and taps, providing holistic visibility and anomaly detection across the network environment. Combining EDR and NDR platforms through integration strategies enhances security posture by correlating endpoint data with network-wide insights, facilitating more comprehensive threat detection and faster incident response.
Use Cases: When to Choose EDR or NDR
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) is ideal for investigating and mitigating threats at the device level, such as malware infections or unauthorized access on endpoints. Network Detection and Response (NDR) excels in monitoring network traffic to identify anomalies and advanced threats that evade traditional security tools. Choose EDR when focused on endpoint-specific incident response and NDR for broad visibility into network-wide suspicious activity and lateral movement.
Performance Metrics: Evaluating EDR and NDR Effectiveness
EDR focuses on endpoint activity, measuring metrics such as detection accuracy, response time, and threat remediation rates to evaluate its effectiveness. NDR emphasizes network traffic analysis, leveraging metrics like anomaly detection precision, false positive rates, and latency in identifying threats. Performance comparison reveals EDR excels in granular endpoint visibility, while NDR offers broader detection across network environments, impacting overall security posture based on organizational needs.
Cost Analysis: EDR vs NDR Investment Considerations
EDR solutions generally require higher upfront costs due to extensive endpoint agents and continuous monitoring but deliver detailed endpoint visibility critical for threat detection. NDR investments focus on network traffic analysis with comparatively lower initial deployment expenses but demand ongoing infrastructure and tuning for effective anomaly detection. Evaluating total cost of ownership involves balancing EDR's detailed endpoint protection against NDR's broad network-level insight and operational scalability.
EDR and NDR in Modern Security Architectures
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and Network Detection and Response (NDR) serve complementary roles in modern security architectures by providing comprehensive threat visibility across endpoints and network traffic. EDR solutions focus on monitoring, detecting, and responding to threats on individual devices through behavior analysis and advanced threat hunting capabilities, while NDR enhances security by monitoring network traffic patterns to identify anomalies and lateral movement. Integrating EDR and NDR enables organizations to establish multi-layered defense mechanisms, improving incident detection, investigation, and response times.
Future Trends: The Evolution of EDR and NDR Technologies
The future evolution of EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) and NDR (Network Detection and Response) technologies emphasizes integration with AI-driven threat intelligence to enhance real-time threat detection and automated response capabilities. Advances in machine learning algorithms enable both EDR and NDR systems to identify sophisticated cyberattacks by analyzing behavioral patterns across endpoints and network traffic. As organizations adopt zero-trust architectures, the convergence of EDR and NDR solutions will play a critical role in delivering comprehensive security visibility and adaptive protection measures.
EDR vs NDR Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com