Bluetooth offers seamless short-range wireless connectivity ideal for low power devices like headphones and fitness trackers, whereas WiFi provides high-speed internet access over larger areas suitable for streaming and online gaming. Bluetooth operates on a simpler, energy-efficient protocol with a limited data transfer rate, while WiFi supports broader bandwidth, enabling faster data transmission and multiple device connections. Choosing between Bluetooth and WiFi depends on the specific requirements of range, speed, power consumption, and network complexity.
Table of Comparison
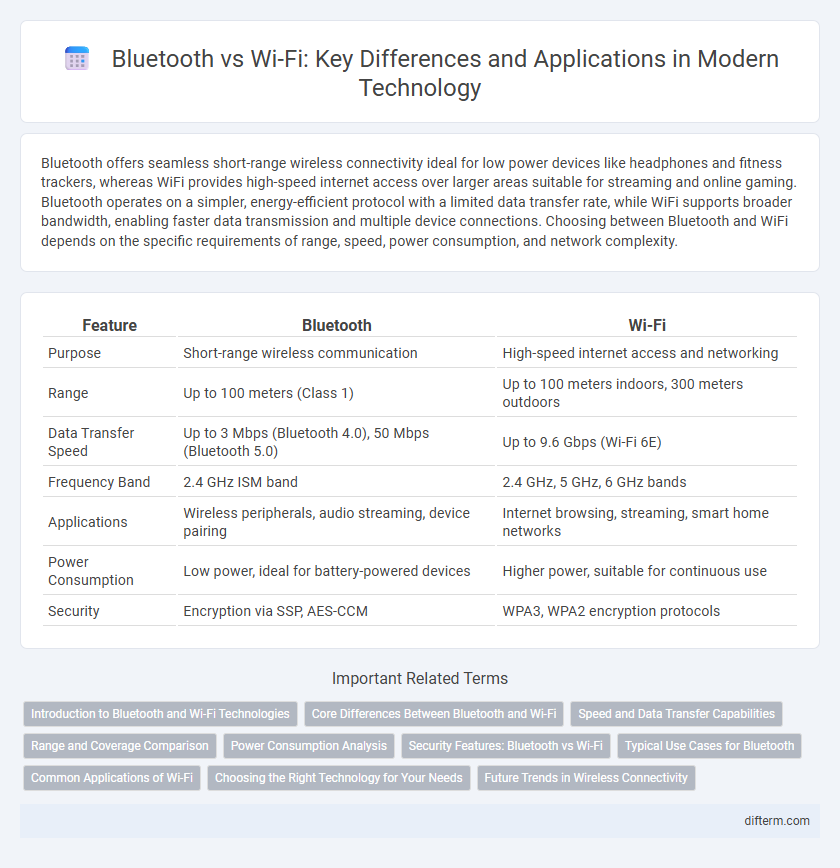
| Feature | Bluetooth | Wi-Fi |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Short-range wireless communication | High-speed internet access and networking |
| Range | Up to 100 meters (Class 1) | Up to 100 meters indoors, 300 meters outdoors |
| Data Transfer Speed | Up to 3 Mbps (Bluetooth 4.0), 50 Mbps (Bluetooth 5.0) | Up to 9.6 Gbps (Wi-Fi 6E) |
| Frequency Band | 2.4 GHz ISM band | 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, 6 GHz bands |
| Applications | Wireless peripherals, audio streaming, device pairing | Internet browsing, streaming, smart home networks |
| Power Consumption | Low power, ideal for battery-powered devices | Higher power, suitable for continuous use |
| Security | Encryption via SSP, AES-CCM | WPA3, WPA2 encryption protocols |
Introduction to Bluetooth and Wi-Fi Technologies
Bluetooth technology facilitates short-range wireless communication between devices, typically within a 10-meter radius, using low energy and frequency-hopping spread spectrum in the 2.4 GHz ISM band. Wi-Fi enables high-speed wireless internet access over broader distances, often up to 100 meters, operating primarily on 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands and supporting complex network infrastructures. Both technologies are essential for modern connectivity, with Bluetooth excelling in device pairing and low-power applications, while Wi-Fi provides robust internet access and data transfer.
Core Differences Between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi
Bluetooth operates on short-range wireless communication primarily designed for device-to-device connections within a range of about 10 meters, using low power and limited data transfer speeds up to 3 Mbps. Wi-Fi provides higher data transfer rates, reaching up to several Gbps depending on the standard (e.g., Wi-Fi 6), and covers a broader range of up to 100 meters, supporting internet access and networked device connectivity. Bluetooth excels in low-energy applications like wearables and peripherals, while Wi-Fi is optimized for high-bandwidth activities such as streaming and large file downloads.
Speed and Data Transfer Capabilities
Wi-Fi offers significantly higher speeds and greater data transfer capacity compared to Bluetooth, supporting data rates up to several gigabits per second with standards like Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7. Bluetooth typically maxes out at around 2 Mbps to 3 Mbps with Bluetooth 5.0 and 5.2, making it suitable for low-power, short-range communication rather than high-bandwidth applications. Wi-Fi's robust bandwidth and longer range make it ideal for streaming, large file transfers, and network connectivity, whereas Bluetooth excels in connecting peripherals and enabling IoT devices with minimal power consumption.
Range and Coverage Comparison
Bluetooth typically covers a range of up to 100 meters with limited bandwidth, making it ideal for short-range, low-power device connections. WiFi offers significantly broader coverage, ranging from 30 meters indoors to over 100 meters outdoors, supporting high-speed internet access across larger areas. The choice between Bluetooth and WiFi depends on the specific need for range, power consumption, and data throughput in technology applications.
Power Consumption Analysis
Bluetooth technology typically consumes significantly less power than WiFi, making it more suitable for battery-powered devices and IoT applications where energy efficiency is crucial. WiFi provides higher data transfer rates but at the cost of increased power usage, which can quickly drain device batteries in continuous operation. Advanced Bluetooth standards like Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) further optimize power consumption by maintaining connections with minimal energy expenditure.
Security Features: Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
Bluetooth employs short-range encryption protocols such as AES-CCM to secure peer-to-peer connections and limit exposure to external threats. Wi-Fi utilizes WPA3 security standards, offering robust encryption and enhanced protection against brute-force attacks through individualized data encryption for each user. While Bluetooth's security is optimized for device pairing and low-power transmissions, Wi-Fi provides comprehensive network-wide security suited for higher data volumes and broader device connectivity.
Typical Use Cases for Bluetooth
Bluetooth technology excels in short-range, low-power wireless communication, making it ideal for connecting peripherals such as wireless headphones, keyboards, and smartwatches to smartphones and computers. Its ability to create personal area networks (PANs) facilitates seamless device interactions in close proximity without the need for internet connectivity. Bluetooth is also widely used in IoT devices and fitness trackers, where energy efficiency and ease of pairing are critical.
Common Applications of Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi technology enables seamless internet connectivity for a wide range of devices, including smartphones, laptops, and smart home systems, supporting high-speed data transfer and reliable network access. It is commonly used in environments such as homes, offices, public hotspots, and industrial settings to facilitate video streaming, online gaming, and cloud computing. Wi-Fi's broad coverage and robust bandwidth make it a preferred choice for applications requiring consistent, high-capacity wireless communication.
Choosing the Right Technology for Your Needs
Bluetooth offers short-range, low-power wireless connectivity ideal for personal devices like headphones and fitness trackers, while Wi-Fi provides high-speed, long-range internet access suited for streaming and large data transfers. Selecting the right technology depends on factors like range requirements, data transfer speed, power consumption, and device compatibility. For seamless home networking or office setups, Wi-Fi is preferable, whereas Bluetooth excels in device pairing and IoT applications.
Future Trends in Wireless Connectivity
Bluetooth is evolving with Bluetooth 5.3, offering improved energy efficiency and faster data transfer rates, making it ideal for IoT devices and wearable technology. Wi-Fi 7 promises ultra-high-speed connections with lower latency and enhanced capacity to support dense urban environments and streaming 8K content. Future trends emphasize seamless integration between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi for smarter, more reliable wireless ecosystems in smart homes and industrial applications.
bluetooth vs wifi Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com