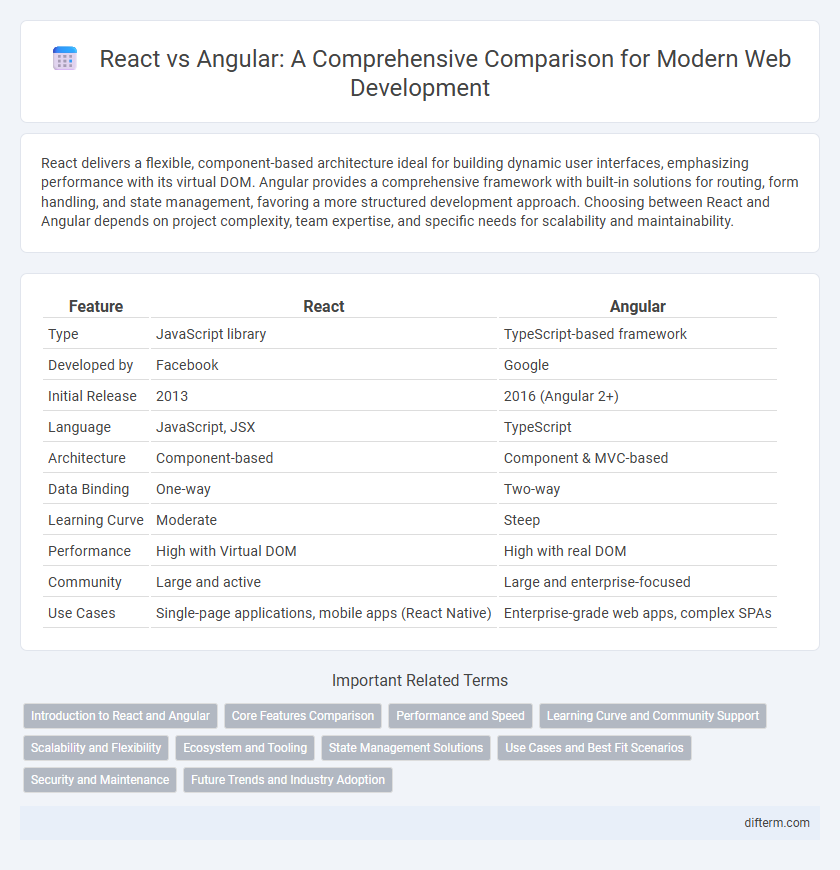
React delivers a flexible, component-based architecture ideal for building dynamic user interfaces, emphasizing performance with its virtual DOM. Angular provides a comprehensive framework with built-in solutions for routing, form handling, and state management, favoring a more structured development approach. Choosing between React and Angular depends on project complexity, team expertise, and specific needs for scalability and maintainability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | React | Angular |
|---|---|---|
| Type | JavaScript library | TypeScript-based framework |
| Developed by | ||
| Initial Release | 2013 | 2016 (Angular 2+) |
| Language | JavaScript, JSX | TypeScript |
| Architecture | Component-based | Component & MVC-based |
| Data Binding | One-way | Two-way |
| Learning Curve | Moderate | Steep |
| Performance | High with Virtual DOM | High with real DOM |
| Community | Large and active | Large and enterprise-focused |
| Use Cases | Single-page applications, mobile apps (React Native) | Enterprise-grade web apps, complex SPAs |
Introduction to React and Angular
React is an open-source JavaScript library developed by Facebook for building user interfaces, emphasizing component-based architecture and virtual DOM for high performance. Angular, created by Google, is a comprehensive front-end framework that offers a two-way data binding system and a modular development structure using TypeScript. Both technologies support scalable web application development but differ in complexity, learning curve, and underlying architecture.
Core Features Comparison
React offers a flexible, component-based architecture with a virtual DOM for efficient updates and supports a unidirectional data flow, enhancing performance in complex applications. Angular provides a full-featured framework with two-way data binding, dependency injection, and a comprehensive CLI, facilitating rapid development and scalability. Both prioritize modularity and reusable components, but React's lightweight library contrasts with Angular's complete, opinionated framework approach.
Performance and Speed
React leverages a virtual DOM for efficient UI updates, resulting in faster rendering and improved performance in dynamic applications compared to Angular's real DOM approach. Angular's built-in change detection can sometimes lead to slower updates in complex applications, whereas React's fine-grained control over rendering enhances responsiveness. React's lightweight architecture and asynchronous rendering capabilities often deliver better speed and smoother user experiences in performance-critical projects.
Learning Curve and Community Support
React offers a gentler learning curve with its component-based architecture and extensive documentation, making it accessible for developers familiar with JavaScript. Angular's steeper learning curve stems from its comprehensive framework features, including dependency injection and TypeScript integration, which require more initial effort to master. React benefits from a larger, more active community with abundant tutorials and third-party libraries, whereas Angular's community, while smaller, provides strong enterprise-level support and robust tooling.
Scalability and Flexibility
React offers superior flexibility with its component-based architecture, allowing developers to integrate diverse libraries and tools for tailored solutions. Angular provides robust scalability through its comprehensive framework, built-in features, and structured approach ideal for large-scale enterprise applications. Choosing between React and Angular depends on project requirements, where React excels in customization and Angular thrives in standardized, scalable development.
Ecosystem and Tooling
React offers a vast ecosystem fueled by a robust community, providing extensive libraries and third-party tools for flexible development. Angular features a comprehensive, all-in-one framework with integrated tooling such as Angular CLI, RxJS, and built-in testing utilities, facilitating a streamlined development process. Both platforms support strong developer productivity, but React's modular ecosystem allows for greater customization, while Angular provides a consistent, opinionated structure.
State Management Solutions
React's state management often relies on libraries like Redux, MobX, or the Context API to handle complex application states efficiently. Angular provides a built-in state management system through RxJS and NgRx, offering reactive programming capabilities that integrate tightly with its framework. Developers choose React for flexible integration with diverse state libraries, while Angular's solution delivers a more structured and opinionated approach to managing state in large-scale applications.
Use Cases and Best Fit Scenarios
React excels in building dynamic, high-performance user interfaces for single-page applications and mobile apps, making it ideal for projects requiring flexibility and extensive component reuse. Angular offers a comprehensive framework with built-in tools for enterprise-level applications, complex workflows, and large-scale projects where a structured architecture and standardized practices are essential. Choosing React suits startups and rapid prototyping, while Angular is best for robust, feature-rich systems demanding strong maintainability and scalability.
Security and Maintenance
React offers a flexible component-based architecture that simplifies regular security updates and maintenance by allowing targeted patches without overhauling the entire codebase. Angular's built-in security features, such as dependency injection and strict contextual escaping, provide robust protection against cross-site scripting and other vulnerabilities, reducing the need for external libraries. Both frameworks benefit from active communities that continuously release security patches and best practices, ensuring long-term maintainability and resilience against emerging threats.
Future Trends and Industry Adoption
React continues to dominate with widespread industry adoption due to its component-based architecture and strong community support, driving innovations in server-side rendering and concurrent features. Angular remains a robust choice in enterprise environments, leveraging TypeScript and comprehensive tooling for large-scale application development. Future trends indicate increasing integration of React with micro-frontend architectures and Angular's advancement in standalone components, enhancing scalability and developer productivity.
React vs Angular Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com