Lead-based paint disclosure is legally required for properties built before 1978, alerting buyers to potential health risks from deteriorating paint. Asbestos disclosure pertains to older buildings and involves informing buyers about the presence of asbestos materials used in insulation or construction, which pose serious respiratory hazards. Both disclosures are critical for protecting buyers and ensuring compliance with federal and state real estate regulations.
Table of Comparison
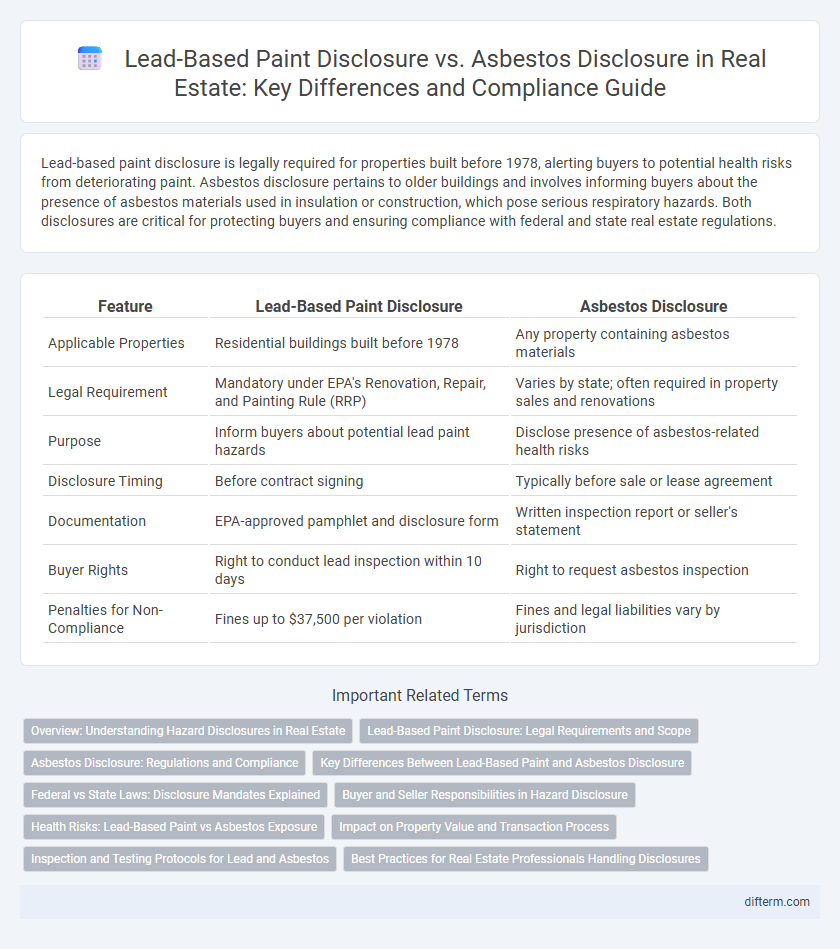
| Feature | Lead-Based Paint Disclosure | Asbestos Disclosure |
|---|---|---|
| Applicable Properties | Residential buildings built before 1978 | Any property containing asbestos materials |
| Legal Requirement | Mandatory under EPA's Renovation, Repair, and Painting Rule (RRP) | Varies by state; often required in property sales and renovations |
| Purpose | Inform buyers about potential lead paint hazards | Disclose presence of asbestos-related health risks |
| Disclosure Timing | Before contract signing | Typically before sale or lease agreement |
| Documentation | EPA-approved pamphlet and disclosure form | Written inspection report or seller's statement |
| Buyer Rights | Right to conduct lead inspection within 10 days | Right to request asbestos inspection |
| Penalties for Non-Compliance | Fines up to $37,500 per violation | Fines and legal liabilities vary by jurisdiction |
Overview: Understanding Hazard Disclosures in Real Estate
Lead-Based Paint Disclosure requires sellers to inform buyers about the presence of lead paint in homes built before 1978, ensuring compliance with federal regulations to prevent lead poisoning. Asbestos Disclosure mandates sellers to reveal any known asbestos-containing materials, which pose health risks if disturbed during renovations or demolitions. Both disclosures aim to protect buyers by promoting transparency about potential environmental hazards in residential properties.
Lead-Based Paint Disclosure: Legal Requirements and Scope
Lead-based paint disclosure is mandated under the Residential Lead-Based Paint Hazard Reduction Act of 1992, requiring sellers and landlords of pre-1978 residential properties to provide buyers or renters with an EPA-approved information pamphlet, disclose known lead paint hazards, and include specific warning language in contracts. This federal requirement applies to target housing units built before 1978, aiming to prevent lead poisoning caused by deteriorating lead-based paint. Unlike asbestos disclosure, which varies by state and often focuses on commercial properties, lead-based paint disclosure involves strict federal guidelines to protect families and children from toxic lead exposure in homes.
Asbestos Disclosure: Regulations and Compliance
Asbestos disclosure regulations mandate that property sellers and landlords inform buyers or tenants about the presence of asbestos-containing materials to ensure safety and compliance with federal and state laws, such as the EPA's Asbestos Hazard Emergency Response Act (AHERA). Compliance involves thorough inspections and providing detailed reports that outline the location, condition, and risk associated with asbestos in residential and commercial real estate transactions. Failure to disclose asbestos can result in significant legal liabilities and fines, emphasizing the importance of transparent communication during property transfers.
Key Differences Between Lead-Based Paint and Asbestos Disclosure
Lead-based paint disclosure requires sellers to inform buyers of any known presence of lead-based paint in homes built before 1978, addressing health risks primarily related to children's developmental issues. Asbestos disclosure mandates disclosure of asbestos materials, commonly found in insulation and older building components, emphasizing respiratory hazards and long-term exposure risks. The key difference lies in the specific materials involved and the distinct regulatory requirements targeting their unique health impacts during real estate transactions.
Federal vs State Laws: Disclosure Mandates Explained
Federal laws mandate Lead-Based Paint Disclosure for properties built before 1978, requiring sellers and landlords to inform buyers or tenants about known lead hazards, while asbestos disclosure regulations vary significantly by state, with no comprehensive federal mandate requiring sellers to disclose asbestos presence. State laws may impose stricter or additional disclosure requirements for asbestos in real estate transactions, reflecting local public health priorities and regulatory frameworks. Understanding the interplay between federal lead disclosure mandates and diverse state asbestos disclosure rules is crucial for compliance in real estate transactions involving older properties.
Buyer and Seller Responsibilities in Hazard Disclosure
Buyers and sellers must understand that Lead-Based Paint Disclosure is federally mandated for homes built before 1978, requiring sellers to provide buyers with the EPA's lead hazard information pamphlet and disclose any known lead-based paint hazards. Asbestos Disclosure, often governed by state or local regulations, obligates sellers to inform buyers about the presence of asbestos-containing materials if known, especially in older properties where asbestos use was common. Both disclosures aim to protect buyers by ensuring transparency about environmental hazards, while sellers are responsible for providing accurate information and allowing inspections to assess potential risks.
Health Risks: Lead-Based Paint vs Asbestos Exposure
Lead-based paint exposure primarily risks cognitive impairment and developmental delays in children, along with hypertension and kidney damage in adults. Asbestos exposure significantly increases the likelihood of severe respiratory diseases, including asbestosis, lung cancer, and mesothelioma. Both disclosures are critical in real estate transactions to inform buyers of potential long-term health hazards linked to property materials.
Impact on Property Value and Transaction Process
Lead-based paint disclosure is critical for properties built before 1978, directly affecting transaction timelines and buyer confidence due to health risk concerns, often necessitating remediation that impacts property value. Asbestos disclosure, commonly required for older properties or those with specific materials, can trigger costly inspections and abatement procedures, which may delay closings and lower market value. Both disclosures serve to protect buyers but impose legal obligations that can influence negotiation dynamics and final sale prices in real estate transactions.
Inspection and Testing Protocols for Lead and Asbestos
Lead-based paint inspection protocols require certified professionals to conduct visual assessments followed by laboratory analysis of paint samples or use of X-ray fluorescence (XRF) devices to detect lead hazards. Asbestos inspection mandates hiring licensed inspectors to perform bulk sampling of suspect materials, with samples analyzed in accredited laboratories to determine fiber content and risk levels. Both disclosures emphasize thorough, regulated testing procedures to ensure accurate identification of health hazards before property transactions.
Best Practices for Real Estate Professionals Handling Disclosures
Real estate professionals must ensure compliance with federal laws by providing accurate Lead-Based Paint Disclosure for properties built before 1978 and Asbestos Disclosure when applicable, prioritizing buyer safety and legal transparency. Implementing thorough property inspections and maintaining updated disclosure documentation minimizes liability risks and strengthens buyer trust. Clear communication of potential hazards, coupled with professional guidance on remediation, fosters informed decision-making in real estate transactions.
Lead-Based Paint Disclosure vs Asbestos Disclosure Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com