Due diligence in real estate involves a thorough investigation of the property's condition, legal status, and financial aspects before finalizing the purchase, ensuring buyers make informed decisions. The contingency period is a specified timeframe within the contract during which buyers can terminate the deal without penalty if certain conditions, such as inspections or financing approvals, are not met. Understanding the distinctions between due diligence and the contingency period helps buyers protect their interests and avoid costly surprises.
Table of Comparison
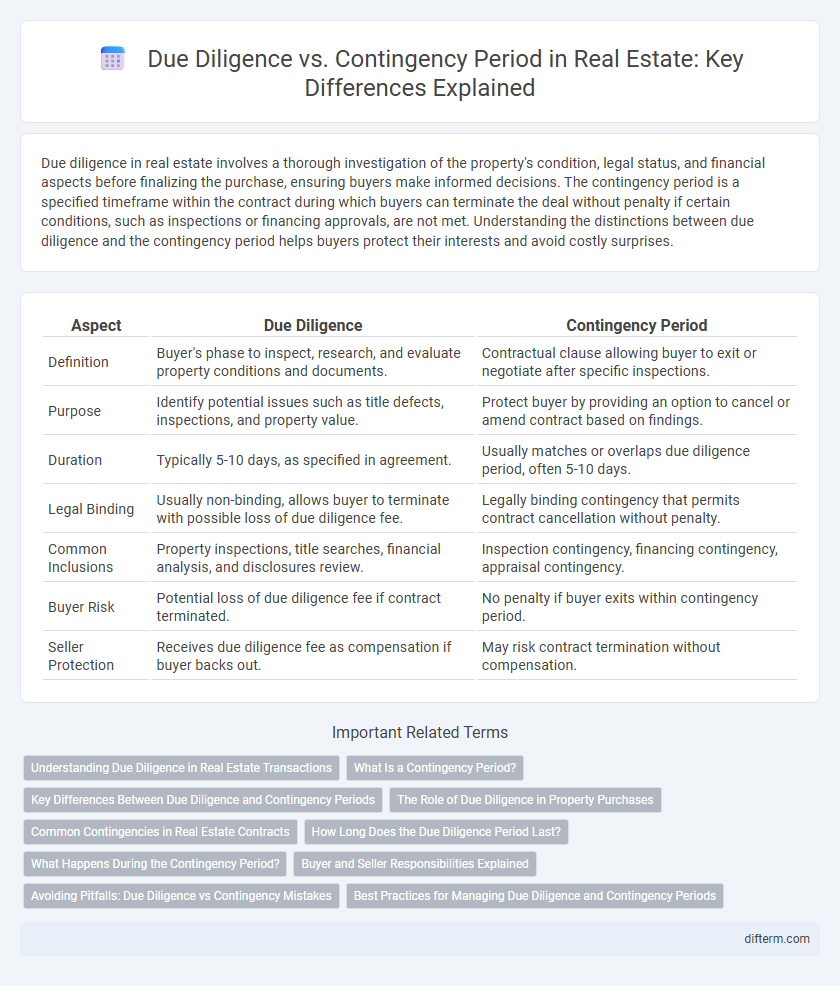
| Aspect | Due Diligence | Contingency Period |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buyer's phase to inspect, research, and evaluate property conditions and documents. | Contractual clause allowing buyer to exit or negotiate after specific inspections. |
| Purpose | Identify potential issues such as title defects, inspections, and property value. | Protect buyer by providing an option to cancel or amend contract based on findings. |
| Duration | Typically 5-10 days, as specified in agreement. | Usually matches or overlaps due diligence period, often 5-10 days. |
| Legal Binding | Usually non-binding, allows buyer to terminate with possible loss of due diligence fee. | Legally binding contingency that permits contract cancellation without penalty. |
| Common Inclusions | Property inspections, title searches, financial analysis, and disclosures review. | Inspection contingency, financing contingency, appraisal contingency. |
| Buyer Risk | Potential loss of due diligence fee if contract terminated. | No penalty if buyer exits within contingency period. |
| Seller Protection | Receives due diligence fee as compensation if buyer backs out. | May risk contract termination without compensation. |
Understanding Due Diligence in Real Estate Transactions
Due diligence in real estate transactions involves a comprehensive investigation to verify property details, assess potential risks, and ensure compliance with legal and financial requirements before finalizing the purchase. This process includes property inspections, title searches, reviewing zoning laws, and evaluating environmental hazards to protect buyers from unforeseen liabilities. Understanding due diligence helps investors make informed decisions and negotiate favorable contract terms during the contingency period.
What Is a Contingency Period?
A contingency period in real estate is a specified timeframe within a purchase contract allowing buyers to conduct inspections, secure financing, and verify property details before finalizing the sale. This period protects buyers by enabling contract termination without penalty if contingencies are unmet. Common contingencies include home inspection, appraisal, and mortgage approval, safeguarding the buyer's interests during the transaction.
Key Differences Between Due Diligence and Contingency Periods
Due diligence in real estate refers to the comprehensive investigation buyers perform to verify property details, including inspections, title searches, and financial assessments before finalizing a purchase. The contingency period is a contractual timeframe allowing buyers to back out or renegotiate based on findings within due diligence, typically linked to financing, inspection, or appraisal outcomes. Key differences lie in due diligence being an active investigation process, while the contingency period serves as a legally binding option for decision-making based on that investigation's results.
The Role of Due Diligence in Property Purchases
Due diligence in property purchases involves a comprehensive investigation of a real estate asset's condition, legal status, and market value to identify potential risks before finalizing the transaction. This process typically includes property inspections, title searches, zoning verification, and review of financial documents to ensure informed decision-making. The due diligence period differs from the contingency period by emphasizing verification and risk assessment, helping buyers avoid costly surprises and negotiate repairs or price adjustments.
Common Contingencies in Real Estate Contracts
Common contingencies in real estate contracts include financing, home inspection, and appraisal contingencies, which protect buyers by allowing contract termination or renegotiation if issues arise during the contingency period. Due diligence involves a thorough investigation of the property's condition, title, and legal status before finalizing the sale. These contingencies establish clear conditions that must be met within the contingency period, ensuring both parties have an opportunity to address unforeseen problems without risking the transaction.
How Long Does the Due Diligence Period Last?
The due diligence period in real estate typically lasts between 7 to 14 days, depending on the terms agreed upon in the purchase contract. During this timeframe, buyers conduct inspections, appraisals, and review property documents to uncover any potential issues. The duration can vary by state and specific agreement, but it is generally shorter than the contingency period, which may extend up to 30 days or more.
What Happens During the Contingency Period?
During the contingency period in real estate transactions, buyers conduct essential inspections, secure financing approvals, and verify property conditions to ensure the investment meets their expectations. This phase allows buyers to request repairs or negotiate terms based on inspection results while maintaining the right to withdraw without penalty if contingencies are unmet. The thorough evaluation during this period protects both parties by confirming property status and financial feasibility before finalizing the sale.
Buyer and Seller Responsibilities Explained
During the due diligence period, buyers thoroughly inspect the property, review documents, and assess potential issues to make informed decisions, while sellers must provide full disclosure and access to information. The contingency period typically allows buyers to negotiate repairs or back out based on findings without penalty, shifting the obligation to sellers to address agreed-upon concerns or accept contract termination. Clear understanding of these phases ensures both parties protect their interests and comply with contractual deadlines.
Avoiding Pitfalls: Due Diligence vs Contingency Mistakes
Avoiding pitfalls in real estate requires a clear understanding of the differences between the due diligence and contingency periods. Due diligence involves thorough property inspections, title searches, and reviewing disclosures to uncover potential issues before finalizing the contract. Mistaking the contingency period--typically the timeframe to negotiate or cancel based on financing, appraisal, or inspections--as an extension of due diligence can lead to missed deadlines and costly legal disputes.
Best Practices for Managing Due Diligence and Contingency Periods
Effective management of due diligence and contingency periods in real estate transactions requires thorough documentation review, including title reports, inspection results, and financing approvals to mitigate risks. Establishing clear timelines and communication protocols between buyers, sellers, and agents ensures all parties meet contractual obligations promptly. Leveraging technology for tracking deadlines and automating reminders enhances transparency and reduces the likelihood of missed contingencies, protecting client interests.
Due Diligence vs Contingency Period Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com