A high savings rate provides the necessary capital for increased investment, fueling economic growth and enhancing productivity. When the investment rate surpasses the savings rate, economies may rely on foreign capital, risking debt accumulation and financial instability. Balancing savings and investment rates is crucial for sustainable development and maintaining long-term economic resilience.
Table of Comparison
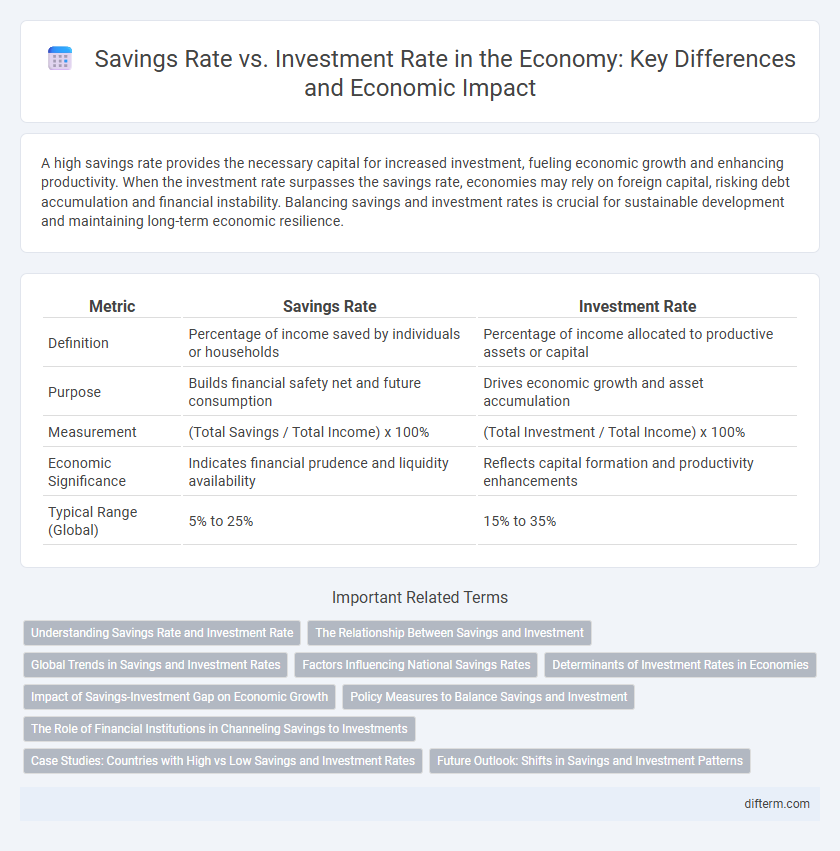
| Metric | Savings Rate | Investment Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Percentage of income saved by individuals or households | Percentage of income allocated to productive assets or capital |
| Purpose | Builds financial safety net and future consumption | Drives economic growth and asset accumulation |
| Measurement | (Total Savings / Total Income) x 100% | (Total Investment / Total Income) x 100% |
| Economic Significance | Indicates financial prudence and liquidity availability | Reflects capital formation and productivity enhancements |
| Typical Range (Global) | 5% to 25% | 15% to 35% |
Understanding Savings Rate and Investment Rate
The savings rate represents the proportion of income that households set aside rather than spend, serving as a critical indicator of an economy's financial health and future consumption potential. In contrast, the investment rate measures the share of GDP dedicated to capital formation, infrastructure, and technological advancement, driving economic growth and productivity improvements. Analyzing the balance between the savings rate and investment rate helps economists assess whether an economy is efficiently channeling resources into productive uses to sustain long-term growth.
The Relationship Between Savings and Investment
The savings rate directly influences the investment rate by supplying the necessary capital for productive assets, fueling economic growth. When households and businesses save more, financial institutions have greater funds available to lend for investments in infrastructure, technology, and business expansion. A balanced increase in savings and investment rates ensures sustainable development by aligning capital accumulation with productive use.
Global Trends in Savings and Investment Rates
Global savings rates have shown significant variation, with emerging economies often exhibiting higher savings rates compared to developed countries due to differing income levels and consumption patterns. Investment rates tend to correlate with savings rates, as countries with higher savings provide more capital for domestic investment, driving economic growth. Recent trends indicate a gradual decline in savings rates in developed nations alongside a steady rise in investment in technology and infrastructure sectors globally.
Factors Influencing National Savings Rates
National savings rates are influenced by factors such as income levels, interest rates, and government fiscal policies, which determine the disposable income available for saving. Demographic trends like aging populations and employment stability also impact household saving behavior and overall national savings. Furthermore, cultural attitudes toward consumption and future planning shape how much income is allocated to savings versus immediate expenditure.
Determinants of Investment Rates in Economies
Investment rates in economies are primarily determined by factors such as interest rates, government policies, and the level of economic stability. High savings rates provide the capital necessary for investment, but efficient financial markets and investor confidence significantly influence the actual investment rate. Access to credit, technological innovation, and infrastructure development also play crucial roles in facilitating higher investment levels.
Impact of Savings-Investment Gap on Economic Growth
A persistent savings-investment gap can constrain economic growth by limiting the capital available for productive investments necessary for expanding output and improving infrastructure. When national savings fall short of investment needs, economies often rely on external borrowing, which may increase vulnerability to financial instability and reduce long-term growth prospects. Closing the savings-investment gap through policies that encourage domestic savings and efficient allocation of capital is crucial for sustainable economic development and enhanced competitiveness.
Policy Measures to Balance Savings and Investment
Policy measures to balance savings and investment often include adjusting interest rates to incentivize consumption or savings, thereby influencing capital availability for investment. Governments may implement tax incentives or subsidies to encourage private sector investment while promoting household savings through retirement plans or savings accounts. Effective coordination of fiscal and monetary policies ensures a stable macroeconomic environment, optimizing the equilibrium between aggregate savings and investment rates for sustainable economic growth.
The Role of Financial Institutions in Channeling Savings to Investments
Financial institutions play a crucial role in channeling high household savings rates into productive investments by efficiently mobilizing and allocating funds. They reduce transaction costs and asymmetric information, facilitating the transformation of individual savings into capital for businesses, infrastructure, and innovation. This effective intermediation boosts economic growth by bridging the gap between savers and investors, enhancing overall financial stability.
Case Studies: Countries with High vs Low Savings and Investment Rates
Countries like China and Germany exhibit high savings and investment rates, driving robust economic growth through substantial capital formation and infrastructure development. In contrast, nations such as the United States and Brazil demonstrate lower savings rates, which often correspond with higher reliance on foreign capital and less predictable investment dynamics. These case studies highlight the critical role of domestic savings in sustaining long-term investment and economic stability.
Future Outlook: Shifts in Savings and Investment Patterns
Future outlooks highlight evolving savings and investment patterns driven by technological advancements and demographic changes. Increasing household savings rates in aging populations contrast with higher corporate investment rates fueled by innovation-driven economies. These shifts suggest a dynamic balance between capital accumulation and consumption, impacting long-term economic growth trajectories.
Savings rate vs Investment rate Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com