Microcredit specifically targets small loans to low-income individuals or entrepreneurs who lack access to traditional banking services, enabling them to start or expand businesses. Microfinance encompasses a broader range of financial services, including savings, insurance, and payment systems, aimed at improving financial inclusion for underserved populations. By offering diverse financial tools, microfinance helps build economic resilience and reduce poverty more effectively than microcredit alone.
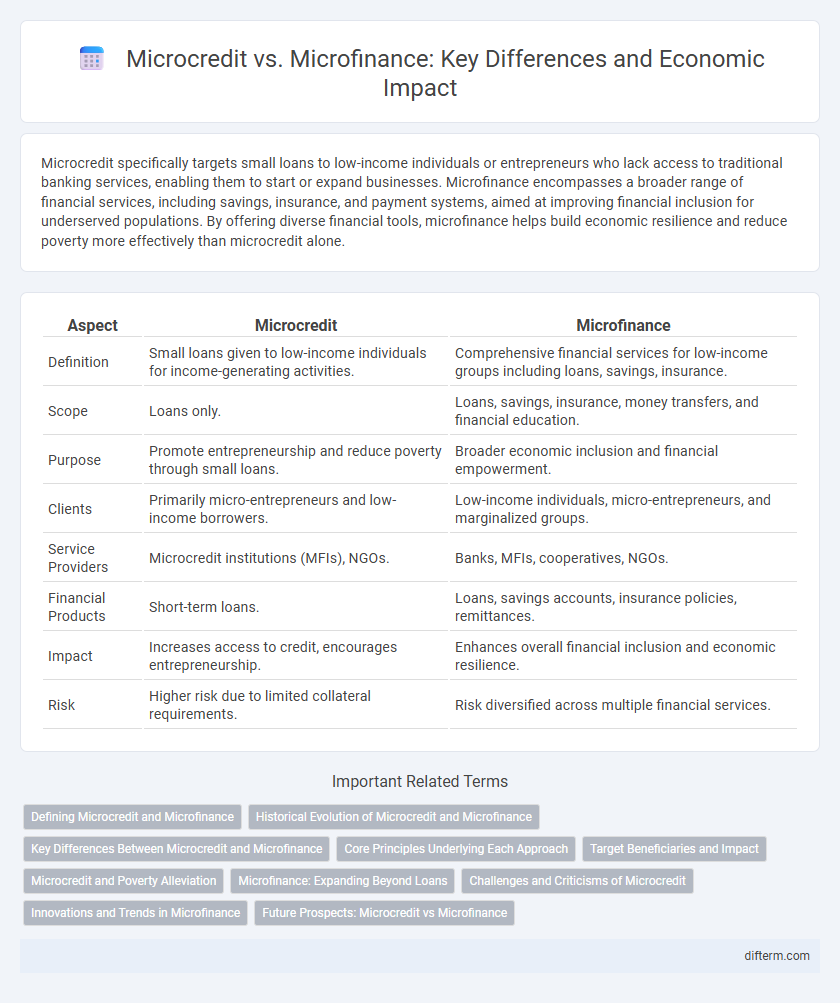
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Microcredit | Microfinance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small loans given to low-income individuals for income-generating activities. | Comprehensive financial services for low-income groups including loans, savings, insurance. |
| Scope | Loans only. | Loans, savings, insurance, money transfers, and financial education. |
| Purpose | Promote entrepreneurship and reduce poverty through small loans. | Broader economic inclusion and financial empowerment. |
| Clients | Primarily micro-entrepreneurs and low-income borrowers. | Low-income individuals, micro-entrepreneurs, and marginalized groups. |
| Service Providers | Microcredit institutions (MFIs), NGOs. | Banks, MFIs, cooperatives, NGOs. |
| Financial Products | Short-term loans. | Loans, savings accounts, insurance policies, remittances. |
| Impact | Increases access to credit, encourages entrepreneurship. | Enhances overall financial inclusion and economic resilience. |
| Risk | Higher risk due to limited collateral requirements. | Risk diversified across multiple financial services. |
Defining Microcredit and Microfinance
Microcredit refers to small loans provided to low-income individuals or entrepreneurs lacking access to traditional banking services, enabling them to start or expand small businesses. Microfinance encompasses a broader range of financial services, including microcredit, savings, insurance, and payment systems, aimed at improving financial inclusion for underserved populations. Both concepts play crucial roles in poverty alleviation and economic development by empowering marginalized communities with essential financial tools.
Historical Evolution of Microcredit and Microfinance
Microcredit originated in the 1970s with Muhammad Yunus's pioneering efforts in Bangladesh, focusing on small loans to empower impoverished entrepreneurs. Microfinance expanded in the 1980s to include a broader range of financial services such as savings, insurance, and remittances, targeting low-income populations globally. This evolution reflects a shift from solely providing credit to fostering comprehensive financial inclusion and economic development.
Key Differences Between Microcredit and Microfinance
Microcredit primarily involves small loans provided to low-income individuals or groups to start or expand microenterprises. Microfinance encompasses a broader range of financial services, including savings, insurance, and credit, aimed at improving financial inclusion for underserved populations. The key difference lies in microcredit's focus on lending, whereas microfinance integrates multiple financial products to support economic empowerment and poverty reduction.
Core Principles Underlying Each Approach
Microcredit centers on providing small loans to low-income entrepreneurs to foster self-employment and income generation, emphasizing financial inclusion and credit accessibility. Microfinance encompasses a broader spectrum of financial services including savings, insurance, and payment systems, aimed at improving overall economic stability and reducing vulnerability among underserved populations. Both models prioritize empowerment and poverty alleviation but differ in scope, with microcredit focusing narrowly on lending and microfinance integrating diverse financial support mechanisms.
Target Beneficiaries and Impact
Microcredit primarily targets low-income individuals and small entrepreneurs who lack access to traditional banking services, providing small loans to support income-generating activities. Microfinance encompasses a broader range of financial services--including savings, insurance, and credit--aimed at improving overall financial inclusion for marginalized populations. Both microcredit and microfinance significantly contribute to poverty alleviation and economic empowerment, but microfinance's comprehensive approach leads to more sustainable and diversified impacts on community development.
Microcredit and Poverty Alleviation
Microcredit involves providing small loans to low-income individuals or groups, enabling them to start or expand small businesses and improve their earnings. This targeted financial support plays a crucial role in poverty alleviation by increasing financial inclusion and promoting entrepreneurial activities in underserved communities. Access to microcredit empowers borrowers to generate sustainable income, reduce vulnerability to economic shocks, and enhance overall living standards.
Microfinance: Expanding Beyond Loans
Microfinance extends beyond microcredit by offering a diverse range of financial services, including savings, insurance, and money transfers, tailored to low-income individuals. This holistic approach empowers underserved communities by fostering financial inclusion and promoting sustainable economic development. By addressing multiple financial needs, microfinance facilitates long-term economic resilience and entrepreneurship.
Challenges and Criticisms of Microcredit
Microcredit faces significant challenges including high interest rates, which can exacerbate debt cycles among low-income borrowers, and limited access for the poorest populations due to strict lending criteria. Critics argue that microcredit often prioritizes financial sustainability over social impact, leading to insufficient support for business development and poverty alleviation. Furthermore, inadequate consumer protection and lack of regulatory oversight contribute to cases of borrower exploitation and over-indebtedness within microcredit systems.
Innovations and Trends in Microfinance
Innovations in microfinance increasingly leverage digital platforms and blockchain technology to enhance transparency and accessibility, driving financial inclusion for underserved populations. Trends show a shift towards integrating artificial intelligence for credit scoring and personalized financial products, reducing risk and improving loan approval rates. Microcredit, as a subset, benefits from these advancements by offering more flexible repayment options and tailored small loans, supporting entrepreneurial growth in emerging markets.
Future Prospects: Microcredit vs Microfinance
Microcredit is expected to evolve with greater integration of digital platforms, enhancing accessibility for underserved populations through mobile banking and AI-driven credit scoring. Microfinance, with its broader scope including savings, insurance, and financial literacy, will likely expand by incorporating sustainable financial products that support long-term economic resilience. Future prospects for both emphasize leveraging technology to improve financial inclusion and empower low-income entrepreneurs globally.
Microcredit vs Microfinance Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com