Pushrod engines feature a camshaft located inside the engine block, using pushrods to actuate the valves, resulting in a more compact design often favored for low-end torque and durability. Overhead cam (OHC) engines place the camshaft directly above the valves, enabling higher engine speeds and improved efficiency thanks to reduced valvetrain mass and more precise valve timing. While pushrod engines excel in simplicity and ruggedness, overhead cam engines deliver better performance and fuel economy, making them popular in modern automotive applications.
Table of Comparison
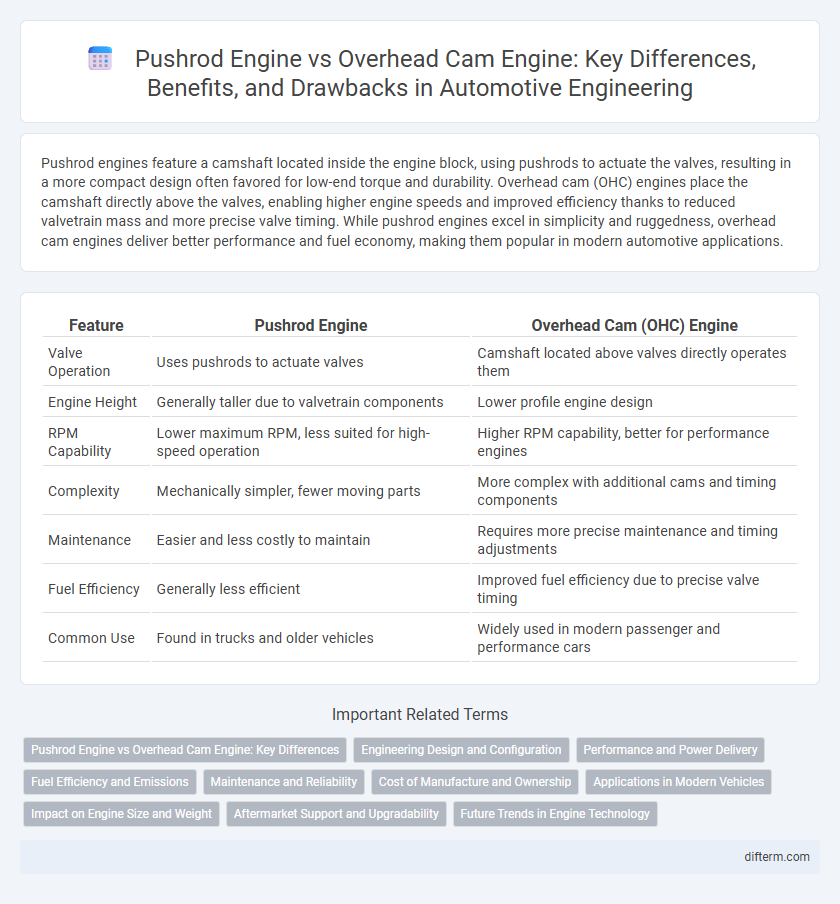
| Feature | Pushrod Engine | Overhead Cam (OHC) Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Valve Operation | Uses pushrods to actuate valves | Camshaft located above valves directly operates them |
| Engine Height | Generally taller due to valvetrain components | Lower profile engine design |
| RPM Capability | Lower maximum RPM, less suited for high-speed operation | Higher RPM capability, better for performance engines |
| Complexity | Mechanically simpler, fewer moving parts | More complex with additional cams and timing components |
| Maintenance | Easier and less costly to maintain | Requires more precise maintenance and timing adjustments |
| Fuel Efficiency | Generally less efficient | Improved fuel efficiency due to precise valve timing |
| Common Use | Found in trucks and older vehicles | Widely used in modern passenger and performance cars |
Pushrod Engine vs Overhead Cam Engine: Key Differences
Pushrod engines feature a camshaft located within the engine block that actuates the valves through pushrods and rocker arms, offering a compact design ideal for lower-revving applications and increased low-end torque. Overhead camshaft (OHC) engines position the camshaft directly above the valves in the cylinder head, enabling more precise valve timing, higher RPM capabilities, and improved fuel efficiency due to reduced valvetrain mass and complexity. The key differences lie in valvetrain layout, engine height, performance potential, and maintenance complexity, influencing choices between durability and high-performance tuning.
Engineering Design and Configuration
Pushrod engines employ a simpler valvetrain design with camshafts located within the engine block, utilizing pushrods to operate the valves, resulting in a compact and lower engine height. Overhead cam (OHC) engines position the camshafts directly above the cylinder head, enabling more precise valve timing, higher engine speeds, and improved airflow efficiency through reduced valvetrain mass and complexity. The OHC configuration supports advanced technologies such as variable valve timing, enhancing performance and fuel efficiency compared to the traditional pushrod layout.
Performance and Power Delivery
Pushrod engines deliver robust low-end torque due to their shorter valvetrain and reduced reciprocating mass, enhancing off-the-line acceleration and drivability in heavy vehicles. Overhead cam (OHC) engines provide superior high-RPM power and efficiency by allowing precise valve timing and increased airflow, contributing to better top-end performance and fuel economy. The choice between pushrod and OHC designs significantly impacts engine responsiveness and power delivery characteristics in automotive applications.
Fuel Efficiency and Emissions
Pushrod engines generally offer lower fuel efficiency compared to overhead cam engines due to increased valvetrain mass and less precise valve timing control. Overhead cam engines optimize combustion processes with higher valve timing accuracy, resulting in reduced emissions and improved fuel economy. As a result, overhead cam designs are preferred in modern vehicles targeting stringent emission standards and better mileage.
Maintenance and Reliability
Pushrod engines feature fewer moving parts and simpler valve train geometry, leading to lower maintenance costs and enhanced long-term reliability compared to overhead cam engines. Overhead cam engines often require more frequent timing belt or chain replacements and precise valve adjustments, increasing maintenance complexity and expense. The robust design of pushrod engines typically results in better durability under harsh operating conditions, favored in heavy-duty automotive applications.
Cost of Manufacture and Ownership
Pushrod engines typically offer lower manufacturing costs due to their simpler design and fewer moving parts compared to overhead cam (OHC) engines, which require more precision machining and additional components. Ownership expenses are also generally reduced with pushrod engines because of their easier maintenance and repairs, as well as longer-lasting valve train components. However, OHC engines may provide better fuel efficiency and performance, potentially offsetting initial higher manufacturing and ownership costs over time.
Applications in Modern Vehicles
Pushrod engines, known for their compact design and durability, are commonly found in American muscle cars, trucks, and SUVs where low-end torque and simplicity are prioritized. Overhead cam (OHC) engines dominate in modern passenger cars and performance vehicles due to their superior efficiency, higher RPM capabilities, and reduced valve train inertia. Hybrid and electric vehicles increasingly favor OHC or camless technologies to optimize fuel economy and emissions while meeting stringent regulatory standards.
Impact on Engine Size and Weight
Pushrod engines generally feature a more compact design with fewer components above the cylinder head, resulting in a smaller overall engine size and reduced weight compared to overhead cam engines. Overhead cam engines require additional camshaft assemblies positioned above the valves, which increases complexity and adds to the engine's height and weight. This size and weight difference can influence vehicle design, affecting factors such as center of gravity, chassis integration, and fuel efficiency.
Aftermarket Support and Upgradability
Pushrod engines benefit from extensive aftermarket support due to their simpler design and widespread use in classic American muscle cars, allowing for a broad range of cost-effective performance upgrades. Overhead cam engines feature more complex valve train components, which can offer higher RPM potential but often come with fewer affordable aftermarket parts and more challenging modifications. Enthusiasts seeking extensive, budget-friendly upgrade paths typically prefer pushrod engines, while those pursuing precision tuning and modern performance may lean toward overhead cam designs despite higher costs.
Future Trends in Engine Technology
Pushrod engines are increasingly limited by their lower RPM capabilities and less precise valve timing compared to overhead cam (OHC) engines, which are gaining traction due to advanced variable valve timing and direct injection compatibility. Future trends in automotive engine technology emphasize OHC designs integrated with electric turbocharging and hybrid systems to boost efficiency and reduce emissions. Innovations in material science and digital engine management further enhance OHC engine performance, making them the preferred choice for next-generation internal combustion engines.
pushrod engine vs overhead cam engine Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com