The axle ratio determines how many times the driveshaft rotates for each turn of the wheels, directly impacting torque and acceleration. The final drive ratio combines the axle ratio with the gear ratio from the transmission, influencing overall vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. Understanding the distinction helps optimize power delivery and handling characteristics in automotive applications.
Table of Comparison
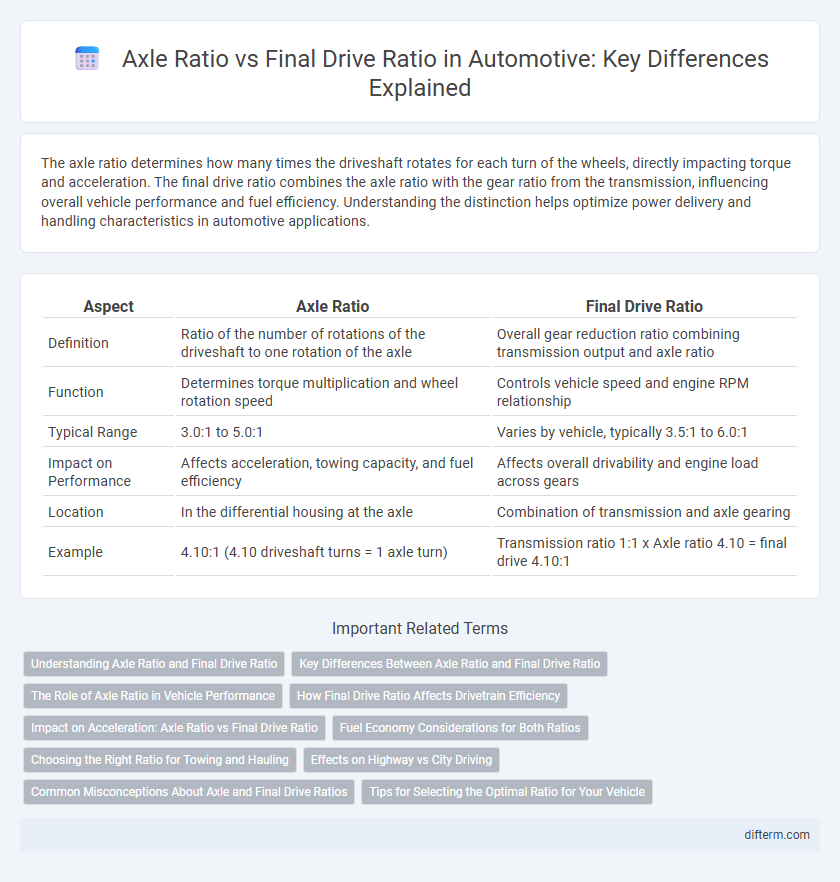
| Aspect | Axle Ratio | Final Drive Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ratio of the number of rotations of the driveshaft to one rotation of the axle | Overall gear reduction ratio combining transmission output and axle ratio |
| Function | Determines torque multiplication and wheel rotation speed | Controls vehicle speed and engine RPM relationship |
| Typical Range | 3.0:1 to 5.0:1 | Varies by vehicle, typically 3.5:1 to 6.0:1 |
| Impact on Performance | Affects acceleration, towing capacity, and fuel efficiency | Affects overall drivability and engine load across gears |
| Location | In the differential housing at the axle | Combination of transmission and axle gearing |
| Example | 4.10:1 (4.10 driveshaft turns = 1 axle turn) | Transmission ratio 1:1 x Axle ratio 4.10 = final drive 4.10:1 |
Understanding Axle Ratio and Final Drive Ratio
Axle ratio refers to the number of rotations the driveshaft makes for each turn of the wheels, directly impacting vehicle acceleration and fuel efficiency by determining torque distribution. The final drive ratio is the last gear reduction in the drivetrain, often housed in the differential, affecting power delivery and engine RPM at a given speed. Understanding the relationship between axle ratio and final drive ratio is critical for optimizing performance, towing capacity, and overall drivetrain efficiency in automotive engineering.
Key Differences Between Axle Ratio and Final Drive Ratio
Axle ratio refers to the ratio of the number of teeth on the ring gear to the number of teeth on the pinion gear within the axle assembly, directly impacting torque delivery to the wheels. Final drive ratio encompasses the overall gear reduction from the transmission output to the wheels, including the axle ratio and any additional gearing in the drivetrain. Key differences lie in scope: axle ratio specifically describes the rear or front axle gearing, while final drive ratio accounts for total gear reduction affecting acceleration, fuel efficiency, and overall vehicle performance.
The Role of Axle Ratio in Vehicle Performance
The axle ratio, defined as the number of revolutions the driveshaft makes to turn the wheels once, directly influences torque multiplication and vehicle acceleration. A higher axle ratio improves low-end power and towing capability by increasing torque delivered to the wheels, while a lower axle ratio enhances fuel efficiency and top speed by reducing engine RPM at highway speeds. Understanding the distinction between the axle ratio and final drive ratio is crucial for optimizing a vehicle's performance characteristics in specific driving conditions.
How Final Drive Ratio Affects Drivetrain Efficiency
The final drive ratio directly influences drivetrain efficiency by determining the torque multiplication and engine RPM required to turn the wheels, with a higher ratio increasing torque but potentially decreasing fuel economy due to higher engine speeds. An optimized final drive ratio balances power delivery and rotational speed, reducing energy losses in the differential and transmission components. Precise calibration of the axle ratio within the final drive system enhances overall vehicle performance by improving acceleration without significantly compromising highway fuel efficiency.
Impact on Acceleration: Axle Ratio vs Final Drive Ratio
Axle ratio and final drive ratio both influence vehicle acceleration by determining torque multiplication delivered to the wheels. A higher axle ratio increases torque at the wheels, enhancing acceleration but reducing fuel efficiency, while a lower ratio favors fuel economy at the expense of quicker acceleration. Understanding the balance between axle ratio and final drive ratio helps optimize performance for specific driving needs in automotive design.
Fuel Economy Considerations for Both Ratios
Axle ratio and final drive ratio significantly impact vehicle fuel economy by influencing engine load and speed. A lower axle ratio reduces engine RPM at highway speeds, improving fuel efficiency by minimizing fuel consumption, while a higher ratio enhances acceleration but increases fuel use. Optimizing these ratios balances power delivery and fuel savings, crucial for both passenger cars and commercial trucks.
Choosing the Right Ratio for Towing and Hauling
Selecting the ideal axle ratio and final drive ratio is crucial for maximizing towing and hauling performance in automotive applications. Higher axle ratios provide increased torque multiplication, enhancing pulling power and control under heavy loads, while lower ratios offer better fuel efficiency and smoother highway driving. Properly balancing these ratios ensures optimal drivetrain efficiency, improved vehicle durability, and safer heavy-duty operation.
Effects on Highway vs City Driving
Axle ratio and final drive ratio critically influence vehicle performance, with higher ratios enhancing acceleration and torque for city driving, while lower ratios optimize fuel efficiency and engine RPM at highway speeds. A higher axle ratio results in quicker throttle response and better hill climbing ability in urban stop-and-go traffic, but increases engine revolutions per mile, reducing fuel economy on highways. Conversely, a lower final drive ratio lowers engine RPM during sustained highway cruising, improving mileage but offering less immediate power for city acceleration.
Common Misconceptions About Axle and Final Drive Ratios
Axle ratio and final drive ratio are often mistakenly used interchangeably, but the axle ratio specifically refers to the ratio between the ring and pinion gears in the differential, while the final drive ratio accounts for the entire drivetrain including the transmission output. Many automotive enthusiasts confuse final drive ratio with the gear ratio in a particular transmission gear, neglecting that the final drive ratio impacts overall vehicle performance and fuel efficiency by altering torque multiplication. Understanding the distinct roles of axle and final drive ratios is critical for optimizing vehicle acceleration, towing capacity, and engine load management.
Tips for Selecting the Optimal Ratio for Your Vehicle
Selecting the optimal axle ratio or final drive ratio for your vehicle depends on balancing performance, fuel efficiency, and towing capacity. A lower axle ratio (numerically higher) provides better acceleration and towing power, ideal for trucks and off-road vehicles, while a higher ratio (numerically lower) improves fuel economy and highway driving stability. Consider your primary driving conditions and consult manufacturer specifications to match the gear ratio with engine torque and transmission type, ensuring optimal drivetrain performance.
axle ratio vs final drive ratio Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com