OEM automotive parts guarantee precise compatibility and maintain the vehicle's original performance standards, ensuring reliability and safety. Aftermarket parts often offer a wider range of options at lower prices, but quality and fitment can vary significantly. Choosing between OEM and aftermarket depends on balancing cost, performance, and warranty considerations.
Table of Comparison
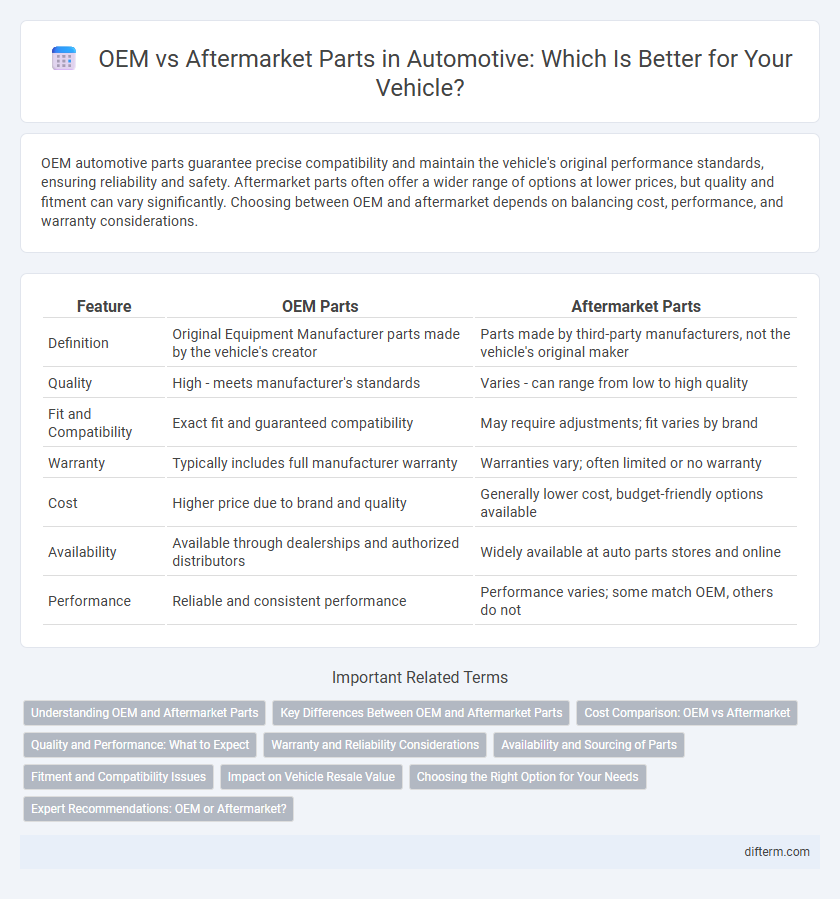
| Feature | OEM Parts | Aftermarket Parts |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Original Equipment Manufacturer parts made by the vehicle's creator | Parts made by third-party manufacturers, not the vehicle's original maker |
| Quality | High - meets manufacturer's standards | Varies - can range from low to high quality |
| Fit and Compatibility | Exact fit and guaranteed compatibility | May require adjustments; fit varies by brand |
| Warranty | Typically includes full manufacturer warranty | Warranties vary; often limited or no warranty |
| Cost | Higher price due to brand and quality | Generally lower cost, budget-friendly options available |
| Availability | Available through dealerships and authorized distributors | Widely available at auto parts stores and online |
| Performance | Reliable and consistent performance | Performance varies; some match OEM, others do not |
Understanding OEM and Aftermarket Parts
OEM parts are manufactured by the original vehicle maker, ensuring exact fit, quality, and compatibility with specific car models. Aftermarket parts are produced by third-party companies, often offering a wider range of options, competitive pricing, and sometimes enhanced performance features. Understanding the differences helps consumers make informed decisions based on reliability, cost-effectiveness, and warranty considerations.
Key Differences Between OEM and Aftermarket Parts
OEM parts are manufactured by the original vehicle maker, ensuring exact fit, quality, and warranty coverage, aligning with the specific design and performance standards of the vehicle. Aftermarket parts are produced by third-party companies and often offer greater variety and cost-efficiency but may vary in quality, fit, and performance reliability. Choosing between OEM and aftermarket parts depends on factors such as budget, intended use, and vehicle maintenance priorities, with OEM favored for guaranteed compatibility and aftermarket popular for customization and affordability.
Cost Comparison: OEM vs Aftermarket
OEM automotive parts typically cost more due to higher manufacturing standards, brand guarantees, and direct compatibility with specific vehicle models. Aftermarket parts offer a cost-effective alternative, often priced 20-40% lower, but may vary in quality and fit, impacting long-term vehicle performance. Choosing between OEM and aftermarket parts depends on budget priorities and the importance of maintaining factory specifications.
Quality and Performance: What to Expect
OEM parts are engineered to meet the exact specifications and standards set by the vehicle manufacturer, ensuring optimal quality and consistent performance. Aftermarket parts vary widely in quality, with some offering comparable or enhanced performance, while others may fall short of OEM standards. Choosing OEM guarantees compatibility and reliability, whereas aftermarket options require careful evaluation to balance cost savings against potential differences in durability and functionality.
Warranty and Reliability Considerations
OEM parts typically offer superior warranty coverage and are designed to meet or exceed original vehicle specifications, ensuring optimal reliability and compatibility. Aftermarket parts may have varying warranty terms and can differ in quality, potentially affecting long-term performance and vehicle integrity. Choosing OEM components often reduces the risk of voiding manufacturer warranties and ensures consistent reliability across repairs.
Availability and Sourcing of Parts
OEM parts are sourced directly from the vehicle manufacturer, ensuring exact fit and original specifications, but availability may be limited to authorized dealers and can involve longer wait times. Aftermarket parts offer wider availability through multiple suppliers and quicker access, often at lower prices, though quality and compatibility can vary significantly. Sourcing strategies for OEM parts emphasize brand reliability and warranty coverage, while aftermarket sourcing prioritizes cost efficiency and broader market reach.
Fitment and Compatibility Issues
OEM parts guarantee precise fitment and compatibility as they are manufactured to original specifications, ensuring optimal performance and safety for vehicles. Aftermarket parts vary widely in quality and adherence to design standards, often leading to fitment issues such as improper alignment or interference with existing components. Compatibility problems with aftermarket components can result in increased wear, potential damage, and voided warranties, emphasizing the importance of selecting parts that match OEM criteria.
Impact on Vehicle Resale Value
OEM parts maintain vehicle integrity with precise fit and manufacturer-approved quality, preserving the original condition and potentially enhancing resale value. Aftermarket parts offer cost-effective alternatives but may vary in quality and compatibility, possibly raising concerns among buyers and reducing resale appeal. Choosing OEM components supports vehicle authenticity, which is a critical factor for maintaining higher resale prices in the automotive market.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Needs
Selecting between OEM and aftermarket automotive parts depends on factors such as quality, cost, and compatibility. OEM parts guarantee exact fit and manufacturer standards, ensuring optimal vehicle performance and warranty compliance. Aftermarket components offer budget-friendly alternatives with diverse options but may vary in durability and precision, making it essential to assess specific vehicle requirements and usage before deciding.
Expert Recommendations: OEM or Aftermarket?
Expert recommendations typically favor OEM parts for ensuring optimal compatibility, reliability, and warranty protection in automotive repairs. Aftermarket parts can offer cost savings and a wider selection but often vary significantly in quality and fit, affecting vehicle performance and safety. Technicians advise choosing OEM components for critical systems like brakes and engine parts, while aftermarket options may be suitable for non-essential accessories.
OEM vs aftermarket Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com