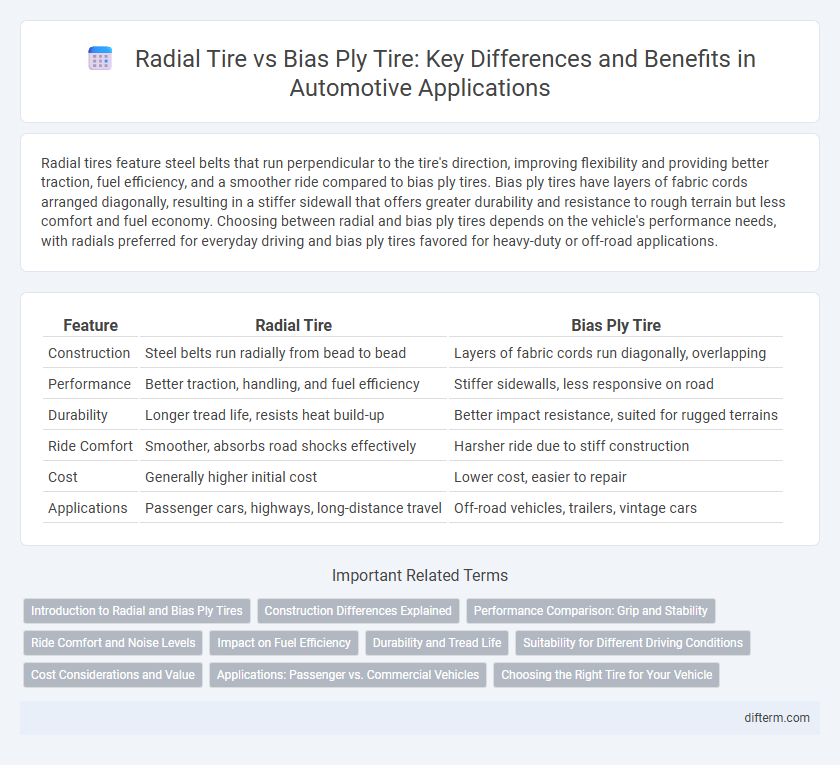
Radial tires feature steel belts that run perpendicular to the tire's direction, improving flexibility and providing better traction, fuel efficiency, and a smoother ride compared to bias ply tires. Bias ply tires have layers of fabric cords arranged diagonally, resulting in a stiffer sidewall that offers greater durability and resistance to rough terrain but less comfort and fuel economy. Choosing between radial and bias ply tires depends on the vehicle's performance needs, with radials preferred for everyday driving and bias ply tires favored for heavy-duty or off-road applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Radial Tire | Bias Ply Tire |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Steel belts run radially from bead to bead | Layers of fabric cords run diagonally, overlapping |
| Performance | Better traction, handling, and fuel efficiency | Stiffer sidewalls, less responsive on road |
| Durability | Longer tread life, resists heat build-up | Better impact resistance, suited for rugged terrains |
| Ride Comfort | Smoother, absorbs road shocks effectively | Harsher ride due to stiff construction |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost | Lower cost, easier to repair |
| Applications | Passenger cars, highways, long-distance travel | Off-road vehicles, trailers, vintage cars |
Introduction to Radial and Bias Ply Tires
Radial tires feature cords that run perpendicular to the tread, providing enhanced flexibility, improved tread contact, and better fuel efficiency compared to bias ply tires, where cords are laid diagonally in overlapping layers for increased sidewall strength and durability. Radial construction dominates modern passenger vehicles and commercial trucks due to superior handling, reduced heat buildup, and longer tread life. Bias ply tires still find use in specialty applications, including off-road and vintage vehicles, where rugged sidewall performance is prioritized.
Construction Differences Explained
Radial tires feature cords that run perpendicular to the tread, enhancing flexibility and providing better road contact, while bias ply tires have cords arranged diagonally, offering increased sidewall strength and durability. The radial construction minimizes heat buildup, improving tire lifespan and fuel efficiency, unlike bias ply tires which tend to generate more heat due to their layered design. These fundamental construction differences influence vehicle handling, ride comfort, and tire performance across various automotive applications.
Performance Comparison: Grip and Stability
Radial tires provide superior grip and stability due to their flexible sidewalls and steel belts, which enhance road contact and traction during acceleration and cornering. Bias ply tires, with their stiffer sidewalls and layered construction, offer less precise handling and reduced stability at higher speeds, often resulting in increased heat buildup and uneven tire wear. The improved grip of radial tires significantly enhances vehicle control, especially on wet and uneven surfaces, making them the preferred choice for modern automotive performance.
Ride Comfort and Noise Levels
Radial tires offer superior ride comfort due to their flexible sidewalls, which absorb road shocks more effectively compared to the stiffer construction of bias ply tires. The design of radial tires minimizes road noise, providing a quieter driving experience, whereas bias ply tires tend to generate higher noise levels due to increased tread block movement. Automotive engineers often prefer radial tires for passenger vehicles aiming to enhance comfort and reduce cabin noise.
Impact on Fuel Efficiency
Radial tires, constructed with steel belts running at a 90-degree angle to the tread, significantly enhance fuel efficiency by reducing rolling resistance compared to bias ply tires, which have crisscrossed layers of fabric. The improved flexibility and heat dissipation of radial tires minimize energy loss during motion, resulting in lower fuel consumption. Studies show vehicles equipped with radial tires can achieve up to a 5-10% increase in miles per gallon over those using bias ply tires.
Durability and Tread Life
Radial tires offer superior durability and longer tread life compared to bias ply tires due to their flexible sidewalls and stronger steel belts that evenly distribute road contact and reduce heat buildup. Bias ply tires have stiffer sidewalls that cause uneven wear and quicker tread degradation under high stress and heat conditions. The enhanced construction of radial tires results in better resistance to punctures and wear, significantly extending overall tire lifespan for automotive applications.
Suitability for Different Driving Conditions
Radial tires excel in providing superior traction and fuel efficiency on highways and dry surfaces due to their flexible sidewalls and enhanced contact with the road. Bias ply tires, with their stiffer construction and reinforced sidewalls, are better suited for off-road conditions and heavy loads where durability and resistance to punctures are essential. Choosing the right tire depends on driving patterns, with radials preferred for everyday urban and highway use while bias ply tires perform optimally in rugged terrain and agricultural applications.
Cost Considerations and Value
Radial tires generally offer better cost efficiency over time due to their superior durability and fuel economy, despite a higher initial purchase price compared to bias ply tires. Bias ply tires tend to have a lower upfront cost but require more frequent replacements, increasing long-term expenses. The value of radial tires increases with their enhanced tread life and improved handling, providing greater overall savings for consumers and fleet operators.
Applications: Passenger vs. Commercial Vehicles
Radial tires dominate passenger vehicles due to superior fuel efficiency, improved traction, and longer tread life, enhancing everyday driving comfort. Bias ply tires remain prevalent in commercial vehicles and heavy-duty trucks, valued for their rugged sidewall strength and durability under heavy loads and rough terrain. The distinct construction differences dictate application suitability, with radial tires excelling in passenger car performance and bias ply tires preferred for demanding commercial use.
Choosing the Right Tire for Your Vehicle
Radial tires offer superior handling, fuel efficiency, and longer tread life compared to bias ply tires, making them ideal for passenger cars and modern vehicles. Bias ply tires provide enhanced sidewall strength and durability, often preferred for heavy-duty trucks, off-road use, and vintage automobiles. Selecting the right tire depends on factors such as vehicle type, driving conditions, and performance requirements to ensure safety and optimal performance.
radial tire vs bias ply tire Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com