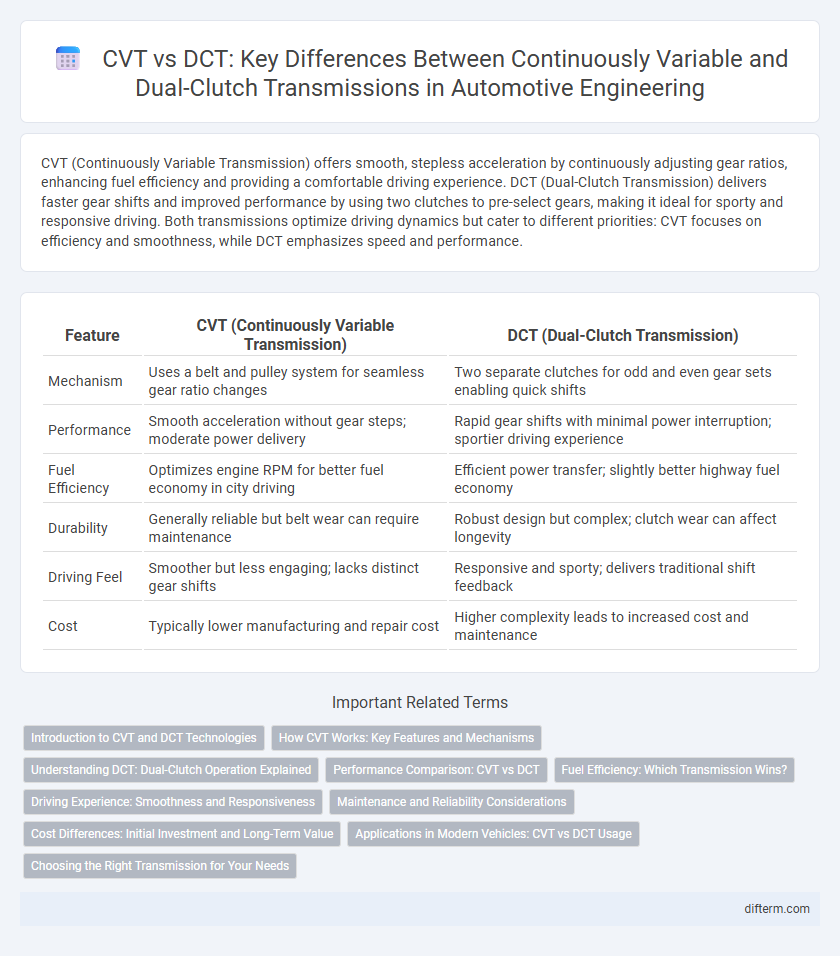
CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission) offers smooth, stepless acceleration by continuously adjusting gear ratios, enhancing fuel efficiency and providing a comfortable driving experience. DCT (Dual-Clutch Transmission) delivers faster gear shifts and improved performance by using two clutches to pre-select gears, making it ideal for sporty and responsive driving. Both transmissions optimize driving dynamics but cater to different priorities: CVT focuses on efficiency and smoothness, while DCT emphasizes speed and performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission) | DCT (Dual-Clutch Transmission) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Uses a belt and pulley system for seamless gear ratio changes | Two separate clutches for odd and even gear sets enabling quick shifts |
| Performance | Smooth acceleration without gear steps; moderate power delivery | Rapid gear shifts with minimal power interruption; sportier driving experience |
| Fuel Efficiency | Optimizes engine RPM for better fuel economy in city driving | Efficient power transfer; slightly better highway fuel economy |
| Durability | Generally reliable but belt wear can require maintenance | Robust design but complex; clutch wear can affect longevity |
| Driving Feel | Smoother but less engaging; lacks distinct gear shifts | Responsive and sporty; delivers traditional shift feedback |
| Cost | Typically lower manufacturing and repair cost | Higher complexity leads to increased cost and maintenance |
Introduction to CVT and DCT Technologies
Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) uses a system of pulleys and belts to provide seamless gear ratio changes, enhancing fuel efficiency and smooth acceleration in vehicles. Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT) combines two separate clutches for odd and even gear sets, allowing for rapid and precise gear shifts with minimal power interruption. Both technologies optimize drivability and performance, with CVT excelling in smoothness and fuel economy, while DCT offers sportier, more responsive shifting.
How CVT Works: Key Features and Mechanisms
CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission) operates using a system of pulleys and a flexible belt or chain, enabling seamless gear ratio changes without distinct gear steps, which optimizes engine performance and fuel efficiency. Key features include an adjustable diameter pulley system that provides infinite gear ratios, allowing for smooth acceleration and reduced engine strain. This mechanism contrasts with traditional gearboxes by eliminating gear shifts, thus enhancing driving comfort and reducing mechanical wear.
Understanding DCT: Dual-Clutch Operation Explained
Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT) utilizes two separate clutches for odd and even gear sets, enabling faster and seamless gear shifts compared to traditional transmissions. This dual-clutch system allows one gear to engage while the other is disengaging, reducing shift time and enhancing acceleration efficiency. DCT technology provides improved fuel economy and driving performance by minimizing power loss during gear changes in automotive applications.
Performance Comparison: CVT vs DCT
Dual-Clutch Transmissions (DCT) deliver faster and more precise gear changes compared to Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVT), enhancing acceleration and driving dynamics. CVTs provide seamless acceleration with infinite gear ratios, optimizing fuel efficiency but often sacrificing sporty performance and responsiveness. DCTs are preferred in performance-oriented vehicles for their ability to combine manual transmission efficiency with automatic convenience, while CVTs are favored in economy models for smoothness and fuel economy.
Fuel Efficiency: Which Transmission Wins?
CVT transmissions optimize fuel efficiency by offering an infinite range of gear ratios, maintaining engine operation at its most efficient RPM for various driving conditions, which reduces fuel consumption compared to traditional gearboxes. DCT systems, while providing quicker and smoother shifts for performance, typically have slightly higher fuel consumption due to torque converter slip and more complex mechanical components. Overall, CVTs generally outperform DCTs in fuel economy, especially in urban and stop-and-go driving environments.
Driving Experience: Smoothness and Responsiveness
CVT offers seamless acceleration through its variable gear ratios, ensuring exceptionally smooth driving without noticeable shifts, ideal for urban commuting and fuel efficiency. DCT delivers rapid, precise gear changes with minimal interruption of power flow, enhancing responsiveness and providing a sportier driving experience favored in performance vehicles. Drivers seeking comfort prioritize CVT's effortless smoothness, while those valuing dynamic control prefer DCT's quick and sharp gear transitions.
Maintenance and Reliability Considerations
CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission) requires regular fluid changes with manufacturer-recommended CVT-specific transmission fluid to maintain its belt and pulley system, as neglect can lead to premature wear and costly repairs. DCT (Dual-Clutch Transmission) relies on precise hydraulic control and clutch actuation, needing periodic fluid replacement and occasional clutch servicing to prevent shuddering and shifting issues. Reliability-wise, CVTs are known for smooth operation but may face durability challenges under high torque, while DCTs offer faster shifts and better performance yet can incur higher maintenance costs due to their complex mechanical components.
Cost Differences: Initial Investment and Long-Term Value
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) typically have a lower initial purchase cost due to fewer moving parts and simpler design compared to Dual-Clutch Transmissions (DCTs), which are more complex and expensive to manufacture. Over time, CVTs may incur higher maintenance and repair expenses because of belt or chain wear, whereas DCTs often demand costly clutch replacements but offer improved fuel efficiency and performance. Evaluating total cost of ownership involves balancing upfront affordability with the potential for increased long-term servicing costs associated with each transmission type.
Applications in Modern Vehicles: CVT vs DCT Usage
CVT is widely used in hybrid and small to mid-sized vehicles due to its seamless acceleration and improved fuel efficiency, especially in urban driving conditions. DCT finds application primarily in high-performance and luxury vehicles, offering faster gear shifts and enhanced driving dynamics for sporty and dynamic experiences. Automotive manufacturers choose CVT or DCT based on target vehicle performance requirements, fuel economy goals, and driver experience preferences.
Choosing the Right Transmission for Your Needs
CVT offers smooth acceleration and improved fuel efficiency by continuously adjusting gear ratios, making it ideal for urban driving and maximizing mileage. DCT provides faster, more precise gear shifts and enhanced performance responsiveness, suited for sporty driving and high-torque applications. Selecting between CVT and DCT depends on whether fuel economy or dynamic driving experience is the primary priority for your vehicle use.
CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission) vs DCT (Dual-Clutch Transmission) Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com