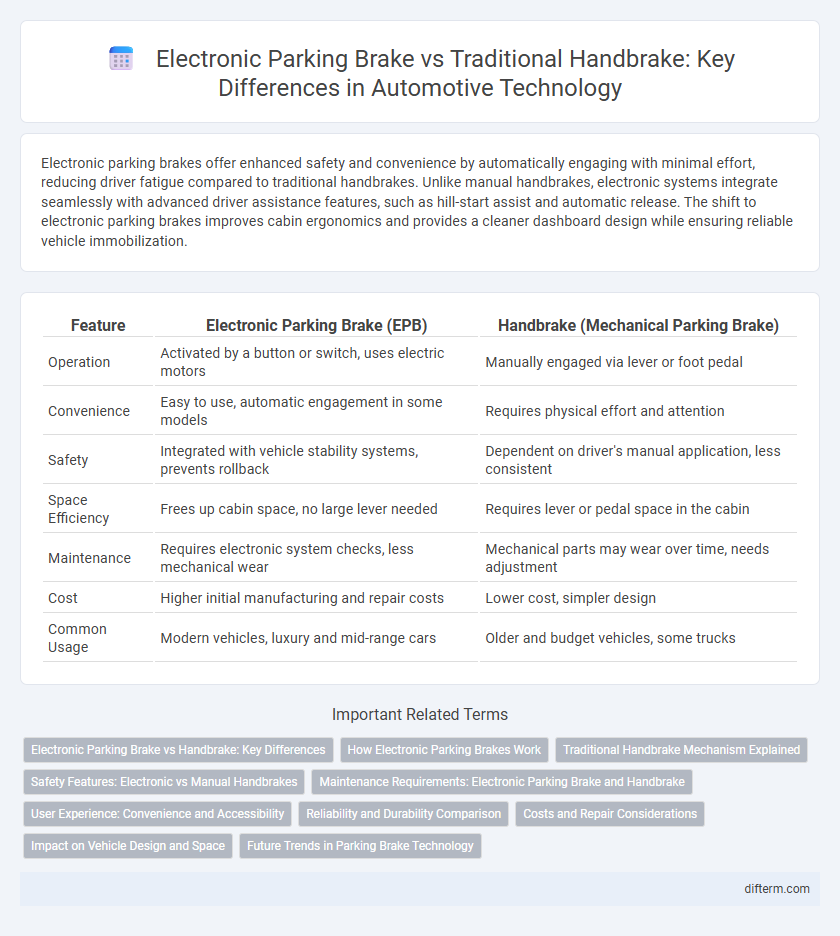
Electronic parking brakes offer enhanced safety and convenience by automatically engaging with minimal effort, reducing driver fatigue compared to traditional handbrakes. Unlike manual handbrakes, electronic systems integrate seamlessly with advanced driver assistance features, such as hill-start assist and automatic release. The shift to electronic parking brakes improves cabin ergonomics and provides a cleaner dashboard design while ensuring reliable vehicle immobilization.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electronic Parking Brake (EPB) | Handbrake (Mechanical Parking Brake) |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Activated by a button or switch, uses electric motors | Manually engaged via lever or foot pedal |
| Convenience | Easy to use, automatic engagement in some models | Requires physical effort and attention |
| Safety | Integrated with vehicle stability systems, prevents rollback | Dependent on driver's manual application, less consistent |
| Space Efficiency | Frees up cabin space, no large lever needed | Requires lever or pedal space in the cabin |
| Maintenance | Requires electronic system checks, less mechanical wear | Mechanical parts may wear over time, needs adjustment |
| Cost | Higher initial manufacturing and repair costs | Lower cost, simpler design |
| Common Usage | Modern vehicles, luxury and mid-range cars | Older and budget vehicles, some trucks |
Electronic Parking Brake vs Handbrake: Key Differences
Electronic parking brakes (EPBs) offer automated engagement and disengagement through electric actuators, contrasting with traditional handbrakes that require manual lever operation. EPBs integrate with vehicle safety systems like ABS and stability control, enhancing precision and reducing driver effort. Handbrakes provide direct mechanical linkage, valued for simplicity and reliability, but lack the convenience and advanced control features present in EPB systems.
How Electronic Parking Brakes Work
Electronic parking brakes operate through an electric motor that applies the brake pads to the rear wheels, replacing the traditional manual handbrake lever. Sensors detect when the vehicle is stationary or on an incline, automatically engaging the brake to prevent rollback and enhance safety. Integration with vehicle systems like the anti-lock braking system (ABS) ensures precise control and reliable performance under various driving conditions.
Traditional Handbrake Mechanism Explained
The traditional handbrake mechanism operates through a manual lever connected to a series of cables that engage the rear brake pads or drums, ensuring vehicle immobilization. This system relies on mechanical force, typically requiring physical effort from the driver to pull the lever and lock the brakes. Despite being less advanced than electronic parking brakes, traditional handbrake mechanisms are valued for their simplicity, reliability, and ease of repair in automotive designs.
Safety Features: Electronic vs Manual Handbrakes
Electronic parking brakes enhance safety by automatically engaging during emergencies and on steep inclines, reducing the risk of roll-back accidents. Manual handbrakes rely on driver strength and positioning, which can lead to inconsistent application and potential failure in critical situations. Advanced electronic systems also integrate with vehicle stability control, providing superior braking performance and enhanced protection.
Maintenance Requirements: Electronic Parking Brake and Handbrake
Electronic parking brakes require less frequent maintenance than traditional handbrakes, as they rely on motors and electronic components rather than mechanical cables that can stretch or corrode. Handbrakes demand regular inspection and adjustment of cables and linkages to ensure proper tension and functionality, especially in harsh weather conditions. Electronic systems also benefit from self-diagnostic capabilities, alerting drivers to potential faults before they become safety issues.
User Experience: Convenience and Accessibility
Electronic parking brakes enhance user experience by offering effortless activation through a simple button, eliminating the physical strain and awkward positioning associated with traditional handbrakes. These systems integrate seamlessly with advanced vehicle technologies like automatic hold and hill-start assist, improving convenience and safety during urban driving and stop-and-go traffic. Accessibility is improved, particularly for drivers with limited strength or mobility, as electronic parking brakes require minimal physical effort and provide consistent performance across various vehicle conditions.
Reliability and Durability Comparison
Electronic parking brakes exhibit higher reliability and durability compared to traditional handbrakes due to advanced sensor technology and fewer mechanical components prone to wear. The use of electric actuators minimizes cable stretch and corrosion risks, enhancing long-term performance and reducing maintenance needs. Automotive studies show electronic parking brakes maintain consistent clamping force over extended periods, outperforming conventional handbrakes in harsh driving conditions.
Costs and Repair Considerations
Electronic parking brakes generally have higher initial costs due to advanced sensors and motors, with repair expenses often exceeding those of traditional handbrakes because of electronic components and software diagnostics. Handbrakes, being mechanically simpler, offer lower installation and maintenance costs while repairs usually involve straightforward cable or lever adjustments. Choosing between them depends on balancing upfront investment with potential long-term repair costs and vehicle complexity.
Impact on Vehicle Design and Space
Electronic parking brakes (EPBs) significantly enhance vehicle design by eliminating the bulky mechanical handbrake lever, freeing up center console space for additional storage or advanced control features. EPBs enable designers to create sleeker, more ergonomic interiors, improving both aesthetic appeal and passenger comfort. The compact actuator modules also reduce weight and complexity, contributing to improved overall vehicle efficiency and manufacturing flexibility.
Future Trends in Parking Brake Technology
Electronic parking brakes (EPBs) are poised to dominate future automotive designs due to their integration with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and improved safety features, enabling automated parking and hill-hold functions. The transition from mechanical handbrakes to EPBs allows for more cabin space, enhanced ergonomics, and smoother vehicle control through electronic actuation. Emerging trends also include integration with autonomous driving systems and energy recovery mechanisms, driving the evolution of smarter, more efficient parking solutions.
electronic parking brake vs handbrake Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com