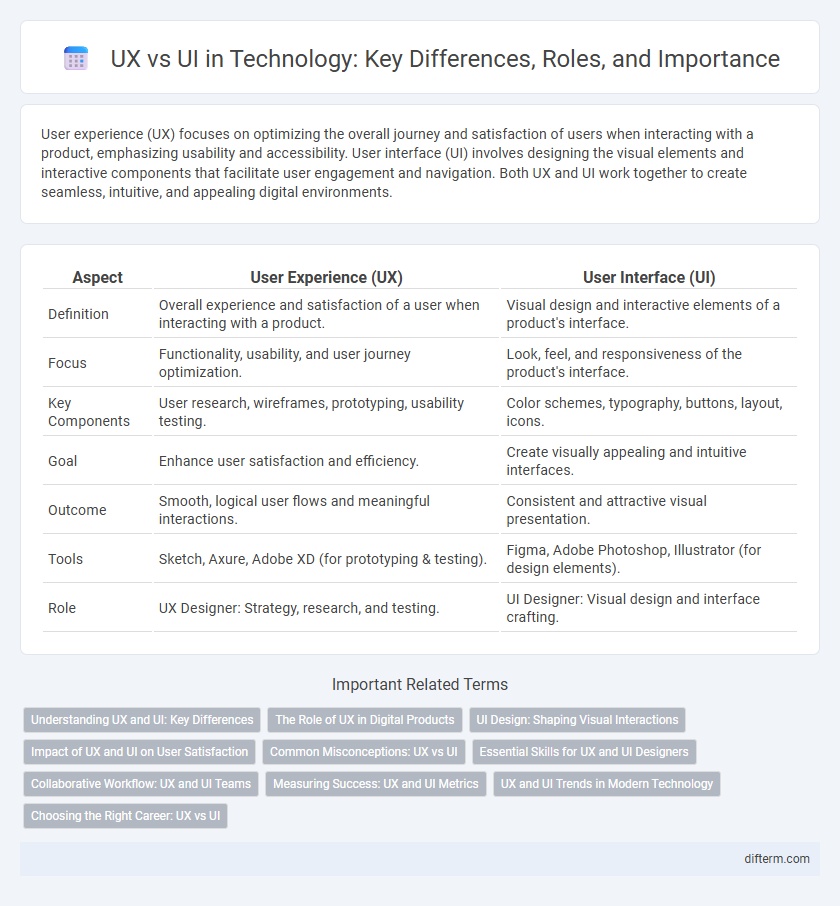
User experience (UX) focuses on optimizing the overall journey and satisfaction of users when interacting with a product, emphasizing usability and accessibility. User interface (UI) involves designing the visual elements and interactive components that facilitate user engagement and navigation. Both UX and UI work together to create seamless, intuitive, and appealing digital environments.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | User Experience (UX) | User Interface (UI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Overall experience and satisfaction of a user when interacting with a product. | Visual design and interactive elements of a product's interface. |
| Focus | Functionality, usability, and user journey optimization. | Look, feel, and responsiveness of the product's interface. |
| Key Components | User research, wireframes, prototyping, usability testing. | Color schemes, typography, buttons, layout, icons. |
| Goal | Enhance user satisfaction and efficiency. | Create visually appealing and intuitive interfaces. |
| Outcome | Smooth, logical user flows and meaningful interactions. | Consistent and attractive visual presentation. |
| Tools | Sketch, Axure, Adobe XD (for prototyping & testing). | Figma, Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator (for design elements). |
| Role | UX Designer: Strategy, research, and testing. | UI Designer: Visual design and interface crafting. |
Understanding UX and UI: Key Differences
User Experience (UX) focuses on optimizing the overall interaction and satisfaction users have with a product, emphasizing usability, accessibility, and functionality. User Interface (UI) involves designing the visual elements and interactive components that users directly engage with, ensuring aesthetic appeal and intuitive navigation. Distinguishing UX from UI is essential for creating effective digital solutions, as UX shapes the user's journey while UI defines the product's look and feel.
The Role of UX in Digital Products
User Experience (UX) in digital products focuses on optimizing overall usability, accessibility, and satisfaction to create seamless interactions between users and technology. Effective UX design involves research, prototyping, and testing to understand user behaviors and needs, ensuring products are intuitive and efficient. Prioritizing UX leads to increased engagement, reduced churn, and higher conversion rates in digital platforms.
UI Design: Shaping Visual Interactions
UI design focuses on crafting intuitive visual interfaces that facilitate seamless user interactions through elements such as buttons, icons, and layout structure. Effective UI design incorporates principles like color theory, typography, and spacing to enhance usability and create aesthetically pleasing digital environments. Prioritizing responsive design and accessibility standards ensures UI interfaces adapt across devices while maintaining consistent user experiences.
Impact of UX and UI on User Satisfaction
User Experience (UX) directly influences user satisfaction by ensuring intuitive navigation, efficient task completion, and emotional engagement, which leads to higher retention and positive feedback. User Interface (UI) enhances satisfaction through visually appealing designs, consistent branding, and accessible layouts that reduce cognitive load and frustration. Both UX and UI collectively shape the overall interaction quality, driving customer loyalty and increasing conversion rates in digital products.
Common Misconceptions: UX vs UI
Common misconceptions about UX and UI often blur their distinct roles; UX (User Experience) focuses on the overall interaction and satisfaction with a product, while UI (User Interface) centers on visual design and interactive elements. Many assume that UI design alone guarantees a positive experience, overlooking the importance of research, usability testing, and information architecture integral to UX. Understanding that UX encompasses the entire user journey, including functionality and ease of use, clarifies why effective design requires both complementary disciplines.
Essential Skills for UX and UI Designers
UX designers must excel in user research, wireframing, and usability testing to create intuitive and accessible interfaces, while UI designers require proficiency in visual design, typography, and interactive elements to craft appealing and functional layouts. Both roles demand strong collaboration, empathy, and knowledge of design tools such as Sketch, Figma, or Adobe XD to deliver seamless digital experiences. Mastery of responsive design principles and understanding user behavior analytics are crucial for optimizing engagement and satisfaction across devices.
Collaborative Workflow: UX and UI Teams
UX and UI teams enhance collaborative workflow by integrating user research insights with visual design principles to create cohesive digital experiences. Effective collaboration tools and agile methodologies streamline communication, ensuring alignment on user needs and design execution. Prioritizing cross-functional teamwork accelerates iterative prototyping, improving overall product usability and aesthetic appeal.
Measuring Success: UX and UI Metrics
Measuring success in UX involves tracking user satisfaction scores, task completion rates, and error frequency to evaluate overall usability and engagement. UI success metrics focus on visual consistency, click-through rates, and interaction speed to assess the effectiveness of design elements. Combining these metrics provides a comprehensive understanding of both user experience and interface performance.
UX and UI Trends in Modern Technology
User Experience (UX) emphasizes creating intuitive interfaces that enhance user satisfaction through seamless interaction and accessibility, while User Interface (UI) focuses on the visual elements like color schemes, typography, and layout to engage users aesthetically. Current UX trends highlight personalization powered by AI, voice-activated interfaces, and minimalistic navigation, improving efficiency and user comfort across devices. UI trends prioritize dark mode designs, micro-interactions, and immersive 3D graphics, driving both functional appeal and emotional connection in modern technology platforms.
Choosing the Right Career: UX vs UI
Choosing between UX and UI careers depends on your passion for user psychology versus visual design. UX professionals analyze user behavior and optimize interactions to create seamless experiences, while UI designers craft the aesthetic and interactive elements of digital interfaces. Understanding key skills like user research for UX and graphic design tools for UI helps align career paths with industry demand and personal strengths.
UX vs UI Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com