Hybrid apps combine elements of both web and native applications, enabling faster development and cross-platform compatibility with a single codebase. Native apps offer superior performance, enhanced security, and seamless access to device-specific features by being built for a particular operating system. Choosing between hybrid and native apps depends on project requirements, budget, and desired user experience.
Table of Comparison
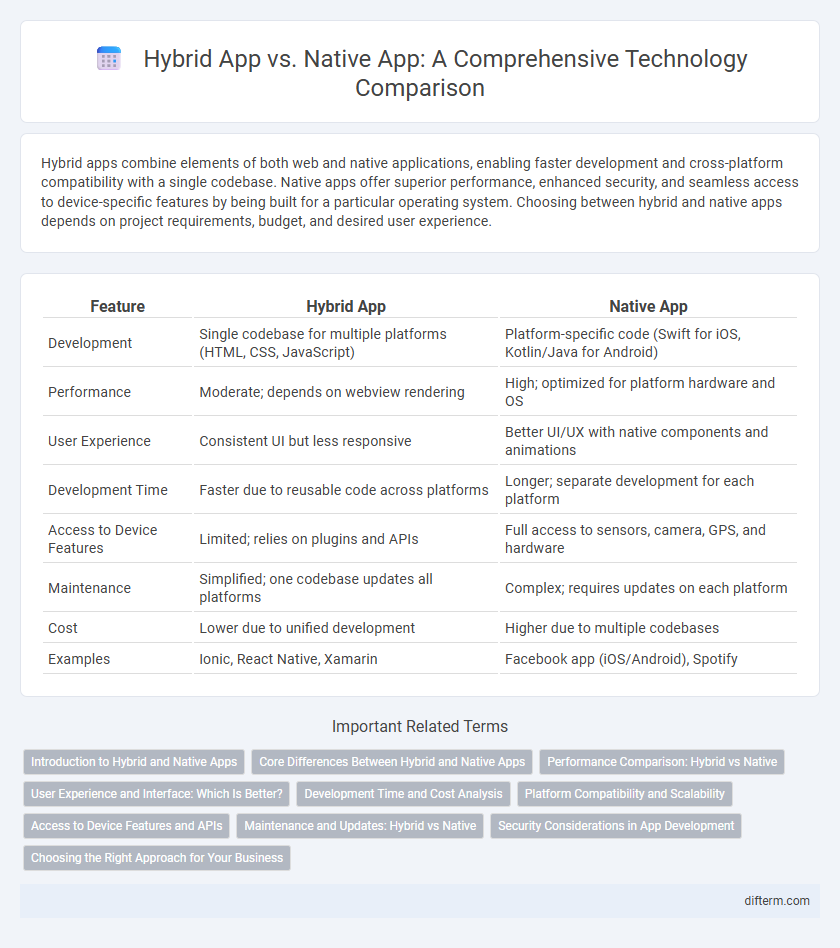
| Feature | Hybrid App | Native App |
|---|---|---|
| Development | Single codebase for multiple platforms (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) | Platform-specific code (Swift for iOS, Kotlin/Java for Android) |
| Performance | Moderate; depends on webview rendering | High; optimized for platform hardware and OS |
| User Experience | Consistent UI but less responsive | Better UI/UX with native components and animations |
| Development Time | Faster due to reusable code across platforms | Longer; separate development for each platform |
| Access to Device Features | Limited; relies on plugins and APIs | Full access to sensors, camera, GPS, and hardware |
| Maintenance | Simplified; one codebase updates all platforms | Complex; requires updates on each platform |
| Cost | Lower due to unified development | Higher due to multiple codebases |
| Examples | Ionic, React Native, Xamarin | Facebook app (iOS/Android), Spotify |
Introduction to Hybrid and Native Apps
Hybrid apps combine elements of both native and web applications, allowing developers to build a single codebase using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript that runs on multiple platforms. Native apps are developed specifically for one operating system, such as iOS or Android, using platform-specific languages like Swift or Kotlin, which results in optimized performance and seamless integration with device features. Choosing between hybrid and native apps depends on factors like development time, budget, performance needs, and the desired user experience.
Core Differences Between Hybrid and Native Apps
Hybrid apps combine web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript within a native container, enabling cross-platform compatibility and faster development cycles. Native apps are built specifically for a single operating system using platform-specific languages such as Swift for iOS or Kotlin for Android, providing superior performance and access to device features. Core differences include development approach, performance capabilities, user experience fidelity, and maintenance complexity.
Performance Comparison: Hybrid vs Native
Native apps generally deliver superior performance by directly leveraging device hardware and operating system capabilities, resulting in faster load times and smoother animations. Hybrid apps, built using web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript wrapped in a native container, may experience slower performance due to an additional abstraction layer. Performance-critical applications, such as mobile games or resource-intensive tools, benefit significantly from native development compared to hybrid solutions.
User Experience and Interface: Which Is Better?
Hybrid apps offer a consistent user interface across multiple platforms by utilizing web technologies like HTML5 and CSS, but they may encounter performance limitations affecting smooth interactions. Native apps deliver superior user experience through optimized performance, responsive interfaces, and seamless integration with device-specific features, enhancing overall usability. Choosing between hybrid and native apps depends on balancing development cost, cross-platform reach, and the importance of delivering high-performance user interfaces.
Development Time and Cost Analysis
Hybrid apps typically require less development time and lower costs compared to native apps due to a single codebase across multiple platforms like iOS and Android. Native apps demand separate coding for each platform, increasing both development time and expenses but often resulting in better performance and user experience. Companies prioritize hybrid apps for faster market entry and cost efficiency, while native apps are preferred for complex functionalities and optimized app performance.
Platform Compatibility and Scalability
Hybrid apps offer greater platform compatibility by enabling a single codebase to run across multiple operating systems such as iOS and Android, reducing development time and costs. Native apps provide superior scalability as they are optimized for specific platforms, allowing for advanced functionalities and seamless performance adjustments based on device capabilities. Choosing between hybrid and native apps depends on the need for cross-platform reach versus high-performance, scalable solutions tailored to individual operating systems.
Access to Device Features and APIs
Native apps provide direct access to device features and APIs, enabling optimal performance and seamless integration with hardware components such as cameras, GPS, and sensors. Hybrid apps rely on plugins and web technologies to access these features, which can result in limited functionality and slower response times compared to native applications. Developers prioritize native solutions when critical access to device capabilities and high efficiency are essential for the user experience.
Maintenance and Updates: Hybrid vs Native
Native apps offer streamlined maintenance and updates through direct access to platform-specific APIs and development tools, ensuring faster deployment of bug fixes and feature enhancements. Hybrid apps require maintaining a single codebase across multiple platforms, potentially leading to complexities in addressing platform-specific issues and delays in updates due to reliance on third-party frameworks. Efficient update cycles for native apps enhance user experience by delivering optimized performance and security patches tailored to each operating system.
Security Considerations in App Development
Hybrid apps often face increased security risks due to their reliance on web technologies and third-party plugins, potentially exposing vulnerabilities such as cross-site scripting (XSS) and inadequate data encryption. Native apps benefit from platform-specific security features like biometric authentication and sandboxing, enhancing protection against unauthorized access and data breaches. Developers must implement rigorous security protocols regardless of app type, including secure coding practices, encryption, and regular vulnerability assessments to safeguard user data effectively.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Business
Hybrid apps combine web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to offer cross-platform compatibility, reducing development time and cost. Native apps, built specifically for iOS or Android using Swift, Objective-C, or Kotlin, deliver superior performance, enhanced security, and better access to device features. Selecting between hybrid and native depends on your business goals, budget constraints, required user experience, and the need for platform-specific functionalities.
Hybrid app vs Native app Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com