Static sites deliver fixed content, offering faster load times and enhanced security by serving pre-built pages without server-side processing. Dynamic sites generate content on-the-fly, providing personalized user experiences and easy content management through databases and server scripts. Choosing between static and dynamic depends on the need for speed and simplicity versus interactivity and frequent updates.
Table of Comparison
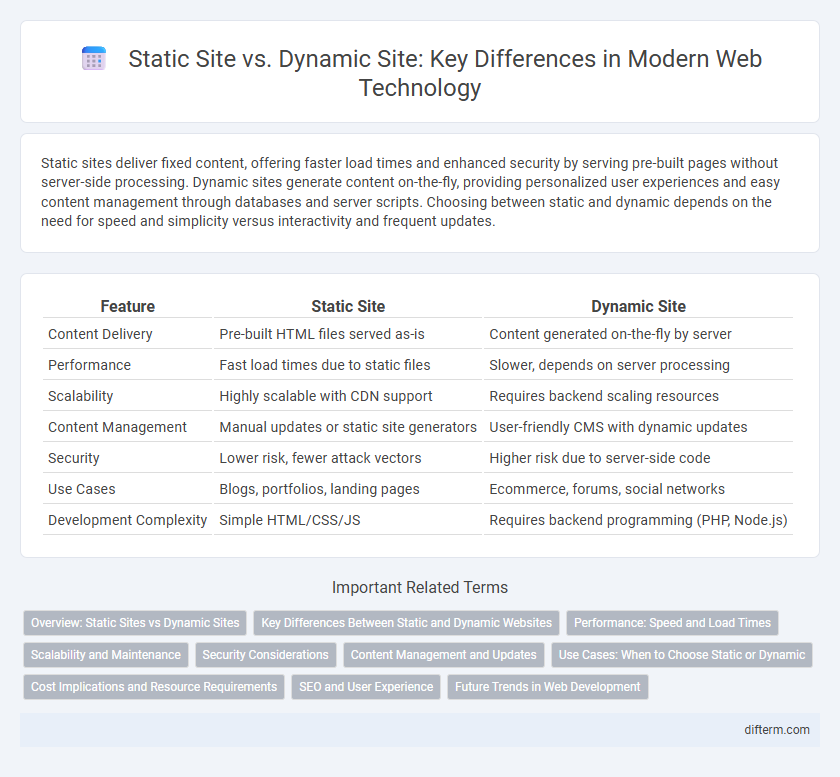
| Feature | Static Site | Dynamic Site |
|---|---|---|
| Content Delivery | Pre-built HTML files served as-is | Content generated on-the-fly by server |
| Performance | Fast load times due to static files | Slower, depends on server processing |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with CDN support | Requires backend scaling resources |
| Content Management | Manual updates or static site generators | User-friendly CMS with dynamic updates |
| Security | Lower risk, fewer attack vectors | Higher risk due to server-side code |
| Use Cases | Blogs, portfolios, landing pages | Ecommerce, forums, social networks |
| Development Complexity | Simple HTML/CSS/JS | Requires backend programming (PHP, Node.js) |
Overview: Static Sites vs Dynamic Sites
Static sites consist of fixed HTML files delivered directly to the user's browser, offering fast load times, enhanced security, and simpler hosting requirements. Dynamic sites generate pages in real-time using server-side languages like PHP or JavaScript frameworks, enabling personalized content and database integration. Choosing between static and dynamic sites depends on factors such as content complexity, scalability needs, and user interaction requirements.
Key Differences Between Static and Dynamic Websites
Static websites deliver fixed content stored directly on the server, ensuring faster load times and enhanced security due to the absence of server-side processing. Dynamic websites generate content on-the-fly using server-side scripts and databases, enabling personalized user experiences and easier content management. Key differences include scalability, with dynamic sites supporting complex functionalities, while static sites excel in simplicity and performance optimization.
Performance: Speed and Load Times
Static sites deliver faster load times by serving pre-rendered HTML files directly from the server or CDN, minimizing server processing. Dynamic sites generate pages in real-time using server-side scripts and databases, which increases load times due to additional processing and database queries. Optimizing performance in dynamic sites often requires caching mechanisms and content delivery networks to reduce latency and improve speed.
Scalability and Maintenance
Static sites offer superior scalability due to their pre-rendered HTML files that can be easily distributed via CDNs, resulting in faster load times and minimal server load. Dynamic sites require continuous backend processing to generate content, which increases maintenance complexity and resource demands as traffic grows. Maintenance for static sites is simpler, often involving only updating content files, whereas dynamic sites necessitate ongoing backend updates, database management, and security monitoring.
Security Considerations
Static sites offer enhanced security due to their simplicity, serving pre-built HTML files without relying on server-side processing, which minimizes vulnerabilities like SQL injection and server exploits. Dynamic sites, while more flexible and interactive, require robust security measures such as regular patching, input validation, and secure authentication to mitigate risks posed by database connections and server-side scripts. Choosing static sites reduces attack surfaces, making them ideal for sensitive content delivery where minimal maintenance and high security are priorities.
Content Management and Updates
Static sites deliver fixed content stored in HTML files, making updates dependent on manual code changes or deployment through version control systems. Dynamic sites utilize server-side scripting and databases, enabling content management systems (CMS) that allow non-technical users to update content through user-friendly interfaces. This flexibility in dynamic sites supports frequent, real-time content updates, while static sites offer faster load times and enhanced security due to their immutable nature.
Use Cases: When to Choose Static or Dynamic
Static sites excel for informational websites, portfolios, and blogs where content changes infrequently, ensuring fast load times and enhanced security. Dynamic sites suit e-commerce platforms, social media, and content management systems requiring frequent updates, user interactions, and personalized experiences. Choosing between static or dynamic depends on the project's content update frequency, user engagement needs, and scalability requirements.
Cost Implications and Resource Requirements
Static sites typically incur lower hosting costs and require minimal server resources, making them ideal for small projects or businesses with limited budgets. Dynamic sites demand more powerful servers and ongoing maintenance, leading to higher operational expenses especially when incorporating complex functionalities or databases. Evaluating the trade-off between initial setup simplicity and long-term scalability is crucial for budget-conscious technology deployment.
SEO and User Experience
Static sites offer faster loading speeds and enhanced security, which positively impact SEO rankings by reducing bounce rates and improving crawl efficiency. Dynamic sites provide personalized user experiences and real-time content updates, driving higher engagement and better retention metrics essential for SEO performance. Balancing static site simplicity with dynamic site interactivity ensures optimal user experience and search engine visibility.
Future Trends in Web Development
Static sites leverage Jamstack architecture to enhance performance and security, increasingly integrating headless CMSs for dynamic content delivery without server overhead. Dynamic sites evolve with AI-driven personalization and serverless functions, enabling real-time data processing and interactive user experiences. Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) and edge computing shape future web development by combining static site speed with dynamic site flexibility, optimizing both scalability and user engagement.
Static Site vs Dynamic Site Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com