Fiber-optic internet delivers significantly faster data transmission speeds and higher bandwidth capacity compared to DSL, enabling seamless streaming, gaming, and large file downloads. Unlike DSL, which relies on traditional copper telephone lines, fiber-optic technology uses light signals through glass or plastic fibers, resulting in lower latency and greater reliability. This makes fiber-optic internet the preferred choice for businesses and households seeking consistent, high-performance connectivity.
Table of Comparison
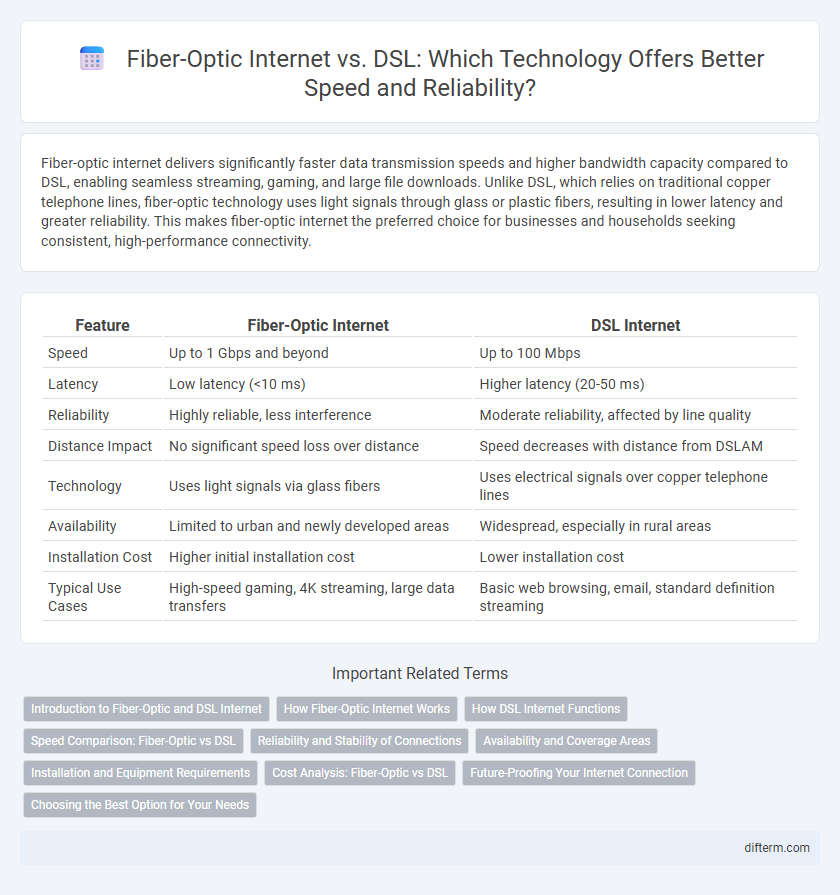
| Feature | Fiber-Optic Internet | DSL Internet |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Up to 1 Gbps and beyond | Up to 100 Mbps |
| Latency | Low latency (<10 ms) | Higher latency (20-50 ms) |
| Reliability | Highly reliable, less interference | Moderate reliability, affected by line quality |
| Distance Impact | No significant speed loss over distance | Speed decreases with distance from DSLAM |
| Technology | Uses light signals via glass fibers | Uses electrical signals over copper telephone lines |
| Availability | Limited to urban and newly developed areas | Widespread, especially in rural areas |
| Installation Cost | Higher initial installation cost | Lower installation cost |
| Typical Use Cases | High-speed gaming, 4K streaming, large data transfers | Basic web browsing, email, standard definition streaming |
Introduction to Fiber-Optic and DSL Internet
Fiber-optic internet uses thin strands of glass or plastic fibers to transmit data as light signals, enabling speeds up to 1 Gbps or higher with low latency, making it ideal for high-demand applications. DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) internet transmits data over traditional copper telephone lines, offering speeds typically ranging from 1 Mbps to 100 Mbps, depending on the distance from the provider's central office. Fiber-optic internet generally provides greater reliability, faster download and upload speeds, and better support for simultaneous users compared to DSL technology.
How Fiber-Optic Internet Works
Fiber-optic internet uses thin strands of glass or plastic fibers to transmit data as pulses of light, enabling extremely high-speed and low-latency connections compared to traditional copper-based DSL. Data transmission through fiber optics relies on total internal reflection, which minimizes signal loss over long distances and supports ultra-broadband speeds, often exceeding 1 Gbps. This technology's capacity for high bandwidth and minimal interference makes it ideal for bandwidth-intensive applications like streaming, gaming, and cloud services.
How DSL Internet Functions
DSL internet transmits digital data over existing copper telephone lines by using higher frequency bands separate from voice channels, allowing simultaneous voice and data transmission. The technology employs a modem to modulate and demodulate signals, converting digital data to analog for transmission and back to digital at the receiving end. Signal quality and data speeds depend on the distance from the DSL access multiplexer (DSLAM), with performance degrading as the copper line length increases.
Speed Comparison: Fiber-Optic vs DSL
Fiber-optic internet delivers significantly faster speeds than DSL, with typical fiber connections offering up to 1 Gbps or higher, while DSL speeds usually range between 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps. The superior bandwidth capacity of fiber-optic technology supports high-demand activities like 4K streaming and online gaming with minimal latency. DSL performance often degrades over longer distances from the provider's central office, whereas fiber-optic maintains consistent speed regardless of distance.
Reliability and Stability of Connections
Fiber-optic internet provides superior reliability and stability compared to DSL, utilizing light signals that are less susceptible to interference and signal degradation over long distances. DSL connections often suffer from fluctuations in speed and reliability due to copper wire quality, distance from the provider, and electromagnetic interference. The inherent design of fiber-optic networks ensures consistent high-speed performance and minimal downtime, making it the preferred choice for critical and bandwidth-intensive applications.
Availability and Coverage Areas
Fiber-optic internet offers significantly higher speeds but is less widely available than DSL due to the extensive infrastructure required, primarily concentrated in urban and suburban areas. DSL leverages existing telephone lines, providing broader coverage in rural and remote locations where fiber deployment is limited or cost-prohibitive. Coverage areas for DSL generally exceed those of fiber, though ongoing fiber expansion projects are rapidly increasing availability in more regions.
Installation and Equipment Requirements
Fiber-optic internet installation requires specialized technicians and advanced optical network terminals (ONTs) to manage high-speed data transmission, often involving new cabling from the provider to the home. DSL uses existing telephone lines with simpler equipment like DSL modems, enabling easier and quicker installation with lower upfront infrastructure costs. Fiber-optic equipment supports significantly faster speeds and greater bandwidth compared to DSL's traditional copper wire setup, impacting long-term network performance and scalability.
Cost Analysis: Fiber-Optic vs DSL
Fiber-optic internet typically demands a higher initial installation cost compared to DSL due to the advanced infrastructure and materials required for fiber cables. However, the monthly service fees for fiber-optic plans often provide better value in terms of speed and reliability, potentially lowering long-term expenses for businesses and households. DSL's lower upfront costs may appeal to budget-conscious users, but slower speeds and higher maintenance costs can lead to increased total expenditure over time.
Future-Proofing Your Internet Connection
Fiber-optic internet offers unparalleled future-proofing with its ability to support multi-gigabit speeds and low latency, making it ideal for emerging technologies like 8K streaming, virtual reality, and IoT expansion. DSL technology, constrained by copper wiring, faces limitations in bandwidth and distance, resulting in slower speeds and higher latency that may hinder future digital demands. Investing in fiber-optic infrastructure ensures scalable, reliable connectivity that can adapt to increasing data consumption and evolving smart home ecosystems.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Needs
Fiber-optic internet delivers significantly higher speeds and greater bandwidth compared to DSL, making it ideal for activities like streaming 4K video, online gaming, and handling multiple connected devices simultaneously. DSL offers a more affordable solution with decent speeds for basic browsing and email, suitable for users with limited internet needs or in areas where fiber-optic infrastructure is unavailable. Evaluating factors such as usage requirements, budget constraints, and service availability ensures selecting the most efficient internet service tailored to your specific needs.
Fiber-optic internet vs DSL Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com