U2F and WebAuthn are essential security protocols enhancing online authentication, with U2F offering a simple, device-based two-factor authentication solution primarily supported by USB security keys. WebAuthn expands on U2F by enabling passwordless logins and biometrics integration across browsers and devices, providing a more versatile and secure authentication experience. Both technologies use public key cryptography to protect against phishing attacks, but WebAuthn supports a broader range of authenticators and platforms, making it the future standard in digital security for pets' smart devices and IoT applications.
Table of Comparison
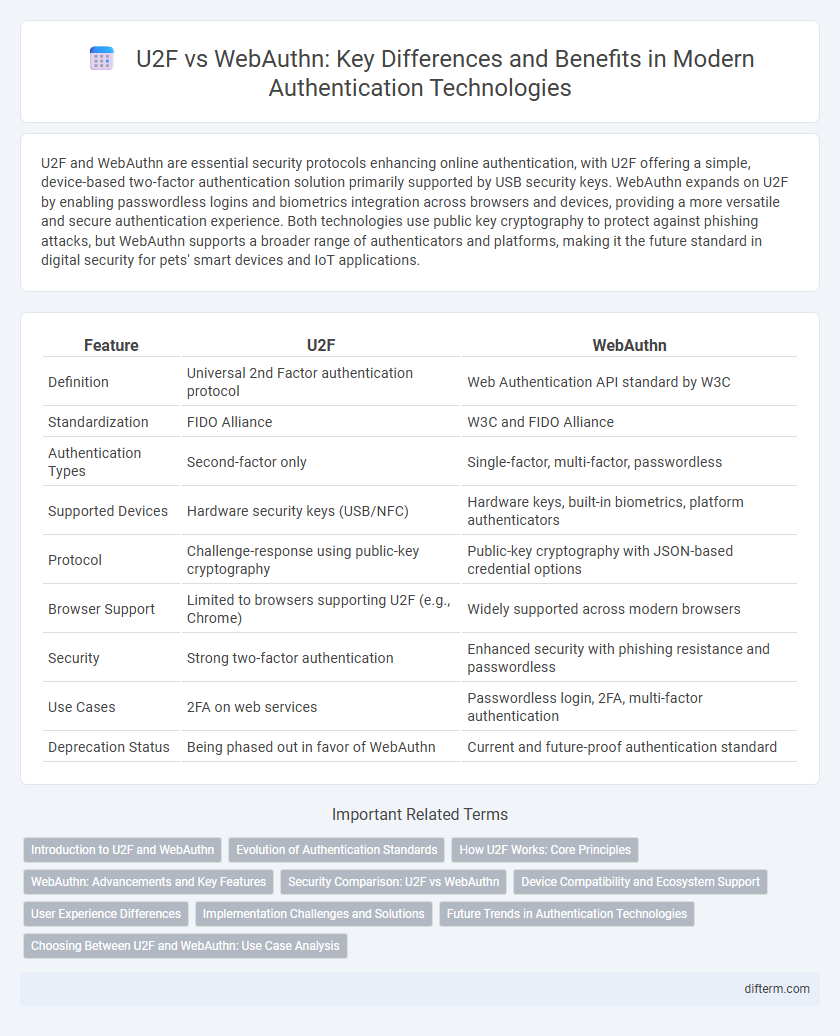
| Feature | U2F | WebAuthn |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Universal 2nd Factor authentication protocol | Web Authentication API standard by W3C |
| Standardization | FIDO Alliance | W3C and FIDO Alliance |
| Authentication Types | Second-factor only | Single-factor, multi-factor, passwordless |
| Supported Devices | Hardware security keys (USB/NFC) | Hardware keys, built-in biometrics, platform authenticators |
| Protocol | Challenge-response using public-key cryptography | Public-key cryptography with JSON-based credential options |
| Browser Support | Limited to browsers supporting U2F (e.g., Chrome) | Widely supported across modern browsers |
| Security | Strong two-factor authentication | Enhanced security with phishing resistance and passwordless |
| Use Cases | 2FA on web services | Passwordless login, 2FA, multi-factor authentication |
| Deprecation Status | Being phased out in favor of WebAuthn | Current and future-proof authentication standard |
Introduction to U2F and WebAuthn
U2F (Universal 2nd Factor) is an open authentication standard developed by the FIDO Alliance that enables secure two-factor authentication using physical security keys. WebAuthn, also standardized by the FIDO Alliance and the W3C, expands on U2F by supporting passwordless authentication, multi-factor options, and greater device compatibility through a web API. Both technologies aim to enhance online security by reducing reliance on passwords and mitigating phishing attacks.
Evolution of Authentication Standards
U2F (Universal 2nd Factor) marked a significant advancement by introducing hardware-based two-factor authentication to reduce phishing risks. WebAuthn, as the successor, expands this approach by supporting passwordless, multi-factor, and biometric authentication through public key cryptography, enhancing both security and user experience. This evolution reflects a shift towards more flexible, phishing-resistant authentication standards integral to modern cybersecurity frameworks.
How U2F Works: Core Principles
U2F (Universal 2nd Factor) operates on the core principle of public key cryptography to enhance authentication security by requiring users to register a physical device that generates a unique cryptographic key pair. During authentication, the U2F device signs a challenge from the service, proving possession of the private key without exposing it, thus preventing phishing and replay attacks. This approach significantly strengthens account protection compared to traditional password-only methods.
WebAuthn: Advancements and Key Features
WebAuthn offers significant advancements over U2F by supporting a wider range of authentication methods, including biometric verification and passwordless logins, enhancing both security and user convenience. It provides stronger cryptographic guarantees through asymmetric key pairs and attestation, reducing the risk of phishing and replay attacks. WebAuthn's compatibility across modern browsers and platforms enables seamless integration into diverse applications, promoting widespread adoption of secure authentication standards.
Security Comparison: U2F vs WebAuthn
U2F (Universal 2nd Factor) provides robust security through hardware-based authentication, significantly reducing phishing risks by requiring physical device presence. WebAuthn extends U2F's capabilities with support for passwordless logins and broader device compatibility, enhancing security with public key cryptography and biometric integration. Both standards mitigate credential theft effectively, but WebAuthn's flexible authentication methods offer superior protection against account takeover in modern threat environments.
Device Compatibility and Ecosystem Support
WebAuthn offers broader device compatibility by supporting a wide range of authenticators, including biometric sensors and security keys, across modern browsers and platforms like Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS. U2F, primarily developed by Google and supported mainly by Chrome and some hardware tokens, has limited ecosystem integration compared to WebAuthn's expansive industry adoption and continuous standardization by the FIDO Alliance and W3C. The enhanced interoperability and forward compatibility of WebAuthn make it the preferred choice for developers seeking robust, future-proof authentication solutions.
User Experience Differences
U2F relies on physical security keys requiring USB or NFC interaction, which can limit accessibility and convenience across devices. WebAuthn supports passwordless authentication using built-in biometric sensors or platform authenticators, providing smoother and faster user experiences on smartphones and laptops. Enhanced compatibility with various devices in WebAuthn reduces friction and streamlines login processes compared to U2F's hardware dependency.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
U2F implementation faces challenges such as limited browser support and reliance on physical security keys, which can restrict user accessibility and increase deployment costs. WebAuthn addresses these issues by offering comprehensive API support across modern browsers and enabling diverse authentication methods, including biometrics and platform authenticators, enhancing flexibility. Developers overcome integration hurdles with WebAuthn by utilizing robust libraries and adaptive UI frameworks to ensure seamless user experiences across devices and platforms.
Future Trends in Authentication Technologies
WebAuthn is rapidly becoming the standard for secure authentication, offering enhanced multi-factor support and biometric integration compared to U2F's simpler, second-factor capabilities. Future trends in authentication technologies point toward passwordless experiences leveraging WebAuthn's robust public key cryptography and device attestation features. The convergence of WebAuthn with decentralized identity solutions and mobile platform adoption is set to revolutionize secure and user-friendly access across digital ecosystems.
Choosing Between U2F and WebAuthn: Use Case Analysis
U2F, a protocol primarily designed for hardware-based two-factor authentication, excels in simplicity and compatibility with legacy systems, making it ideal for environments requiring straightforward, device-bound security. WebAuthn extends U2F capabilities by supporting passwordless authentication, biometric data, and software authenticators, offering enhanced flexibility and broader platform support for modern web applications. Choosing between U2F and WebAuthn depends on use case specifics such as device ecosystem, security requirements, and user experience preferences, where WebAuthn is preferable for future-proof, scalable authentication strategies.
U2F vs WebAuthn Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com