Stateless technology in pet devices offers streamlined data processing by not retaining user interactions, enabling faster performance and easier scalability. Stateful technology, however, maintains information from previous interactions, allowing for personalized experiences and adaptive behavior in smart pet gadgets. Choosing between stateless and stateful approaches impacts device responsiveness, memory usage, and the overall user experience in pet technology solutions.
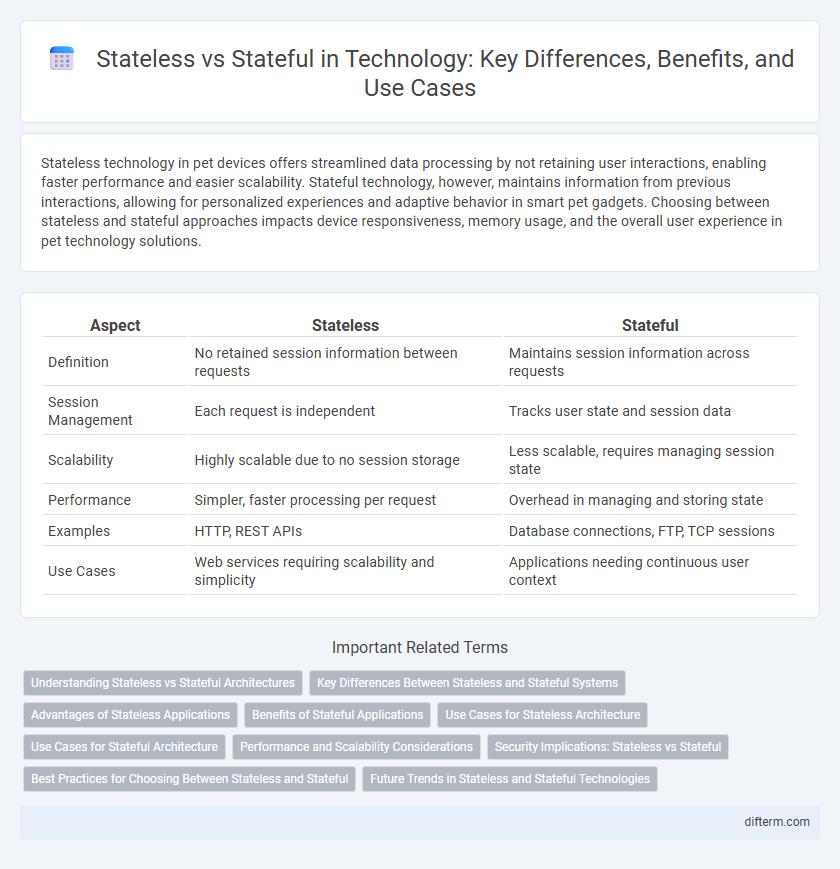
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Stateless | Stateful |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | No retained session information between requests | Maintains session information across requests |
| Session Management | Each request is independent | Tracks user state and session data |
| Scalability | Highly scalable due to no session storage | Less scalable, requires managing session state |
| Performance | Simpler, faster processing per request | Overhead in managing and storing state |
| Examples | HTTP, REST APIs | Database connections, FTP, TCP sessions |
| Use Cases | Web services requiring scalability and simplicity | Applications needing continuous user context |
Understanding Stateless vs Stateful Architectures
Stateless architectures process each request independently without retaining client context, enhancing scalability and fault tolerance. Stateful architectures maintain session information, enabling personalized interactions but requiring resource management and state synchronization. Choosing between stateless and stateful designs impacts system performance, reliability, and complexity in distributed computing environments.
Key Differences Between Stateless and Stateful Systems
Stateless systems do not retain any client information between requests, ensuring each interaction is independent and simplifying scalability and failure recovery. Stateful systems maintain session data across multiple interactions, allowing personalized experiences but requiring more complex resource management and data synchronization. The choice between stateless and stateful architectures impacts system performance, user experience, and development complexity in technology applications.
Advantages of Stateless Applications
Stateless applications offer enhanced scalability by handling each request independently, allowing seamless distribution across multiple servers without session dependency. They simplify recovery and fault tolerance as no client information is stored on the server, reducing system complexity and improving reliability. This architecture also enables easier maintenance and deployment, accelerating development cycles and reducing operational overhead.
Benefits of Stateful Applications
Stateful applications retain user session data, enabling personalized experiences and seamless interaction continuity across multiple requests. This persistent state management supports complex transactions and real-time responsiveness essential for collaborative tools, gaming, and financial services. By maintaining context, stateful systems reduce latency and improve error recovery, enhancing overall user satisfaction and operational reliability.
Use Cases for Stateless Architecture
Stateless architecture excels in use cases like RESTful APIs, where each request is independent and can be processed without relying on stored context, enhancing scalability and reliability. It is ideal for cloud-native applications and microservices that require efficient load balancing and fault tolerance by avoiding session persistence. This approach also supports stateless authentication mechanisms such as JWT, improving security and simplifying horizontal scaling in distributed environments.
Use Cases for Stateful Architecture
Stateful architecture excels in applications requiring continuous tracking of user interactions, such as online banking and e-commerce platforms, where preserving session data ensures secure transactions and personalized experiences. Real-time multiplayer gaming relies on stateful systems to maintain consistent game state and player progress across sessions. Stateful design is also critical in telecommunication networks to manage call states and maintain connection reliability.
Performance and Scalability Considerations
Stateless systems enhance performance by eliminating the need to store session information, enabling faster request processing and easier load balancing across distributed servers. Stateful systems, while potentially offering richer user experiences, face challenges in scalability due to session data management and synchronization overhead. Optimizing for scalability often involves leveraging stateless architectures to achieve consistent response times under high traffic.
Security Implications: Stateless vs Stateful
Stateless systems enhance security by reducing attack surfaces, as they do not store client session data, minimizing risks related to session hijacking or data breaches. Stateful systems, while offering richer functionalities through persistent sessions, require robust security measures like encrypted storage and strict access controls to prevent unauthorized access and session manipulation. Implementing stateless architectures, often via JSON Web Tokens (JWT), favors scalability and simplifies threat mitigation, whereas stateful designs demand continuous monitoring to safeguard session integrity.
Best Practices for Choosing Between Stateless and Stateful
Choosing between stateless and stateful design depends heavily on application requirements, with stateless architectures offering scalability and simplicity by not retaining client session data, ideal for RESTful services and microservices. Stateful designs, which maintain session information on the server, are better suited for complex transactions and interactive applications requiring user context, such as gaming or online shopping carts. Best practices involve evaluating factors like performance needs, fault tolerance, and resource management to determine the optimal balance between scalability and user experience.
Future Trends in Stateless and Stateful Technologies
Future trends in stateless and stateful technologies emphasize increased adoption of serverless architectures and edge computing to enhance scalability and reduce latency. Innovations in distributed ledger technology and AI-driven state management are poised to optimize stateful applications by ensuring data consistency and real-time analytics. Emerging protocols focusing on hybrid models aim to balance the efficiency of stateless systems with robust stateful capabilities for complex, interactive applications.
stateless vs stateful Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com