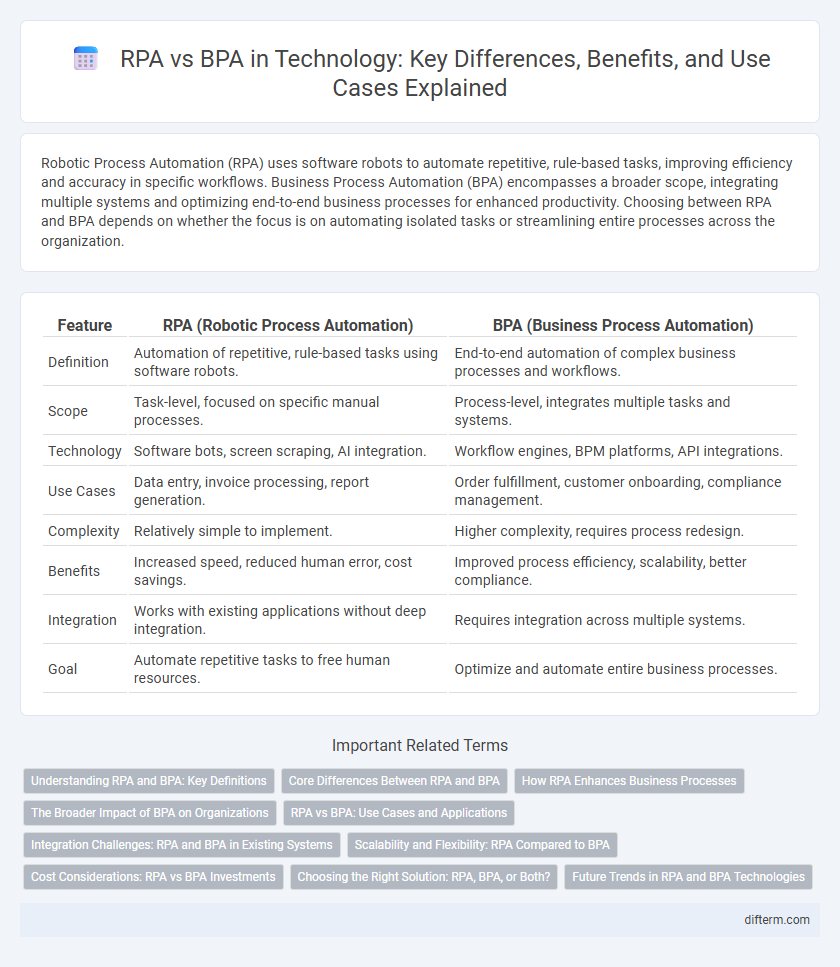
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) uses software robots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks, improving efficiency and accuracy in specific workflows. Business Process Automation (BPA) encompasses a broader scope, integrating multiple systems and optimizing end-to-end business processes for enhanced productivity. Choosing between RPA and BPA depends on whether the focus is on automating isolated tasks or streamlining entire processes across the organization.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | RPA (Robotic Process Automation) | BPA (Business Process Automation) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automation of repetitive, rule-based tasks using software robots. | End-to-end automation of complex business processes and workflows. |
| Scope | Task-level, focused on specific manual processes. | Process-level, integrates multiple tasks and systems. |
| Technology | Software bots, screen scraping, AI integration. | Workflow engines, BPM platforms, API integrations. |
| Use Cases | Data entry, invoice processing, report generation. | Order fulfillment, customer onboarding, compliance management. |
| Complexity | Relatively simple to implement. | Higher complexity, requires process redesign. |
| Benefits | Increased speed, reduced human error, cost savings. | Improved process efficiency, scalability, better compliance. |
| Integration | Works with existing applications without deep integration. | Requires integration across multiple systems. |
| Goal | Automate repetitive tasks to free human resources. | Optimize and automate entire business processes. |
Understanding RPA and BPA: Key Definitions
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) involves using software robots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks, enhancing efficiency in processes such as data entry and transaction processing. Business Process Automation (BPA) encompasses a broader strategy that integrates multiple automated systems and workflow optimizations to improve end-to-end business operations and decision-making. Understanding these definitions highlights RPA's role as a tactical tool within the comprehensive scope of BPA's transformational approach to organizational workflows.
Core Differences Between RPA and BPA
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive, rule-based tasks by mimicking human interactions with software, primarily enhancing task efficiency and accuracy. Business Process Automation (BPA) encompasses a broader scope by streamlining entire business processes through integration and orchestration of multiple systems and workflows to improve overall organizational performance. Core differences lie in RPA targeting specific task automation using software bots, while BPA focuses on end-to-end process optimization across departments and systems.
How RPA Enhances Business Processes
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances business processes by automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, significantly increasing operational efficiency and accuracy. Unlike traditional process automation, RPA integrates seamlessly with existing systems without requiring extensive IT changes, enabling faster implementation and scalability. By reducing human error and freeing employees from mundane activities, RPA drives improved productivity and cost savings across various business functions.
The Broader Impact of BPA on Organizations
Business Process Automation (BPA) transforms organizational efficiency by integrating technologies like AI, machine learning, and advanced analytics to automate complex workflows beyond repetitive tasks, which are typically handled by Robotic Process Automation (RPA). BPA drives digital transformation by enabling end-to-end process optimization, resulting in enhanced decision-making, reduced operational costs, and improved compliance risk management. Organizations leveraging BPA experience accelerated innovation cycles and increased scalability through seamless collaboration across departments and intelligent data-driven insights.
RPA vs BPA: Use Cases and Applications
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) excels in automating repetitive, rule-based tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, and customer service interactions, enhancing efficiency in finance, HR, and IT departments. Business Process Automation (BPA) addresses end-to-end process optimization by integrating multiple systems and workflows, supporting complex processes like order-to-cash, compliance management, and supply chain coordination. Enterprises leverage RPA for task-level automation while employing BPA for strategic process redesign to achieve comprehensive operational improvement.
Integration Challenges: RPA and BPA in Existing Systems
RPA and BPA integration challenges stem from their distinct approaches to automation within existing IT infrastructures. RPA often faces limitations due to its reliance on surface-level interactions with applications, leading to potential issues with scalability and system compatibility. In contrast, BPA typically requires deeper integration, involving complex API connections and data consistency management, which can complicate implementation but result in more robust and sustainable automation solutions.
Scalability and Flexibility: RPA Compared to BPA
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) offers high scalability for repetitive, rule-based tasks by quickly deploying bots across processes without extensive redesign. Business Process Automation (BPA) provides greater flexibility in integrating complex workflows and adapting to changing business environments through comprehensive process reengineering. Scalability in RPA is limited by task complexity, while BPA supports scalable transformation across diverse organizational functions.
Cost Considerations: RPA vs BPA Investments
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) typically involves lower upfront costs due to its ease of deployment and reliance on existing user interfaces, making it cost-effective for automating repetitive tasks. Business Process Automation (BPA) requires higher initial investments as it involves comprehensive workflow redesign and integration with enterprise systems for end-to-end process optimization. Evaluating total cost of ownership requires assessing factors such as scalability, maintenance, and long-term operational efficiency in both RPA and BPA implementations.
Choosing the Right Solution: RPA, BPA, or Both?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) excels in automating repetitive, rule-based tasks such as data entry and invoice processing, boosting efficiency with minimal disruption to existing systems. Business Process Automation (BPA) offers a broader approach by optimizing entire workflows, integrating multiple applications, and enabling process redesign for strategic improvements. Organizations should evaluate task complexity, scalability needs, and integration requirements to decide between RPA, BPA, or a hybrid solution that combines the agility of RPA with the comprehensive scope of BPA.
Future Trends in RPA and BPA Technologies
Emerging trends in RPA and BPA technologies emphasize enhanced AI integration, enabling more intelligent automation and decision-making processes. Future developments focus on hyperautomation, combining RPA with machine learning, analytics, and process mining to optimize end-to-end workflows. Scalability and cloud-based automation platforms are set to dominate, offering greater flexibility and real-time adaptability in business operations.
RPA vs BPA Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com