Single-tenant architecture offers dedicated resources and enhanced security, making it ideal for businesses with strict compliance requirements. Multi-tenant environments maximize resource efficiency and scalability by sharing infrastructure among multiple users, reducing costs. Choosing between single-tenant and multi-tenant depends on the business's need for customization, control, and budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
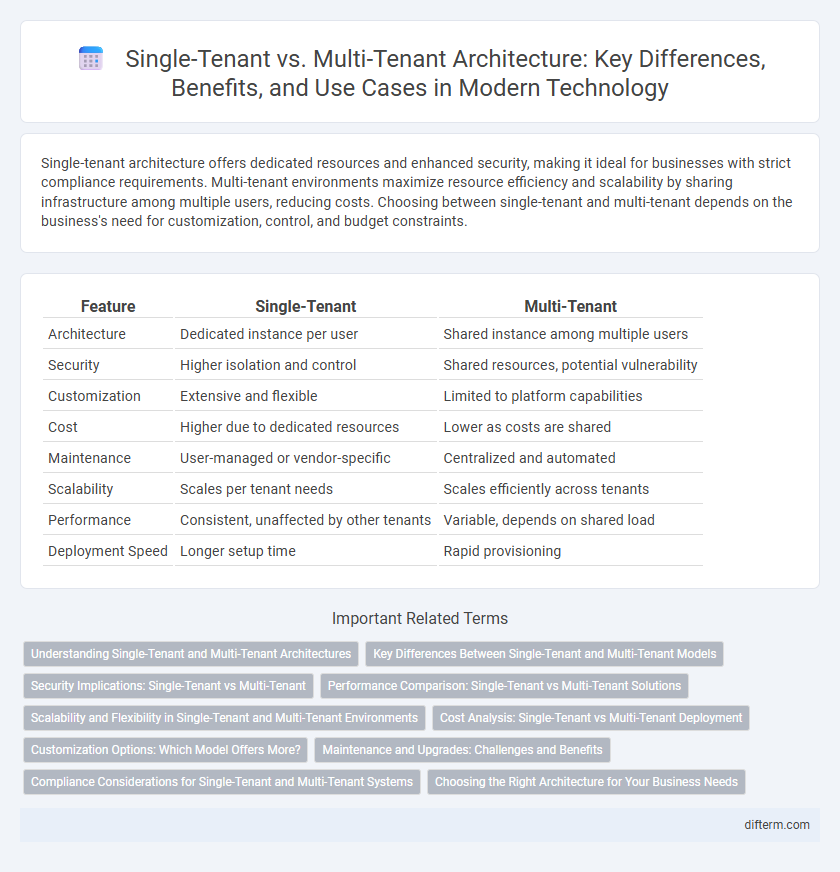
| Feature | Single-Tenant | Multi-Tenant |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Dedicated instance per user | Shared instance among multiple users |
| Security | Higher isolation and control | Shared resources, potential vulnerability |
| Customization | Extensive and flexible | Limited to platform capabilities |
| Cost | Higher due to dedicated resources | Lower as costs are shared |
| Maintenance | User-managed or vendor-specific | Centralized and automated |
| Scalability | Scales per tenant needs | Scales efficiently across tenants |
| Performance | Consistent, unaffected by other tenants | Variable, depends on shared load |
| Deployment Speed | Longer setup time | Rapid provisioning |
Understanding Single-Tenant and Multi-Tenant Architectures
Single-tenant architecture assigns a dedicated instance of software and infrastructure to a single client, offering enhanced security, customization, and control compared to multi-tenant systems. In contrast, multi-tenant architecture hosts multiple clients on a shared infrastructure, optimizing resource utilization and reducing operational costs through shared services. Understanding these architectures is crucial for selecting the right cloud deployment model based on specific business needs, compliance requirements, and scalability goals.
Key Differences Between Single-Tenant and Multi-Tenant Models
Single-tenant architecture dedicates an entire software instance and infrastructure to a single client, offering enhanced data isolation, customization, and control compared to multi-tenant systems, where multiple clients share the same software instance and resources. Single-tenant models typically incur higher costs due to individualized deployment, while multi-tenant solutions optimize resource efficiency and scalability by leveraging shared infrastructure. Security and compliance requirements often dictate the choice, with single-tenant preferred for stringent regulatory environments and multi-tenant favored for cost-effective SaaS applications.
Security Implications: Single-Tenant vs Multi-Tenant
Single-tenant architectures isolate each client's data and resources, significantly reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access, making them ideal for organizations with stringent security requirements. Multi-tenant environments share infrastructure and software instances across multiple clients, increasing exposure to potential vulnerabilities but benefiting from centralized security updates and automated compliance controls. Choosing between single-tenant and multi-tenant solutions depends on balancing security priorities against cost efficiency and scalability needs in cloud computing deployments.
Performance Comparison: Single-Tenant vs Multi-Tenant Solutions
Single-tenant solutions offer dedicated resources, resulting in consistent, high-performance levels tailored to specific organizational needs, minimizing latency and maximizing throughput. Multi-tenant architectures share resources among multiple users, which can lead to variable performance due to resource contention but enables scalable and cost-efficient operations. Performance in single-tenant environments is typically superior for workloads demanding intensive processing, while multi-tenant solutions optimize resource utilization for standardized, less resource-heavy applications.
Scalability and Flexibility in Single-Tenant and Multi-Tenant Environments
Single-tenant environments offer enhanced scalability by allowing dedicated resources tailored to specific organizational needs, ensuring optimal performance during peak demands. In contrast, multi-tenant architectures provide flexibility through shared infrastructure, enabling cost-efficient scalability and rapid deployment across multiple users or clients. Scalability in multi-tenant systems benefits from elastic resource allocation, while single-tenant setups prioritize customization and isolated scaling.
Cost Analysis: Single-Tenant vs Multi-Tenant Deployment
Single-tenant deployment typically incurs higher upfront and maintenance costs due to dedicated infrastructure and individualized customization, while multi-tenant environments offer cost efficiency by sharing resources among multiple users. Operational expenses in single-tenant systems include isolated scalability and security management, contrasting with the streamlined updates and lower per-user costs prevalent in multi-tenant architectures. Cost analysis should weigh total cost of ownership (TCO), considering factors like infrastructure investment, licensing fees, and long-term scalability for each deployment model.
Customization Options: Which Model Offers More?
Single-tenant architecture provides extensive customization options, allowing organizations to tailor software features, security settings, and infrastructure according to specific business needs. Multi-tenant systems offer limited customization as multiple clients share the same application instance, restricting changes to ensure stability and uniform updates. Enterprises requiring deep personalization usually benefit from single-tenant solutions, whereas those prioritizing cost-efficiency may opt for multi-tenant models despite fewer customization capabilities.
Maintenance and Upgrades: Challenges and Benefits
Single-tenant architecture offers easier customization and controlled maintenance schedules, reducing conflicts during upgrades but increasing operational costs due to dedicated resources. Multi-tenant environments benefit from centralized maintenance and faster deployment of updates, ensuring consistent system versions across users while facing challenges in managing diverse tenant requirements. Balancing upgrade frequency with minimal service disruption is critical in both models to maintain performance and user satisfaction.
Compliance Considerations for Single-Tenant and Multi-Tenant Systems
Single-tenant systems offer enhanced compliance control by isolating data and infrastructure, reducing risks associated with data breaches and meeting stringent regulatory requirements such as HIPAA and GDPR more effectively. Multi-tenant environments require robust data segregation techniques and continuous monitoring to ensure compliance across multiple clients sharing the same infrastructure. Organizations must evaluate compliance frameworks and industry-specific standards when choosing between single-tenant and multi-tenant architectures to maintain data security and regulatory adherence.
Choosing the Right Architecture for Your Business Needs
Choosing between single-tenant and multi-tenant architectures depends on factors such as data security requirements, customization needs, and scalability goals. Single-tenant environments offer dedicated resources and enhanced control, ideal for businesses with strict compliance standards. Multi-tenant architectures provide cost-efficient scalability and simplified maintenance, benefiting organizations seeking flexible, shared infrastructure solutions.
Single-Tenant vs Multi-Tenant Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com