Web3 revolutionizes internet interactions by enabling decentralized applications and blockchain integration, enhancing user control over data and digital assets. In contrast, Web 2.0 relies on centralized platforms where user-generated content is controlled by corporate entities, leading to data privacy concerns. This shift from Web 2.0 to Web3 promotes transparency, security, and peer-to-peer connectivity in digital ecosystems.
Table of Comparison
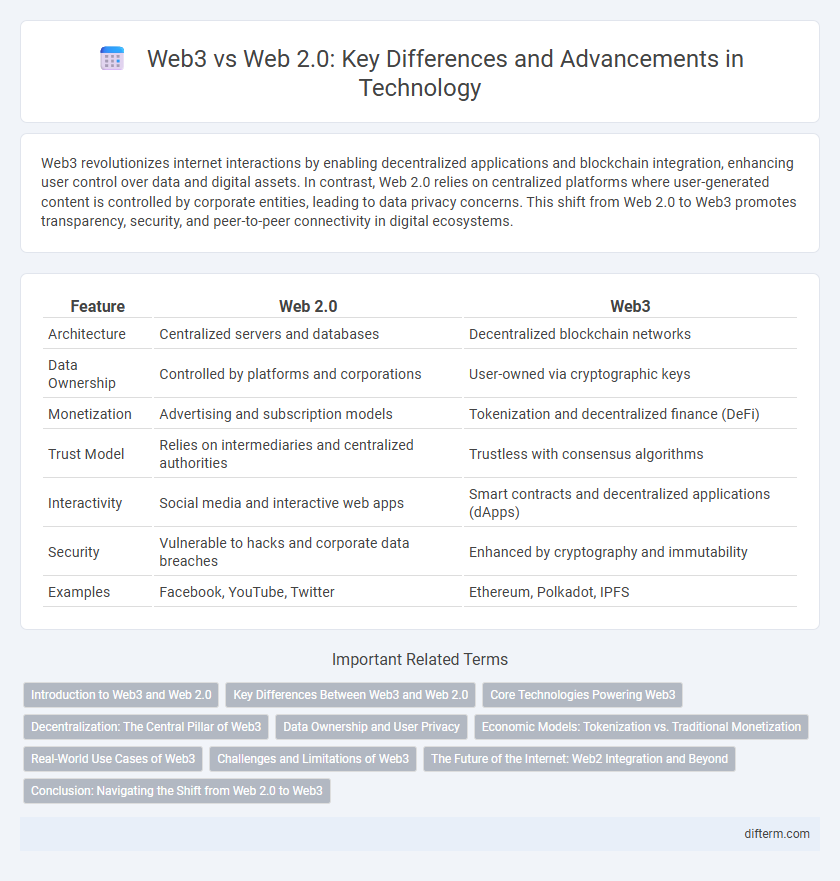
| Feature | Web 2.0 | Web3 |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Centralized servers and databases | Decentralized blockchain networks |
| Data Ownership | Controlled by platforms and corporations | User-owned via cryptographic keys |
| Monetization | Advertising and subscription models | Tokenization and decentralized finance (DeFi) |
| Trust Model | Relies on intermediaries and centralized authorities | Trustless with consensus algorithms |
| Interactivity | Social media and interactive web apps | Smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps) |
| Security | Vulnerable to hacks and corporate data breaches | Enhanced by cryptography and immutability |
| Examples | Facebook, YouTube, Twitter | Ethereum, Polkadot, IPFS |
Introduction to Web3 and Web 2.0
Web 2.0 revolutionized the internet by enabling user-generated content, social networking, and interactive web applications through centralized platforms controlled by major corporations. In contrast, Web3 introduces a decentralized internet infrastructure leveraging blockchain technology, smart contracts, and peer-to-peer networks to enhance data ownership, privacy, and trustless interactions. This evolution shifts control from centralized entities to individual users, promoting transparency and enabling new economic models like token economies and decentralized finance (DeFi).
Key Differences Between Web3 and Web 2.0
Web3 is characterized by decentralization using blockchain technology, enabling peer-to-peer interactions without intermediaries, unlike Web 2.0 which relies heavily on centralized platforms and servers. Web3 incorporates token-based economies and smart contracts to facilitate trustless transactions and data ownership, whereas Web 2.0 primarily focuses on user-generated content and social networking managed by centralized entities. Privacy and control over personal data are enhanced in Web3 through cryptographic security and user sovereignty, contrasting with the data aggregation and monetization models prevalent in Web 2.0.
Core Technologies Powering Web3
Web3 is powered by decentralized technologies such as blockchain, smart contracts, and peer-to-peer networks, ensuring enhanced security, transparency, and user control over data compared to Web 2.0's centralized servers and databases. Core protocols like Ethereum enable programmable transactions and decentralized applications (dApps), while distributed ledger technology eliminates single points of failure inherent in traditional Web 2.0 infrastructure. Decentralized identity systems and token economies further empower users by enabling ownership and monetization of digital assets without intermediaries.
Decentralization: The Central Pillar of Web3
Web3 redefines internet interactions by leveraging blockchain technology to enable true decentralization, removing intermediaries and returning control to users. Unlike Web 2.0's centralized platforms where data is stored on proprietary servers, Web3 distributes data across a network of nodes, enhancing transparency and security. This fundamental shift supports peer-to-peer applications and empowers individuals with ownership over their digital identities and assets.
Data Ownership and User Privacy
Web3 redefines data ownership by leveraging decentralized blockchain technology, enabling users to control their personal information without relying on centralized intermediaries common in Web 2.0 platforms. Unlike Web 2.0, where corporations aggregate and monetize user data, Web3 protocols emphasize privacy through cryptographic security and decentralized identity management. This shift enhances user sovereignty and mitigates vulnerabilities associated with central data repositories, fundamentally transforming online interactions and data privacy norms.
Economic Models: Tokenization vs. Traditional Monetization
Web3 introduces tokenization as a revolutionary economic model, enabling users to earn and trade digital assets securely through blockchain technology. In contrast, Web 2.0 relies on traditional monetization methods like advertising revenue, subscription fees, and data brokerage, which centralize control and profits within a few dominant platforms. Token economies in Web3 foster decentralized value exchange, empowering creators and users with greater financial participation and transparency.
Real-World Use Cases of Web3
Web3 leverages blockchain technology to enable decentralized applications that enhance data ownership and security, exemplified by decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms that allow users to lend, borrow, and trade assets without intermediaries. Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) revolutionize digital art and intellectual property management by providing verifiable ownership and provenance on-chain. Supply chain management benefits from Web3 by enabling transparent, tamper-proof tracking of products from origin to consumer, improving accountability and reducing fraud.
Challenges and Limitations of Web3
Web3 faces significant challenges including scalability issues, limited user adoption, and high transaction costs driven by blockchain technology. Interoperability between diverse decentralized platforms remains underdeveloped, hindering seamless user experiences. Security vulnerabilities and regulatory uncertainties also pose major obstacles to widespread Web3 integration compared to established Web 2.0 ecosystems.
The Future of the Internet: Web2 Integration and Beyond
Web3 represents the evolution of the internet by integrating decentralized technologies such as blockchain and smart contracts, enhancing security, transparency, and user control compared to Web 2.0's centralized platforms. The future of the internet lies in combining Web 2.0's user-friendly interfaces and widespread adoption with Web3's decentralized infrastructure to create seamless, interoperable digital experiences. This hybrid approach aims to empower users with data ownership and privacy while maintaining the scalability and functionality necessary for mainstream web applications.
Conclusion: Navigating the Shift from Web 2.0 to Web3
The transition from Web 2.0 to Web3 signifies a fundamental shift towards decentralized internet infrastructure, enhancing user control over data and digital assets. Web3 leverages blockchain technology, smart contracts, and decentralized applications (dApps) to create a more transparent and secure online environment. Embracing this evolution requires stakeholders to adapt to new protocols and governance models that prioritize privacy, security, and user empowerment.
Web3 vs Web 2.0 Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com